Abstract
Background
The most frequent mode of progression in the majority of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients treated with Epidermal growth factor – receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors (EGFR-TKIs) is failure to respond to treatment at the primary lesion, suggesting that concurrent radiotherapy (CRT) to the primary lesion (CPRT) during first-line treatment with EGFR-TKI may be a novel therapeutic approach with a potential of additional benefit for metastatic NSCLC. Therefore, this study investigated the progression-free survival (PFS) and safety of CPRT during first-line icotinib treatment in NSCLC patients with EGFR mutations.
Methods
EGFR-mutant NSCLC patients diagnosed with limited multiple metastases were treated with first-line icotinib. The decision to treat the primary lesions with radiation largely depended on the patient’s preference. The study endpoints included PFS, toxicity, progression pattern, and acquisition of the T790M mutation.
Results
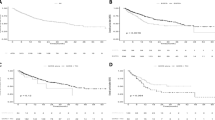
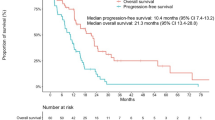
The median PFS in the CPRT and Non-CPRT groups was 13.6 and 10.6 months (hazard ratio [HR] 0.23, 95% confidence interval [CI] 0.15–0.37, P < 0.001). Subgroup analysis showed that the results were statistically significant with 14.7 and 11.5 months for the 19del mutation (HR 0.20, 95% CI 0.10–0.40, P < 0.001) and 12.9 and 9.9 months for the L858R mutation (HR 0.25, 95% CI 0.13–0.48, P < 0.001). There were no reports of interstitial pneumonia associated with treatment at grade 4 or above. Patients who received CPRT during first-line icotinib treatment had the potential to decrease the primary lesion progression (P < 0.05) without increasing newly metastatic lesions (P > 0.05). The proportion of acquired T790M mutations was 26.7% and 45.7% in both groups (P > 0.05).
Conclusion
This study suggests that CPRT is a viable option for patients with EGFR-sensitive mutations in NSCLC with limited multiple metastases during first-line icotinib treatment, which can significantly improve PFS with acceptable toxicities. Data on progression patterns and T790M mutations suggest the need to further investigate the benefits of radiation treatment from a molecular perspective.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, Bray F (2021) Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 71(3):209–249. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21660
Abdallah SM, Hirsh V (2018) Irreversible tyrosine kinase inhibition of epidermal growth factor receptor with afatinib in EGFR activating mutation-positive advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Curr Oncol 25(Suppl 1):S9–S17. https://doi.org/10.3747/co.25.3732
Detterbeck FC, Boffa DJ, Kim AW, Tanoue LT (2017) The eighth edition lung cancer stage classification. Chest 151(1):193–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chest.2016.10.010
Zhao Y, Liu J, Cai X, Pan Z, Liu J, Yin W, Chen H, Xie Z, Liang H, Wang W, Guo Z, Zhao S, Liang W, He J (2019) Efficacy and safety of first line treatments for patients with advanced epidermal growth factor receptor mutated, non-small cell lung cancer: systematic review and network meta-analysis. BMJ 367:l5460. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.l5460
Mitsudomi T, Morita S, Yatabe Y, Negoro S, Okamoto I, Tsurutani J, Seto T, Satouchi M, Tada H, Hirashima T, Asami K, Katakami N, Takada M, Yoshioka H, Shibata K, Kudoh S, Shimizu E, Saito H, Toyooka S, Nakagawa K, Fukuoka M (2010) Gefitinib versus cisplatin plus docetaxel in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring mutations of the epidermal growth factor receptor (WJTOG3405): an open label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 11(2):121–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1470-2045(09)70364-x
