Abstract
Purpose
Cerebral hemodynamics are important for the management of intracranial atherosclerotic stenosis (ICAS). The quantitative flow ratio (QFR) is a novel angiography-derived index for assessing the functional relevance of ICAS without pressure wires and adenosine. Good diagnostic yield with the hyperemic fractional flow reserve (FFR) have been reported, while data on the comparison of QFR to FFR are scarce.
Methods
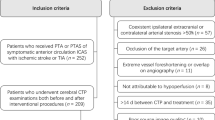
In this prospective study 56 patients with anterior circulation symptomatic ICAS who received endovascular treatment were included. The new method of computing QFR from a single angiographic view, i.e., the Murray law-based QFR (μQFR), was applied to the examined vessels. An artificial intelligence algorithm was developed to realize the automatic delineation of vascular contour. Pressure gradients were measured before and after treatment within the lesion vessel using a pressure guidewire and the FFR was calculated.
Results
There was a good correlation between μQFR and FFR. Preoperative FFR predicted DWI watershed infarction (FFR optimal cut-off level: 0.755). Preoperative μQFR predicted DWI watershed infarction (μQFR optimal cut-off level: 0.51). Preoperative FFR predicted CTP hypoperfusion (FFR best predictive value: 0.62). Preoperative μQFR predicted CTP hypoperfusion (μQFR best predictive value: 0.375).
Conclusion
The μQFR based on DSA images can be used as an indicator to assess the functional status of the lesion in patients with ICAS.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gorelick PB, Wong KS, Bae HJ, Pandey DK. Large artery intracranial occlusive disease: a large worldwide burden but a relatively neglected frontier. Stroke. 2008 ;39(8):2396–9. CrossRef Medline
Wong LK. Global burden of intracranial atherosclerosis. Int J Stroke. 2006 ;1(3):158–9. CrossRef Medline
Wang Y, Zhao X, Liu L, Soo YO, Pu Y, Pan Y, Wang Y, Zou X, Leung TW, Cai Y, Bai Q, Wu Y, Wang C, Pan X, Luo B, Wong KS; CICAS Study Group. Prevalence and outcomes of symptomatic intracranial large artery stenoses and occlusions in China: the Chinese Intracranial Atherosclerosis (CICAS) Study. Stroke. 2014 ;45(3):663–9. CrossRef Medline
Kim SJ, Morales JM, Yaghi S, Honda T, Scalzo F, Hinman JD, Raychev R, Sharma LK, Feldmann E, Romano JG, Prabhakaran S, Liebeskind DS. Intracranial atherosclerotic disease mechanistic subtypes drive hypoperfusion patterns. J Neuroimaging. 2021;31(4):686–90.
Wabnitz AM, Derdeyn CP, Fiorella DJ, Lynn MJ, Cotsonis GA, Liebeskind DS, Waters MF, Lutsep H, López-Cancio E, Turan TN, Montgomery J, Janis LS, Lane B, Chimowitz MI, SAMMPRIS Investigators. Hemodynamic Markers in the Anterior Circulation as Predictors of Recurrent Stroke in Patients With Intracranial Stenosis. Stroke.. 50(1). 2019. pp. 143–7.
Sacchetti DC, Cutting SM, McTaggart RA, Chang AD, Hemendinger M, Grory MB, Siket MS, Burton T, Thompson B, Rostanski SK, Prabhakaran S, Willey JZ, Marshall RS, Elkind MS, Khatri P, Furie KL, Jayaraman MV, Yaghi S. Perfusion imaging and recurrent cerebrovascular events in intracranial atherosclerotic disease or carotid occlusion. Int J Stroke. 2018;13(6):592–9.
Yaghi S, Khatri P, Prabhakaran S, Yeatts SD, Cutting S, Jayaraman M, Chang AD, Sacchetti D, Liebeskind DS, Furie KL. What Threshold Defines Penumbral Brain Tissue in Patients with Symptomatic Anterior Circulation Intracranial Stenosis: An Exploratory Analysis. J Neuroimaging. 2019;29(2):203–5.
Amin-Hanjani S, Pandey DK, Rose-Finnell L, Du X, Richardson D, Thulborn KR, Elkind MS, Zipfel GJ, Liebeskind DS, Silver FL, Kasner SE, Aletich VA, Caplan LR, Derdeyn CP, Gorelick PB, Charbel FT; Vertebrobasilar Flow Evaluation and Risk of Transient Ischemic Attack and Stroke Study Group. Effect of Hemodynamics on Stroke Risk in Symptomatic Atherosclerotic Vertebrobasilar Occlusive Disease. JAMA Neurol. 2016;73(2):178–85.
