Abstract
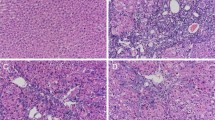
The study was to explore the hepatoprotective effect and possible mechanism of calycosin on carbon tetrachloride (CCl4)–induced liver fibrosis in mice. Hepatic fibrosis was induced by intraperitoneal injection of CCl4 in C57BL/6 male mice. Serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate transaminase (AST) activity, superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity, and hydroxyproline (Hyp) and malondialdehyde (MDA) levels were determined by biochemical assays. Liver histopathology was assessed by H&E and Masson trichrome staining. The mRNA expressions of α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA), collagen-I (Col-I), Janus kinase 2 (JAK2) and signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) were determined using qRT-PCR. The protein levels of α-SMA, Col-I, estrogen receptor α (ERα), estrogen receptor β (ERβ), tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 (TIMP-1), matrix metalloproteinase-1 (MMP-1), JAK2, phospho-JAK2 (p-JAK2), STAT3, and phospho-STAT3 (p-STAT3) were detected by Western blotting. The levels of α-SMA and ERβ were measured by immunohistochemistry. Calycosin significantly reduced liver index, MDA level, and ALT and AST activity and increased SOD activity. The α-SMA, Col-I, and Hyp of the calycosin group were significantly lower than those of the model group. Calycosin increased MMP-1 and inhibited TIMP-1 expression resulting in the improvement of MMP-1/TIMP-1 ratio. Importantly, calycosin improved ERβ protein expression, JAK2 and STAT3 mRNA expressions, p-JAK2/JAK2, and p-STAT3/STAT3 relative protein expressions. However, ERα, JAK2, and STAT3 protein expressions were relatively unchanged. Calycosin significantly inhibits liver fibrosis in mice, and its mechanism may involve the following: calycosin inhibits oxidative stress; calycosin inhibits collagen synthesis and balances MMP-1/TIMP-1 system; calycosin increases ERβ expression and activates JAK2-STAT3 pathway.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aaronson DS, Horvath CM (2002) A road map for those who don't know JAK-STAT. Science 296:1653–1655
Avouac J, Furnrohr BG, Tomcik M, Palumbo K, Zerr P, Horn A, Dees C, Akhmetshina A, Beyer C, Distler O, Schett G, Allanore Y, Distler JH (2011) Inactivation of the transcription factor STAT-4 prevents inflammation-driven fibrosis in animal models of systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheum 63:800–809
Bataller R, Brenner DA (2005) Liver fibrosis. J Clin Invest 115:209–218
Cai X, Li Z, Zhang Q, Qu Y, Xu M, Wan X, Lu L (2018) CXCL6-EGFR-induced Kupffer cells secrete TGF-beta1 promoting hepatic stellate cell activation via the SMAD2/BRD4/C-MYC/EZH2 pathway in liver fibrosis. J Cell Mol Med 22:5050–5061
Cao Q, Mak KM, Lieber CS (2007) Leptin represses matrix metalloproteinase-1 gene expression in LX2 human hepatic stellate cells. J Hepatol 46:124–133
Chen X, Meng Q, Wang C, Liu Q, Sun H, Huo X, Sun P, Yang X, Peng J, Liu K (2015) Protective effects of calycosin against CCl4-induced liver injury with activation of FXR and STAT3 in mice. Pharm Res 32:538–548
Chen HL, Tsai TC, Tsai YC, Liao JW, Yen CC, Chen CM (2016) Kefir peptides prevent high-fructose corn syrup-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in a murine model by modulation of inflammation and the JAK2 signaling pathway. Nutr Diabetes 6:e237
Chen Y, Lu W, Jin Z, Yu J, Shi B (2019) Carbenoxolone ameliorates hepatic lipid metabolism and inflammation in obese mice induced by high fat diet via regulating the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway. Int Immunopharmacol 74:105498
Codes L, Asselah T, Cazals-Hatem D, Tubach F, Vidaud D, Parana R, Bedossa P, Valla D, Marcellin P (2007) Liver fibrosis in women with chronic hepatitis C: evidence for the negative role of the menopause and steatosis and the potential benefit of hormone replacement therapy. Gut 56:390–395
