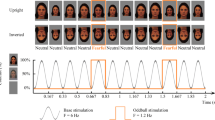
Abstract
Infants are particularly vulnerable to the effects of pain and discomfort, which can lead to abnormal brain development, yielding long-term adverse neurodevelopmental outcomes. In this study, we propose a video-based method for automated detection of their discomfort. The infant face is first detected and normalized. A two-phase classification workflow is then employed, where Phase 1 is subject-independent, and Phase 2 is subject-dependent. Phase 1 derives geometric and appearance features, while Phase 2 incorporates facial landmark-based template matching. An SVM classifier is finally applied to video frames to recognize facial expressions of comfort or discomfort. The method is evaluated using videos from 22 infants. Experimental results show an AUC of 0.87 for the subject-independent phase and 0.97 for the subject-dependent phase, which is promising for clinical use.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acharya, R., Kumar, A., Bhat, P., Lim, C., Kannathal, N., Krishnan, S., et al.: Classification of cardiac abnormalities using heart rate signals. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 42(3), 288–293 (2004)
Ahonen, T., Hadid, A., Pietikainen, M.: Face description with local binary patterns: application to face recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 28(12), 2037–2041 (2006)
Ambuel, B., Hamlett, K.W., Marx, C.M., Blumer, J.L.: Assessing distress in pediatric intensive care environments: the comfort scale. J. Pediatr. Psychol. 17(1), 95–109 (1992)
American Academy of Pediatrics, and Fetus and Newborn Committee: Prevention and management of pain in the neonate: an update. Pediatrics 118(5), 2231–2241 (2006)
Ashraf, A.B., Lucey, S., Cohn, J.F., Chen, T., Ambadar, Z., Prkachin, K.M., Solomon, P.E.: The painful face-pain expression recognition using active appearance models. Image Vis. Comput. 27(12), 1788–1796 (2009)
Behrman, R., Butler, A.S.: Institute of Medicine Committee on Understanding Premature Birth and Assuring Healthy Outcomes Board on Health Sciences Outcomes: Preterm Birth: Causes, Consequences, and Prevention. Preterm Birth: Causes, Consequences, and Prevention. National Academies Press, Washington (2007)
Blum, A.L., Langley, P.: Selection of relevant features and examples in machine learning. Artif. Intell. 97(1–2), 245–271 (1997)
Brahnam, S., Chuang, C.F., Shih, F.Y., Slack, M.R.: Machine recognition and representation of neonatal facial displays of acute pain. Artif. Intell. Med. 36(3), 211–222 (2006)
Brown, S., Timmins, F.: An exploration of nurses’ knowledge of, and attitudes towards, pain recognition and management in neonates. J. Neonatal Nurs. 11(2), 65–71 (2005)
Chang, F.J., Tran, A.T., Hassner, T., Masi, I., Nevatia, R., Medioni, G.: Expnet: landmark-free, deep, 3D facial expressions. arXiv preprint arXiv:1802.00542 (2018)
Déniz, O., Bueno, G., Salido, J., De la Torre, F.: Face recognition using histograms of oriented gradients. Pattern Recogn. Lett. 32(12), 1598–1603 (2011)
Fitzgerald, M.: The development of nociceptive circuits. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 6(7), 507–520 (2005)
Fitzgerald, M., Millard, C., McIntosh, N.: Cutaneous hypersensitivity following peripheral tissue damage in newborn infants and its reversal with topical anaesthesia. Pain 39(1), 31–36 (1989)
Fotiadou, E., Zinger, S., Tjon A Ten, W., Bambang Oetomo, S., et al.: Video-based facial discomfort analysis for infants. In: IS&T/SPIE Electronic Imaging, pp. 90290F–90290F. International Society for Optics and Photonics (2014)
Gholami, B., Haddad, W.M., Tannenbaum, A.R.: Relevance vector machine learning for neonate pain intensity assessment using digital imaging. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 57(6), 1457–1466 (2010)
Grunau, R., Craig, K.: Pain expression in neonates: facial action and cry. Pain 28(3), 395–410 (1987)
Grunau, R.E., Whitfield, M.F., Petrie-Thomas, J., Synnes, A.R., Cepeda, I.L., Keidar, A., Rogers, M., MacKay, M., Hubber-Richard, P., Johannesen, D.: Neonatal pain, parenting stress and interaction, in relation to cognitive and motor development at 8 and 18 months in preterm infants. Pain 143(1), 138–146 (2009)
Hammal, Z., Cohn, J.F.: Towards multimodal pain assessment for research and clinical use. In: Workshop on Roadmapping the Future of Multimodal Interaction Research Including Business Opportunities and Challenges (2014)
Hsieh, R., Mochizuki, Y., Asano, T., Higashida, M., Shirai, A.: Real baby-real family: Vr entertainment baby interaction system. In: ACM SIGGRAPH 2017 Emerging Technologies, p. 20. ACM (2017)
Johnston, C.C., Stevens, B.J., Yang, F., Horton, L.: Differential response to pain by very premature neonates. Pain 61(3), 471–479 (1995)