Rosell R, Carcereny E, Gervais R, Vergnenegre A, Massuti B, Felip E, Palmero R, Garcia-Gomez R, Pallares C, Sanchez JM, Porta R, Cobo M, Garrido P, Longo F, Moran T, Insa A, De Marinis F, Corre R, Bover I, Illiano A, Dansin E, de Castro J, Milella M, Reguart N, Altavilla G, Jimenez U, Provencio M, Moreno MA, Terrasa J, Muñoz-Langa J, Valdivia J, Isla D, Domine M, Molinier O, Mazieres J, Baize N, Garcia-Campelo R, Robinet G, Rodriguez-Abreu D, Lopez-Vivanco G, Gebbia V, Ferrera-Delgado L, Bombaron P, Bernabe R, Bearz A, Artal A, Cortesi E, Rolfo C, Sanchez-Ronco M, Drozdowskyj A, Queralt C, de Aguirre I, Ramirez JL, Sanchez JJ, Molina MA, Taron M, Paz-Ares L (2012) Erlotinib versus standard chemotherapy as first-line treatment for European patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (EURTAC): a multicentre, open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 13(3):239–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1470-2045(11)70393-x
Shi YK, Wang L, Han BH, Li W, Yu P, Liu YP, Ding CM, Song X, Ma ZY, Ren XL, Feng JF, Zhang HL, Chen GY, Han XH, Wu N, Yao C, Song Y, Zhang SC, Song W, Liu XQ, Zhao SJ, Lin YC, Ye XQ, Li K, Shu YQ, Ding LM, Tan FL, Sun Y (2017) First-line icotinib versus cisplatin/pemetrexed plus pemetrexed maintenance therapy for patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive lung adenocarcinoma (CONVINCE): a phase 3, open-label, randomized study. Annals of oncology: official journal of the European Society for. Med Oncol 28(10):2443–2450. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdx359
Soria JC, Ohe Y, Vansteenkiste J, Reungwetwattana T, Chewaskulyong B, Lee KH, Dechaphunkul A, Imamura F, Nogami N, Kurata T, Okamoto I, Zhou C, Cho BC, Cheng Y, Cho EK, Voon PJ, Planchard D, Su WC, Gray JE, Lee SM, Hodge R, Marotti M, Rukazenkov Y, Ramalingam SS (2018) Osimertinib in untreated EGFR-mutated advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 378(2):113–125. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1713137
Shi Y, Zhang L, Liu X, Zhou C, Zhang L, Zhang S, Wang D, Li Q, Qin S, Hu C, Zhang Y, Chen J, Cheng Y, Feng J, Zhang H, Song Y, Wu YL, Xu N, Zhou J, Luo R, Bai C, Jin Y, Liu W, Wei Z, Tan F, Wang Y, Ding L, Dai H, Jiao S, Wang J, Liang L, Zhang W, Sun Y (2013) Icotinib versus gefitinib in previously treated advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (ICOGEN): a randomised, double-blind phase 3 non-inferiority trial. Lancet Oncol 14(10):953–961. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1470-2045(13)70355-3
Al-Halabi H, Sayegh K, Digamurthy SR, Niemierko A, Piotrowska Z, Willers H, Sequist LV (2015) Pattern of failure analysis in metastatic EGFR-mutant lung cancer treated with tyrosine kinase inhibitors to identify candidates for consolidation stereotactic body radiation therapy. J Thorac Oncol 10(11):1601–1607. https://doi.org/10.1097/jto.0000000000000648
Patel SH, Rimner A, Foster A, Zhang Z, Woo KM, Yu HA, Riely GJ, Wu AJ (2017) Patterns of initial and intracranial failure in metastatic EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer treated with erlotinib. Lung Cancer 108:109–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lungcan.2017.03.010
Peng P, Chen Y, Han G, Meng R, Zhang S, Liao Z, Zhang Y, Gong J, Xiao C, Liu X, Zhang P, Zhang L, Xia S, Chu Q, Chen Y, Zhang L (2019) MA01.09 concomitant SBRT and EGFR-TKI versus EGFR-TKI alone for oligometastatic NSCLC: a multicenter, randomized phase II study. J Thorac Oncol 14(10):S250-S251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtho.2019.08.499
Xu Q, Zhou F, Liu H, Jiang T, Li X, Xu Y, Zhou C (2018) Consolidative local ablative therapy improves the survival of patients with synchronous oligometastatic NSCLC harboring EGFR activating mutation treated with first-line EGFR-TKis. J Thorac Oncol 13(9):1383–1392. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtho.2018.05.019
Dingemans AC, Hendriks LEL, Berghmans T, Levy A, Hasan B, Faivre-Finn C, Giaj-Levra M, Giaj-Levra N, Girard N, Greillier L, Lantuéjoul S, Edwards J, O’Brien M, Reck M, Smit EF, Van Schil P, Postmus PE, Ramella S, Lievens Y, Gaga M, Peled N, Scagliotti GV, Senan S, Paz-Ares L, Guckenberger M, McDonald F, Ekman S, Cufer T, Gietema H, Infante M, Dziadziuszko R, Peters S, Porta RR, Vansteenkiste J, Dooms C, de Ruysscher D, Besse B, Novello S (2019) Definition of synchronous oligometastatic non-small cell lung cancer—a consensus report. J Thorac Oncol 14(12):2109–2119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtho.2019.07.025