Deng T, Liu J, Zhang M, Wang Y, Zhu G, Wang J (2018) Inhibition effect of phytoestrogen calycosin on TGF-beta1-induced hepatic stellate cell activation, proliferation, and migration via estrogen receptor beta. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 96:1268–1275
Duan X, Meng Q, Wang C, Liu Z, Liu Q, Sun H, Sun P, Yang X, Huo X, Peng J, Liu K (2017) Calycosin attenuates triglyceride accumulation and hepatic fibrosis in murine model of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis via activating farnesoid X receptor. Phytomedicine 25:83–92
El-Serag HB, Rudolph KL (2007) Hepatocellular carcinoma: epidemiology and molecular carcinogenesis. Gastroenterology 132:2557–2576
Friedman SL (2008) Hepatic stellate cells: protean, multifunctional, and enigmatic cells of the liver. Physiol Rev 88:125–172
Friedman SL (2010) Evolving challenges in hepatic fibrosis. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 7:425–436
Gao B, Wang H, Lafdil F, Feng D (2012) STAT proteins - key regulators of anti-viral responses, inflammation, and tumorigenesis in the liver. J Hepatol 57:430–441
Gong AG, Lau KM, Xu ML, Lin HQ, Dong TT, Zheng KY, Zhao KJ, Tsim KW (2016) The estrogenic properties of Danggui Buxue Tang, a Chinese herbal decoction, are triggered predominantly by calycosin in MCF-7 cells. J Ethnopharmacol 189:81–89
Gui SY, Wei W, Wang H, Wu L, Sun WY, Chen WB, Wu CY (2006) Effects and mechanisms of crude astragalosides fraction on liver fibrosis in rats. J Ethnopharmacol 103:154–159
Han SJ, Lee JE, Cho YJ, Park MJ, O'Malley BW (2019) Genomic function of estrogen receptor beta in endometriosis. Endocrinology 160:2495–2516
Hyun J, Wang S, Kim J, Rao KM, Park SY, Chung I, Ha CS, Kim SW, Yun YH, Jung Y (2016) MicroRNA-378 limits activation of hepatic stellate cells and liver fibrosis by suppressing Gli3 expression. Nat Commun 7:10993
Ibrahim A, Hugerth LW, Hases L, Saxena A, Seifert M, Thomas Q, Gustafsson JA, Engstrand L, Williams C (2019) Colitis-induced colorectal cancer and intestinal epithelial estrogen receptor beta impact gut microbiota diversity. Int J Cancer 144:3086–3098
Iorga A, Umar S, Ruffenach G, Aryan L, Li J, Sharma S, Motayagheni N, Nadadur RD, Bopassa JC, Eghbali M (2018) Estrogen rescues heart failure through estrogen receptor Beta activation. Biol Sex Differ 9:48
Itagaki T, Shimizu I, Cheng X, Yuan Y, Oshio A, Tamaki K, Fukuno H, Honda H, Okamura Y, Ito S (2005) Opposing effects of oestradiol and progesterone on intracellular pathways and activation processes in the oxidative stress induced activation of cultured rat hepatic stellate cells. Gut 54:1782–1789
Jaeschke H, McGill MR, Ramachandran A (2012) Oxidant stress, mitochondria, and cell death mechanisms in drug-induced liver injury: lessons learned from acetaminophen hepatotoxicity. Drug Metab Rev 44:88–106
Jian L, Xin L, Yufang M, Yifan H (2015) Protective effect of calycosin-7-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside against oxidative stress of BRL-3A cells induced by thioacetamide. Pharmacogn Mag 11:524–532
Kao TL, Kuan YP, Cheng WC, Chang WC, Jeng LB, Yeh S, Ma WL (2018) Estrogen receptors orchestrate cell growth and differentiation to facilitate liver regeneration. Theranostics 8:2672–2682
Kim SH, Cheon HJ, Yun N, Oh ST, Shin E, Shim KS, Lee SM (2009) Protective effect of a mixture of Aloe vera and Silybum marianum against carbon tetrachloride-induced acute hepatotoxicity and liver fibrosis. J Pharmacol Sci 109:119–127
Kong X, Horiguchi N, Mori M, Gao B (2012) Cytokines and STATs in liver fibrosis. Front Physiol 3:69
Leung KC, Johannsson G, Leong GM, Ho KK (2004) Estrogen regulation of growth hormone action. Endocr Rev 25:693–721
Levy DE, Darnell JE Jr (2002) Stats: transcriptional control and biological impact. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 3:651–662
Li N, Dou Z, Liu J, Chai B, Li Y, An X, Chu P, Zhang X (2018) Therapeutic effect of HGF on NASH mice through HGF/c-Met and JAK2-STAT3 signalling pathway. Ann Hepatol 17:501–510
