Abstract
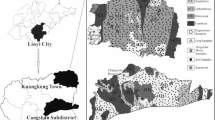
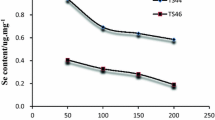
Selenium (Se) is an essential trace element for animals and plants. Se in soil has an important influence on the Se intake by animals and plants. To explore the source of Se in soils of the zinc-smelting area in northwest Guizhou, China, 271 topsoils and 50 deep soil samples were collected, and the concentration, speciation and distribution of Se in soils were analysed. The results showed that the concentration of Se in topsoils ranged from 0.2 mg/kg to 1.79 mg/kg, with an average of 0.84 mg/kg, which was more than 2 times of that in deep soil. These observations indicated that Se was enriched in the surface layer of soil. In terms of spatial distribution, high-Se topsoils (> 1.0 mg/kg) were mainly distributed near the zinc smelting area, and topsoil samples with relatively low content of Se were mainly distributed in areas with less human activities influence. The Se occurrence species in topsoils were in the order of residue, organic-binding, humic-acid binding, water-soluble, Fe/Mn/Al oxide-binding, carbonate-binding and ion-exchange. The contribution of residual Se to total Se in topsoil was decisive, and the content of other species of selenium changed slightly. The Se speciation that was residual in soil is difficult for plants to utilize, which is consistent with previous studies on seleniferous soils caused by zinc smelting. These results indicated that the main reason for Se enrichment in the topsoils of northwest Guizhou Province was indigenous zinc smelting.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bi XY, Feng XB, Yang YG, Qiu GL, Li GH, Li FL, Liu TZ, Fu ZY, Jin ZS (2006) Environmental contamination of heavy metals from zinc smelting areas in Hezhang County, western Guizhou, China. Environ Int 32:883–890. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2006.05.010
Bi XY, Feng XB, Yang YG, Li XD, Sin GPY, Qiu GL, Qian XL, Li FL, He TR, Li P, Liu TZ, Fu ZY (2007) Heavy metals in an impacted wetland system: a typical case from southwestern China. Sci Total Environ 387:257–268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2007.07.059
CCME (2009) Canadian soil quality guidelines for the protection of environmental and human health: selenium. In: Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment (ed) Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment, Winnipeg
Cheng HX, Li M, Zhao CD, Li K, Peng M, Qin AH, Cheng XM (2014) Overview of trace metals in the urban soil of 31 metropolises in China. J Geochem Explor 139:31–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2013.08.012
Dinh QT, Cui ZW, Huang J, Tran TAT, Wang D, Yang WX, Zhou F, Wang MK, Yu DS, Liang DI (2018) Selenium distribution in the Chinese environment and its relationship with human health: a review. Environ Int 112:294–309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2017.12.035
Duan PP, Wang WF, Sang SX, Qian FC, Shao P, Zhao X (2018) Partitioning of hazardous elements during preparation of high-uranium coalfrom Rongyang, Guizhou, China. J Geochem Explor 185:81–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2017.10.022
Fan HF, Wen HJ, Hu RZ, Zhao H (2011) Selenium speciation in Lower Cambrian Se-enriched strata in South China and its geological implications. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 75:7725–7740. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2011.09.027
Feng XB, Li GH, Qiu GL (2004) A preliminary study on mercury contamination to the environment from artisanal zinc smelting using indigenous methods in Hezhang county, Guizhou, China – Part 1:mercury emission from zinc smelting and its influences on the surface waters. Atmos Environ 38:6223–6230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2004.07.020
Floor GH, Romá n-Ross G (2012) Selenium in volcanic environments: a review. Appl Geochem 27:517–531. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2011.11.010
Fordyce FM (2013) Selenium deficiency and toxicity in the environment. In: Selinus O, Alloway B, Centeno JA, Finkelman RB, Fuge R, Lindh U, Smedley P (eds) Essentials of medical geology. Springer, New York, pp 375–416