Liu K, Jiang G, Zhang A, Li Z, Jia J (2020) Icotinib is as efficacious as gefitinib for brain metastasis of EGFR mutated non-small-cell lung cancer. BMC Cancer 20(1):76. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-020-6543-y
He J, Su C, Liang W, Xu S, Wu L, Fu X, Zhang X, Ge D, Chen Q, Mao W, Xu L, Chen C, Hu B, Shao G, Hu J, Zhao J, Liu X, Liu Z, Wang Z, Xiao Z, Gong T, Lin W, Li X, Ye F, Liu Y, Ma H, Huang Y, Zhou J, Wang Z, Fu J, Ding L, Mao L, Zhou C (2021) Icotinib versus chemotherapy as adjuvant treatment for stage II-IIIA EGFR-mutant non-small-cell lung cancer (EVIDENCE): a randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Respir Med 9(9):1021–1029. https://doi.org/10.1016/s2213-2600(21)00134-x
Zhang Z, Luo F, Zhang Y, Ma Y, Hong S, Yang Y, Fang W, Huang Y, Zhang L, Zhao H (2019) The ACTIVE study protocol: apatinib or placebo plus gefitinib as first-line treatment for patients with EGFR-mutant advanced non-small cell lung cancer (CTONG1706). Cancer Commun 39(1):69. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40880-019-0414-4
Saito H, Fukuhara T, Furuya N, Watanabe K, Sugawara S, Iwasawa S, Tsunezuka Y, Yamaguchi O, Okada M, Yoshimori K, Nakachi I, Gemma A, Azuma K, Kurimoto F, Tsubata Y, Fujita Y, Nagashima H, Asai G, Watanabe S, Miyazaki M, Hagiwara K, Nukiwa T, Morita S, Kobayashi K, Maemondo M (2019) Erlotinib plus bevacizumab versus erlotinib alone in patients with EGFR-positive advanced non-squamous non-small-cell lung cancer (NEJ026): interim analysis of an open-label, randomised, multicentre, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 20(5):625–635. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1470-2045(19)30035-x
Landre T, Guetz DG, Chouahnia K, Duchemann B, Assié JB, Chouaid C (2020) First-line angiogenesis inhibitor plus erlotinib versus erlotinib alone for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer harboring an EGFR mutation. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-020-03311-w
Cheng Y, Murakami H, Yang PC, He J, Nakagawa K, Kang JH, Kim JH, Wang X, Enatsu S, Puri T, Orlando M, Yang JC (2016) Randomized phase II trial of gefitinib with and without pemetrexed as first-line therapy in patients with advanced Nonsquamous non-small-cell lung cancer with activating epidermal growth factor receptor mutations. Clin Oncol 34(27):3258–3266. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2016.66.9218
Iyengar P, Wardak Z, Gerber DE, Tumati V, Ahn C, Hughes RS, Dowell JE, Cheedella N, Nedzi L, Westover KD, Pulipparacharuvil S, Choy H, Timmerman RD (2018) Consolidative radiotherapy for limited metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer: a phase 2 randomized clinical trial. JAMA 4(1):e173501. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaoncol.2017.3501
Xu Y, Zhang S, Xia B, Zhu L, Ma S (2019) Mechanism of radiotherapy in reduction/delay of T790M-mediated EGFR TKI resistance. J Thorac Oncol 14(10):S1033. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtho.2016.11.1439
Jia W, Gao Q, Wang M, Li J, Jing W, Yu J, Zhu H (2021) Overlap time is an independent risk factor of radiation pneumonitis for patients treated with simultaneous EGFR-TKI and thoracic radiotherapy. Radiat Oncol 16(1):41. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13014-021-01765-x
Palma DA, Senan S, Tsujino K, Barriger RB, Rengan R, Moreno M, Bradley JD, Kim TH, Ramella S, Marks LB, De Petris L, Stitt L, Rodrigues G (2013) Predicting radiation pneumonitis after chemoradiation therapy for lung cancer: an international individual patient data meta-analysis. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 85(2):444–450. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2012.04.043