Li L, Li Q, Wei L, Wang Z, Ma W, Liu F, Shen Y, Zhang S, Zhang X, Li H, Qian Y (2019) Chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 14 contributes to lipopolysaccharide-induced fibrogenesis in mouse L929 fibroblasts via modulating PPM1A. J Cell Biochem 120:13372–13381
Liu J, Deng T, Wang Y, Zhang M, Zhu G, Fang H, Wang J (2019) Calycosin inhibits intestinal fibrosis on CCD-18Co cells via modulating transforming growth factor-beta/Smad signaling pathway. Pharmacology 104:81–89
Marti-Rodrigo A, Alegre F, Moragrega AB, Garcia-Garcia F, Marti-Rodrigo P, Fernandez-Iglesias A, Gracia-Sancho J, Apostolova N, Esplugues JV, Blas-Garcia A (2019) Rilpivirine attenuates liver fibrosis through selective STAT1-mediated apoptosis in hepatic stellate cells. Gut
Nicolas CS, Peineau S, Amici M, Csaba Z, Fafouri A, Javalet C, Collett VJ, Hildebrandt L, Seaton G, Choi SL, Sim SE, Bradley C, Lee K, Zhuo M, Kaang BK, Gressens P, Dournaud P, Fitzjohn SM, Bortolotto ZA, Cho K, Collingridge GL (2012) The Jak/STAT pathway is involved in synaptic plasticity. Neuron 73:374–390
Piperigkou Z, Bouris P, Onisto M, Franchi M, Kletsas D, Theocharis AD, Karamanos NK (2016) Estrogen receptor beta modulates breast cancer cells functional properties, signaling and expression of matrix molecules. Matrix Biol 56:4–23
Ponnusamy S, Tran QT, Thiyagarajan T, Miller DD, Bridges D, Narayanan R (2017) An estrogen receptor beta-selective agonist inhibits non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in preclinical models by regulating bile acid and xenobiotic receptors. Exp Biol Med 242:606–616
Que R, Shen Y, Ren J, Tao Z, Zhu X, Li Y (2018) Estrogen receptorbetadependent effects of saikosaponind on the suppression of oxidative stressinduced rat hepatic stellate cell activation. Int J Mol Med 41:1357–1364
Randelli F, Menon A, Giai Via A, Mazzoleni MG, Sciancalepore F, Brioschi M, Gagliano N (2018) Effect of a collagen-based compound on morpho-functional properties of cultured human tenocytes. Cells:7
Roeb E (2018) Matrix metalloproteinases and liver fibrosis (translational aspects). Matrix Biol 68-69:463–473
Sekine Y, Yamamoto T, Yumioka T, Imoto S, Kojima H, Matsuda T (2004) Cross-talk between endocrine-disrupting chemicals and cytokine signaling through estrogen receptors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 315:692–698
Shahzad M, Shabbir A, Wojcikowski K, Wohlmuth H, Gobe GC (2016) The antioxidant effects of Radix Astragali (Astragalus membranaceus and related species) in protecting tissues from injury and disease. Curr Drug Targets 17:1331–1340
Shiratori Y, Geerts A, Ichida T, Kawase T, Wisse E (1986) Kupffer cells from CCl4-induced fibrotic livers stimulate proliferation of fat-storing cells. J Hepatol 3:294–303
Sodek J, Overall CM (1992) Matrix metalloproteinases in periodontal tissue remodelling. Matrix 1:352–362
Song DG, Kim D, Jung JW, Nam SH, Kim JE, Kim HJ, Kim JH, Lee SJ, Pan CH, Kim S, Lee JW (2019) Glutamyl-prolyl-tRNA synthetase induces fibrotic extracellular matrix via both transcriptional and translational mechanisms. FASEB J 33:4341–4354
Uchida NS, Silva-Filho SE, Aguiar RP, Wiirzler LAM, Cardia GFE, Cavalcante HAO, Silva-Comar FMS, Becker TCA, Silva EL, Bersani-Amado CA, Cuman RKN (2017) Protective effect of Cymbopogon citratus essential oil in experimental model of acetaminophen-induced liver injury. Am J Chin Med 45:515–532
Visse R, Nagase H (2003) Matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases: structure, function, and biochemistry. Circ Res 92:827–839
Vuda M, D'Souza R, Upadhya S, Kumar V, Rao N, Kumar V, Boillat C, Mungli P (2012) Hepatoprotective and antioxidant activity of aqueous extract of Hybanthus enneaspermus against CCl4-induced liver injury in rats. Exp Toxicol Pathol 64:855–859
Wang TH, Xiang QL, Chen JW, Pan H, Cui YH (2007) Raloxifene plus 17beta-estradiol inhibits proliferation of primary cultured vascular smooth muscle cells and human mammary endothelial cells via the janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription3 cascade. Eur J Pharmacol 561:7–13