Gustafsson JP, Johnsson L (1992) Selenium retention in the organic matter of Swedish forest soils. J Soil Sci 43:461–472. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2389.1992.tb00152.x
Horvata M, Nolde N, Fajon V, Jereb V, Logar M, Lojen S, Jacimovic R, Falnoga I, Qu LY, Faganeli J, Drobne D (2003) Total mercury, methylmercury and selenium in mercury polluted areas in the province Guizhou, China. Sci Total Environ 304:231–256. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0048-9697(02)00572-7
Hu GQ, Liu GJ, Wu D, Fu B (2018) Geochemical behavior of hazardous volatile elements in coals with different geological origin during combustion. Fuel 233:361–376. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2018.06.069
Huang YJ, Gulson BL (2002) Selenium in soils, spermatophytes and bryophytes around a Zn–Pb smelter, New South Wales, Australia. Sci Total Environ 293:129–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0048-9697(02)00002-5
Jones DL, Winkel LHE (2016) Global predictions of selenium distributions in soils. In: Banuelos GS (ed) Global advances in selenium research from theory to application. Taylor & Francis Group, London, pp 13–14
Leverington DW, Schindler M (2018) Delineating areas of past environmental degradation near smelters using rock coatings: a case study at Rouyn-Noranda, Quebec. Sci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-35742-4
Liu WC, Ma L, Liu HQ, Pan TY, Xu HL (2005) Research on speciation analysis of chemical elements in soil samples for ecosystem geochemistry study. Rock Miner Anal 24:181–188 (in Chinese)
Long J, Luo Kl (2017) Trace element distribution and enrichment patterns of ediacaran-early cambrian, ziyang selenosis area, central china: constraints for the origin of selenium. J Geochem Explor 172:211–230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2016.11.010
Long J, Zhang SX, Luo KL (2019) Discovery of anomalous molybdenum enrichment in lower carboniferous coal and its availability and origin. J Geochem Explor 200:104–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2019.02.003
Lopes G, Ávila FW, Guilherme LRG (2017) Selenium behavior in the soil environment and its implication for human health. Ciência e Agrotecnologia 41:605–615. https://doi.org/10.1590/1413-70542017416000517
Malcolma KJ, Leveringtonb DW, Schindlera M (2015) A Landsat-based study of black rock coatings proximal to base metal smelters, Sudbury, Ontario, Canada. Int J Remote Sens 36:3932–3960. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431161.2015.1054963
Morrison AL, Swierczek Z, Gulson BL (2016) Visualisation and quantification of heavy metal accessibility in smelter slags: the influence of morphology on availability. Environ Pollut 210:271–281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2015.11.030
Ni RX, Luo KL, Tian XL, Yan SG, Zhong JT, Liu MQ (2016) Distribution and geological sources of selenium in environmental materials in Taoyuan County, Hunan Province, China. Environ Geochem Health 38:927–938. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-015-9772-2
Peng YS, Yang RD, Jin T, Chen J, Zhang J (2018) Risk assessment for potentially toxic metal(loid)s in potatoes in the indigenous zinc smelting area of northwestern Guizhou Province, China. Food Chem Toxicol 120:328–339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2018.07.026
Qin HB, Zhu JM, Lin ZQ, Xu WP, Tan DC, Zheng LR, Takahashi YS (2017) Selenium speciation in seleniferous agricultural soils under different cropping systems using sequential extraction and X-ray absorption spectroscopy. Environ Pollut 225:361–369. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.02.062
Shao Y, Cai CF, Zhang HT, Fu W, Zhong XM, Tang S (2018) Controlling factors of soil selenium distribution in a watershed in Se-enriched and longevity region of South China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 15:20048–20056. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2091-2