Yamauchi H, Nishii R, Higashi T, Kagawa S, Fukuyama H. Hemodynamic compromise as a cause of internal border-zone infarction and cortical neuronal damage in atherosclerotic middle cerebral artery disease. Stroke. 2009;40(12):3730–5.
Donahue MJ, Strother MK, Hendrikse J. Novel MRI approaches for assessing cerebral hemodynamics in ischemic cerebrovascular disease. Stroke. 2012;43(3):903–15.
de Havenon A, Khatri P, Prabhakaran S, Yeatts SD, Peterson C, Sacchetti D, Alexander M, Cutting S, Grory BM, Furie K, Liebeskind DS, Yaghi S. Hypoperfusion Distal to Anterior Circulation Intracranial Atherosclerosis is Associated with Recurrent Stroke. J Neuroimaging. 2020;30(4):468–70.
Liebeskind DS, Fong AK, Scalzo F, Lynn MJ, Derdeyn CP, Fiorella DJ.The SAMMPRIS Investigators. SAMMPRIS angiography discloses hemodynamic effects of intracranial stenosis. computational fluid dynamics of fractional flow. Stroke. 2013;44:A156.
Miao Z, Zhang Y, Shuai J, Jiang C, Zhu Q, Chen K, Liu L, Li B, Shi X, Gao L, Liu Y, Wang F, Li Y, Liu T, Zheng H, Wang Y, Wang Y, Study Group of Registry Study of Stenting for Symptomatic Intracranial Artery Stenosis in China. Thirty-Day Outcome of a Multicenter Registry Study of Stenting for Symptomatic Intracranial Artery Stenosis in China. Stroke.. 46(10). 2015. pp. 2822–9.
Alexander MJ, Zauner A, Chaloupka JC, Baxter B, Callison RC, Gupta R, Song SS, Yu W, WEAVE Trial Sites and Interventionalists. WEAVE Trial. Final Results in 152 On-Label Patients. Stroke. 2019;50(4):889–94.
Alexander MJ, Zauner A, Gupta R, Alshekhlee A, Fraser JF, Toth G, Given C, Mackenzie L, Kott B, Hassan AE, Shownkeen H, Baxter BW, Callison RC, Yu W. The WOVEN trial: Wingspan One-year Vascular Events and Neurologic Outcomes. J Neurointerv Surg. 2021;13(4):307–10.
Leng X, Wong KS, Liebeskind DS. Evaluating intracranial ather-osclerosis rather than intracranial stenosis. Stroke. 2014;45(2):645–51.
Xu B, Tu S, Song L, Jin Z, Yu B, Fu G, Zhou Y, Wang J, Chen Y, Pu J, Chen L, Qu X, Yang J, Liu X, Guo L, Shen C, Zhang Y, Zhang Q, Pan H, Fu X, Liu J, Zhao Y, Escaned J, Wang Y, Fearon WF, Dou K, Kirtane AJ, Wu Y, Serruys PW, Yang W, Wijns W, Guan C, Leon MB, Qiao S, Stone GW; FAVOR III China study group. Angiographic quantitative flow ratio-guided coronary intervention (FAVOR III China): a multicentre, randomised, sham-controlled trial. Lancet. 2021 ;398(10317):2149–2159.
Xu B, Tu S, Qiao S, Qu X, Chen Y, Yang J, Guo L, Sun Z, Li Z, Tian F, Fang W, Chen J, Li W, Guan C, Holm NR, Wijns W, Hu S. Diagnostic Accuracy of Angiography-Based Quantitative Flow Ratio Measurements for Online Assessment of Coronary Stenosis. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2017;70(25):3077–87.
Chimowitz MI, Lynn MJ, Howlett-Smith H, Stern BJ, Hertzberg VS, Frankel MR, Levine SR, Chaturvedi S, Kasner SE, Benesch CG, Sila CA, Jovin TG, Romano JG, Warfarin-Aspirin Symptomatic Intracranial Disease Trial Investigators. Comparison of warfarin and aspirin for symptomatic intracranial arterial stenosis. N Engl J Med.. 352(13). Mar, Vol. 31. 2005. pp. 1305–16.