Wang JJ, Li J, Shi L, Lv XW, Cheng WM, Chen YY (2010) Preventive effects of a fractioned polysaccharide from a traditional Chinese herbal medical formula (Yu Ping Feng San) on carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatic fibrosis. J Pharm Pharmacol 62:935–942
Wang Y, Qu A, Wang H (2015) Signal transducer and activator of transcription 4 in liver diseases. Int J Biol Sci 11:448–455
Wang A, Zhou F, Li D, Lu JJ, Wang Y, Lin L (2019a) Gamma-Mangostin alleviates liver fibrosis through Sirtuin 3-superoxide-high mobility group box 1 signaling axis. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 363:142–153
Wang B, Li X, Hu W, Zhou Y, Din Y (2019b) Silencing of lncRNA SNHG20 delays the progression of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease to hepatocellular carcinoma via regulating liver Kupffer cells polarization. IUBMB Life 71:1952–1961
Xu Y, Xiong J, Zhao Y, He B, Zheng Z, Chu G, Zhu Q (2015) Calycosin rebalances advanced glycation end products-induced glucose uptake dysfunction of hepatocyte in vitro. Am J Chin Med 43:1191–1210
Yamamoto T, Matsuda T, Junicho A, Kishi H, Saatcioglu F, Muraguchi A (2000) Cross-talk between signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 and estrogen receptor signaling. FEBS Lett 486:143–148
Yang W, Lu Y, Xu Y, Xu L, Zheng W, Wu Y, Li L, Shen P (2012) Estrogen represses hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) growth via inhibiting alternative activation of tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs). J Biol Chem 287:40140–40149
Yasuda M, Shimizu I, Shiba M, Ito S (1999) Suppressive effects of estradiol on dimethylnitrosamine-induced fibrosis of the liver in rats. Hepatology 29:719–727
Yu HC, Qin HY, He F, Wang L, Fu W, Liu D, Guo FC, Liang L, Dou KF, Han H (2011) Canonical notch pathway protects hepatocytes from ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice by repressing reactive oxygen species production through JAK2/STAT3 signaling. Hepatology 54:979–988
Zhang B, Zhang CG, Ji LH, Zhao G, Wu ZY (2018) Estrogen receptor beta selective agonist ameliorates liver cirrhosis in rats by inhibiting the activation and proliferation of hepatic stellate cells. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 33:747–755
Zhou Y, Shimizu I, Lu G, Itonaga M, Okamura Y, Shono M, Honda H, Inoue S, Muramatsu M, Ito S (2001) Hepatic stellate cells contain the functional estrogen receptor beta but not the estrogen receptor alpha in male and female rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 286:1059–1065
Zhou HC, Wang H, Shi K, Li JM, Zong Y, Du R (2018) Hepatoprotective effect of baicalein against acetaminophen-induced acute liver injury in mice. Molecules:24
Acknowledgments
The drug identification (Fig. 2) was from Professor Jingbo Shi (School of Pharmacy, Anhui Medical University, Anhui, China).
Funding
This work was supported by the University Natural Science Research Project of Anhui Province (NO. KJ2016A342).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Mengmeng Zhang and Jiajia Wang designed research. Mengmeng Zhang and Yaxin Wang conducted experiments. Mengmeng Zhang and Guannan Zhu analyzed data. Mengmeng Zhang and Cheng Sun wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the manuscript. All experimental data were generated in-house and we did not use a paper mill.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
In our study, all animal experiments were reviewed and approved by the Ethical Committee and the China National Institutes of Healthy Guidelines for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(ZIP 2.51 mb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, M., Wang, Y., Zhu, G. et al. Hepatoprotective effect and possible mechanism of phytoestrogen calycosin on carbon tetrachloride–induced liver fibrosis in mice. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 394, 189–204 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-020-01891-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-020-01891-5