Si RJ, Gu XX, Pan XC, Fu SH, Li FY, Zhang M, Li YH, Li XY, Li J (2006) Geochemical character of dispersed element in sphalerite from Fule Pb-Zn polymetal deposit, Yunnan Province. J Mineral Petrol 26:75–80 (in chinese)
Sun GX, Andrew AM, Li G, Chen Z, Yang L, Chen SC, Zhu YG (2016) Distribution of soil selenium in China is potentially controlled by deposition and volatilization? Sci Rep 6:20953. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep20953
Tan JA, Zhu WY, Wang WY, Li RB, Hou SF, Wang DC, Yang LS (2002) Selenium in soil and endemic diseases in China. Sci Total Environ 284:227–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0048-9697(01)00889-0
Tian H, Ma ZZ, Chen XL, Zhang HY, Bao ZY, Wei CH, Xie SY, Wu ST (2016) Geochemical characteristics of selenium and its correlation to other elements and minerals in selenium-enriched rocks in Ziyang County, Shaanxi Province, China. J Earth Sci 27:763–776. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-016-0700-x
Tolu J, Thiry Y, Bueno M, Jolivet C, Potin-Gautier M, Le Hécho I (2014) Distribution and speciation of ambient selenium in contrasted soils, from mineral to organic rich. Sci Total Environ 479-480:93–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.01.079
Wadgaonkar SL, Ferraro A, Race M, Nancharaiah YV, Dhillon KS, Fabbricino M, Esposito G, Piet NLL (2018) Optimization of soil washing to reduce the selenium levels of seleniferous soil from Punjab, Northwestern India. J Environ Qual 47:1530–1537. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq2018.05.0187
Wang GI, Zhu XQ (2003) A study on the selenium background level in the soils in Guizhou. Res Environ Sci 16:23–26 (in chinese)
Wu P, Liu CQ, Yang YG, Zhang GP, Li SL (2002) Heavy metals and their release in the wastes residue pile at the indigenous zinc smelting area. China Environ Sci 22:109–113 (in Chinese)
Yang Y, Wu P, Li XX, Zha XF (2018) Distribution and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in selenium-rich soil with high cadmium content of coal mining area in upper reaches of Guancheng river in Zhijin County, Guizhou. Chin J Ecol 37:1797–1806 (in Chinese)
Zhang H, Feng X, Zhu J, Sapkota A, Meng B, Yao H, Qin H, Larssen T (2012) Selenium in soil inhibits mercury uptake and translocation in Rice (Oryza sativa L.). Environ Sci Technol 46:10040–10046. https://doi.org/10.1021/es302245r
Zhang H, Feng XB, Jiang CX, Li QH, Liu Y, Gu CH, Shang LH, Li P, Lin Y, Larssen T (2014) Understanding the paradox of selenium contamination in mercury mining areas: high soil content and low accumulation in rice. Environ Pollut 188:27–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2014.01.012
Zhang ZZ, Yuan LX, Qi SH, Yin XB (2019) The threshold effect between the soil bioavailable molar Se:Cd ratio and the accumulation of Cd in corn (Zea mays L.) from natural Se-Cd rich soils. Sci Total Environ. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.06.331
Zhou JX, Huang ZL, Zhou ZL, Li GF, Ding XB, Wei GJ (2009) The occurrence states and regularities of dispersed elements in Tianqiao Pb-Zn ore deposit, Guizhou Province, China. Acta Mineral Sin 29:471–480 (in chinese)
Zhu JM, Johnson TM, Finkelman RB, Zheng BS, Sýkorová I, Pešek J (2012) The occurrence and origin of selenium minerals in Se-rich stone coals, spoils and their adjacent soils in Yutangba, China. Chem Geol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2012.08.023
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, Project of Karst Scientific Research Center of the People’s Government of Guizhou Province(U1612442), the science and technology projects of Guizhou Province (Qian Ke He [2020]1Y186; [2016]1078), the High Level Talent Training Program in Guizhou ([2016]5664) and the First Class Discipline Construction Project in Guizhou (GNYL[2017]007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meng, W., Li, XX. & Wu, P. New Insights into Selenium Enrichment in the Soil of Northwestern Guizhou, Southwest China. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 107, 1095–1102 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-021-03256-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-021-03256-x