Zaidat OO, Yoo AJ, Khatri P, Tomsick TA, von Kummer R, Saver JL, Marks MP, Prabhakaran S, Kallmes DF, Fitzsimmons BF, Mocco J, Wardlaw JM, Barnwell SL, Jovin TG, Linfante I, Siddiqui AH, Alexander MJ, Hirsch JA, Wintermark M, Albers G, Woo HH, Heck DV, Lev M, Aviv R, Hacke W, Warach S, Broderick J, Derdeyn CP, Furlan A, Nogueira RG, Yavagal DR, Goyal M, Demchuk AM, Bendszus M, Liebeskind DS. Cerebral Angiographic Revascularization Grading (CARG) Collaborators; STIR Revascularization working group; STIR Thrombolysis in Cerebral Infarction (TICI) Task Force. Recommendations on angiographic revascularization grading standards for acute ischemic stroke: a consensus statement. Stroke. 2013;44(9:2650–63.
Tu S, Ding D, Chang Y, Li C, Wijns W, Xu B. Diagnostic accuracy of quantitative flow ratio for assessment of coronary stenosis significance from a single angiographic view: A novel method based on bifurcation fractal law. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2021;97(Suppl 2):1040–7.
Suo S, Zhao Z, Zhao H, Zhang J, Zhao B, Xu J, Zhou Y, Tu S. Cerebral hemodynamics in symptomatic anterior circulation intracranial stenosis measured by angiography-based quantitative flow ratio: association with CT perfusion. Eur Radiol. 2023;33(8):5687–97.
Li Y, Li M, Zhang X, Yang S, Fan H, Qin W, Yang L, Yuan J, Hu W. Clinical features and the degree of cerebrovascular stenosis in different types and subtypes of cerebral watershed infarction. BMC Neurol. 2017;17(1):166.
Quintero-Consuegra MD, Toscano JF, Babadjouni R, Nisson P, Kayyali MN, Chang D, Almallouhi E, Saver JL, Gonzalez NR. Encephaloduroarteriosynangiosis Averts Stroke in Atherosclerotic Patients With Border-Zone Infarct: Post Hoc Analysis From a Performance Criterion Phase II Trial. Neurosurgery. 2021;88(4):E312–E8.
Kernan WN, Ovbiagele B, Black HR, Bravata DM, Chimowitz MI, Ezekowitz MD, Fang MC, Fisher M, Furie KL, Heck DV, Johnston SC, Kasner SE, Kittner SJ, Mitchell PH, Rich MW, Richardson D, Schwamm LH, Wilson JA; American Heart Association Stroke Council, Council on Cardiovascular and Stroke Nursing, Council on Clinical Cardiology, and Council on Peripheral Vascular Disease. Guidelines for the prevention of stroke in patients with stroke and transient ischemic attack: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2014 ;45(7):2160–236.
Zaidat OO, Fitzsimmons BF, Woodward BK, Wang Z, Killer-Oberpfalzer M, Wakhloo A, Gupta R, Kirshner H, Megerian JT, Lesko J, Pitzer P, Ramos J, Castonguay AC, Barnwell S, Smith WS, Gress DR, VISSIT Trial Investigators. Effect of a balloon-expandable intracranial stent vs medical therapy on risk of stroke in patients with symptomatic intracranial stenosis. the VISSIT randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2015;313(12):1240–8.
Gao P, Wang T, Wang D, Liebeskind DS, Shi H, Li T, Zhao Z, Cai Y, Wu W, He W, Yu J, Zheng B, Wang H, Wu Y, Dmytriw AA, Krings T, Derdeyn CP, Jiao L, CASSISS Trial Investigators. Effect of Stenting Plus Medical Therapy vs Medical Therapy Alone on Risk of Stroke and Death in Patients With Symptomatic Intracranial Stenosis. The CASSISS Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA. 2022;328(6):534–42.
Pu Y, Lan L, Leng X, Wong LK, Liu L. Intracranial atherosclerosis: From anatomy to pathophysiology. Int J Stroke. 2017;12(3):236–45.
Kim KH, Doh JH, Koo BK, Min JK, Erglis A, Yang HM, Park KW, Lee HY, Kang HJ, Kim YJ, Lee SY, Kim HS. A novel noninvasive technology for treatment planning using virtual coronary stenting and computed tomography-derived computed fractional flow reserve. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2014;7(1):72–8.
Fearon WF, Bornschein B, Tonino PA, Gothe RM, Bruyne BD, Pijls NH, Siebert U, Fractional Flow Reserve Versus Angiography for Multivessel Evaluation (FAME) Study Investigators. Economic evaluation of fractional flow reserve-guided percutaneous coronary intervention in patients with multivessel disease. Circulation.. 122(24). 2010. pp. 2545–50.