Liu H, Zhang X, Vinogradskiy YY, Swisher SG, Komaki R, Chang JY (2012) Predicting radiation pneumonitis after stereotactic ablative radiation therapy in patients previously treated with conventional thoracic radiation therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 84(4):1017–1023. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2012.02.020
Jiang T, Cheng R, Zhang G, Su C, Zhao C, Li X, Zhang J, Wu F, Chen X, Gao G, Li W, Cai W, Zhou F, Zhao J, Xiong A, Ren S, Zhang G, Zhou C, Zhang J (2017) Characterization of liver metastasis and its effect on targeted therapy in EGFR-mutant NSCLC: a multicenter study. Clin Lung Cancer 18(6):631–639.e632. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cllc.2017.04.015
Cha YK, Lee HY, Ahn MJ, Choi YL, Lee JH, Park K, Lee KS (2015) Survival outcome assessed according to tumor burden and progression patterns in patients with epidermal growth factor receptor mutant lung adenocarcinoma undergoing epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy. Clin Lung Cancer 16(3):228–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cllc.2014.11.002
Gerlinger M, Rowan AJ, Horswell S, Math M, Larkin J, Endesfelder D, Gronroos E, Martinez P, Matthews N, Stewart A, Tarpey P, Varela I, Phillimore B, Begum S, McDonald NQ, Butler A, Jones D, Raine K, Latimer C, Santos CR, Nohadani M, Eklund AC, Spencer-Dene B, Clark G, Pickering L, Stamp G, Gore M, Szallasi Z, Downward J, Futreal PA, Swanton C (2012) Intratumor heterogeneity and branched evolution revealed by multiregion sequencing. N Engl J Med 366(10):883–892. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1113205
Li J, Wu X, Wang Z, Shen Z, Sun N, Zhu X (2015) Ionizing radiation reduces TKI resistance caused by T790M mutation in NSCLC cell lines. Chin J Lung Cance 18(8):475–480. https://doi.org/10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2015.08.02
Xu Y, Zhang S, Xia B, Zhu L, Ma S (2017) P2.05-005 mechanism of radiotherapy in reduction/delay of T790M-mediated EGFR TKI resistance. J Thorac Oncol 12(1):1033. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtho.2016.11.1439
Zhuang H (2018) Research progress on the impact of radiation on TKI resistance mechanisms in NSCLC. J Cancer 9(20):3797–3801. https://doi.org/10.7150/jca.26364
Tang Y, Xia B, Xie R, Xu X, Zhang M, Wu K, Wang B, Ma S (2020) Timing in combination with radiotherapy and patterns of disease progression in non-small cell lung cancer treated with EGFR-TKI. Lung Cancer 140:65–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lungcan.2019.12.009
Funding
This work was supported by the Guiding Project of the Hubei Provincial Health and Health Commission (WJ2021F047).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RD wrote the manuscript, JL, TS data collection, TX, YL, and LD conceived and performed analyses, LX, XY, and JL review and editing the manuscript and provided expertise, FC supervised the study and revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
R. Deng, J. Liu, T. Song, T. Xu, Y. Li, L. Duo, L. Xiang, X. Yu, J. Lei and F. Cao declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical standards
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional review board and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. Patient medical records were analyzed retrospectively, with no individual patient identifiable information used. This work was approved by the ethics committee of Renmin Hospital, Hubei University of Medicine (No.: syrmyy2020—034).
Additional information
Data availability statement
All data relevant to the study are included in the article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deng, R., Liu, J., Song, T. et al. Primary lesion radiotherapy during first-line icotinib treatment in EGFR-mutated NSCLC patients with multiple metastases and no brain metastases: a single-center retrospective study. Strahlenther Onkol 198, 1082–1093 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00066-022-01971-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00066-022-01971-w