Kazemi, V., Josephine, S.: One millisecond face alignment with an ensemble of regression trees. In: 27th IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR 2014, Columbus, United States, 23 June 2014 through 28 June 2014, pp. 1867–1874. IEEE Computer Society (2014)
Kharghanian, R., Peiravi, A., Moradi, F.: Pain detection from facial images using unsupervised feature learning approach. In: 2016 IEEE 38th Annual International Conference of the Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), pp. 419–422. IEEE (2016)
King, D.E.: Dlib-ml: a machine learning toolkit. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 10((Jul)), 1755–1758 (2009)
Kotsia, I., Pitas, I.: Facial expression recognition in image sequences using geometric deformation features and support vector machines. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 16(1), 172–187 (2007)
Lindh, V., Wiklund, U., Håkansson, S.: Heel lancing in term new-born infants: an evaluation of pain by frequency domain analysis of heart rate variability. Pain 80(1–2), 143–148 (1999)
Littlewort, G.C., Bartlett, M.S., Lee, K.: Automatic coding of facial expressions displayed during posed and genuine pain. Image Vis. Comput. 27(12), 1797–1803 (2009)
Lowe, D.G.: Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 60(2), 91–110 (2004)
Lucey, P., Cohn, J.F., Matthews, I., Lucey, S., Sridharan, S., Howlett, J., Prkachin, K.M.: Automatically detecting pain in video through facial action units. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part B Cybern. 41(3), 664–674 (2011)
Mima, Y., Arakawa, K.: Cause estimation of younger babies’ cries from the frequency analyses of the voice-classification of hunger, sleepiness, and discomfort. In: International Symposium on Intelligent Signal Processing and Communications, 2006. ISPACS’06, pp. 29–32. IEEE (2006)
Norden, J., Hannallah, R., Getson, P., O’Donnell, R., Kelliher, G., Walker, N.: Reliability of an objective pain scale in children. J. Pain Symptom Manag. 6(3), 196 (1991)
Ojala, T., Pietikainen, M., Maenpaa, T.: Multiresolution gray-scale and rotation invariant texture classification with local binary patterns. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 24(7), 971–987 (2002)
Petrini, J.R., Dias, T., McCormick, M.C., Massolo, M.L., Green, N.S., Escobar, G.J.: Increased risk of adverse neurological development for late preterm infants. J. Pediatr. 154(2), 169–176 (2009)
Raju, T.N., Higgins, R.D., Stark, A.R., Leveno, K.J.: Optimizing care and outcome for late-preterm (near-term) infants: a summary of the workshop sponsored by the national institute of child health and human development. Pediatrics 118(3), 1207–1214 (2006)
Riddell, R.P., Racine, N.: Assessing pain in infancy: the caregiver context. Pain Res. Manag. 14(1), 27–32 (2009)
Schiavenato, M., Byers, J.F., Scovanner, P., McMahon, J.M., Xia, Y., Lu, N., He, H.: Neonatal pain facial expression: evaluating the primal face of pain. Pain 138(2), 460–471 (2008)
Shan, C., Gong, S., McOwan, P.W.: Robust facial expression recognition using local binary patterns. In: 2005 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, ICIP 2005, vol. 2, pp. II–370. IEEE (2005)
Shan, C., Gong, S., McOwan, P.W.: Facial expression recognition based on local binary patterns: a comprehensive study. Image Vis. Comput. 27(6), 803–816 (2009)
Sikka, K., Ahmed, A.A., Diaz, D., Goodwin, M.S., Craig, K.D., Bartlett, M.S., Huang, J.S.: Automated assessment of children’s postoperative pain using computer vision. Pediatrics 136(1), 124–131 (2015)
Stevens, B., Johnston, C., Petryshen, P., Taddio, A.: Premature infant pain profile: development and initial validation. Clin. J. Pain 12(1), 13–22 (1996)
US Department of Health and Human Services: Acute Pain Management in Infants, Children, and Adolescents: Operative and Medical Procedures. Agency for Health Care Policy and Research, Rockville (1992)
Vu, N.S., Caplier, A.: Face recognition with patterns of oriented edge magnitudes. In: European conference on computer vision, pp. 313–326. Springer, Berlin (2010)
Whit Hall, R., Anand, K.: Short-and long-term impact of neonatal pain and stress. NeoReviews 6, 69–75 (2005)
Zamzmi, G., Pai, C.Y., Goldgof, D., Kasturi, R., Ashmeade, T., Sun, Y.: An approach for automated multimodal analysis of infants’ pain. In: 23rd International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR 2016)
Zamzmi, G., Pai, C.Y., Goldgof, D., Kasturi, R., Sun, Y., Ashmeade, T.: Automated pain assessment in neonates. In: 20th Scandinavian Conference on Image Analysis (SCIA 2017)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, Y., Shan, C., Tan, T. et al. Video-based discomfort detection for infants. Machine Vision and Applications 30, 933–944 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00138-018-0968-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00138-018-0968-1