Pijls NH, Fearon WF, Tonino PA, Siebert U, Ikeno F, Bornschein B, van’t Veer M, Klauss V, Manoharan G, Engstrøm T, Oldroyd KG, Ver Lee PN, MacCarthy PA, De Bruyne B; FAME Study Investigators. Fractional flow reserve versus angiography for guiding percutaneous coronary intervention in patients with multivessel coronary artery disease: 2‑year follow-up of the FAME (Fractional Flow Reserve Versus Angiography for Multivessel Evaluation) study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2010 ;56(3):177–84.
Liu CP, Ling YH, Kao HL. Use of a pressure-sensing wire to detect sequential pressure gradients for ipsilateral vertebral and subclavian artery stenoses. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2005;26(7):1810–2.
Han YF, Liu WH, Chen XL, Xiong YY, Yin Q, Xu GL, Zhu WS, Zhang RL, Ma MM, Li M, Dai QL, Sun W, Liu DZ, Duan LH, Liu XF. Severity assessment of intracranial large artery stenosis by pressure gradient measurements: A feasibility study. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2016;88(2):255–61.
Miao Z, Liebeskind DS, Lo W, Liu L, Pu Y, Leng X, Song L, Xu X, Jia B, Gao F, Mo D, Sun X, Liu L, Ma N, Wang B, Wang Y, Wang Y. Fractional Flow Assessment for the Evaluation of Intracranial Atherosclerosis: A Feasibility Study. Interv Neurol. 2016;5(1–2:65–75.
Li L, Yang B, Dmytriw AA, Wang T, Luo J, Li Y, Ma Y, Chen J, Wang Y, Gao P, Feng Y, Bai X, Zhang X, Dong J, Yang R, Jiao L, Ling F. Hemodynamic Versus Anatomic Assessment of Symptomatic Atherosclerotic Middle Cerebral Artery Stenosis: the Relationship Between Pressure Wire Translesional Gradient and Angiographic Lesion Geometry. Front Neurol. 2021;12:671778.
Huang K, Yao W, Du J, Wang F, Han Y, Chang Y, Liu R, Ye R, Zhu W, Tu S, Liu X. Functional Assessment of Cerebral Artery Stenosis by Angiography-Based Quantitative Flow Ratio: A Pilot Study. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022;14:813648.
Leung TWH, Fan SY, Ip HL, Lau AYL, Siu DYW, Dai EYL, Wong LKS, Liebeskind DS. Effects of collateral circulation on haemodynamic flow status in intracranial artery stenosis depicted by computational fluid dynamics. Hong Kong Med J. 2019;25(Suppl 5(4):18–21.
Feng X, Chan KL, Lan L, Abrigo J, Liu J, Fang H, Xu Y, Soo Y, Leng X, Leung TW. Stroke Mechanisms in Symptomatic Intracranial Atherosclerotic Disease: Classification and Clinical Implications. Stroke. 2019;50(10:2692–9.
Lan L, Leng X, Abrigo J, Fang H, Ip VH, Soo YO, Leung TW, Yu SC, Wong LK. Diminished Signal Intensities Distal to Intracranial Arterial Stenosis on Time-of-Flight MR Angiography Might Indicate Delayed Cerebral Perfusion. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2016;42(3–4:232–9.
Ge X, Zhao H, Zhou Z, Li X, Sun B, Wu H, Wan J, Xu J, Villablanca JP, Liu X. Association of Fractional Flow on 3D-TOF-MRA with Cerebral Perfusion in Patients with MCA Stenosis. Ajnr Am J Neuroradiol. 2019;40(7):1124–31.
Hoffman SJ, Yee AH, Slusser JP, Rihal CS, Holmes DR Jr, Rabinstein AA, Gulati R. Neuroimaging patterns of ischemic stroke after percutaneous coronary intervention. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2015;85(6):1033–40.
Wong KS, Gao S, Chan YL, Hansberg T, Lam WW, Droste DW, Kay R, Ringelstein EB. Mechanisms of acute cerebral infarctions in patients with middle cerebral artery stenosis: a diffusion-weighted imaging and microemboli monitoring study. Ann Neurol. 2002;52(1):74–81.
Wang M, Leng X, Mao B, Zou R, Lin D, Gao Y, Wang N, Lu Y, Fiehler J, Siddiqui AH, Wu J, Xiang J, Wan S. Functional evaluation of intracranial atherosclerotic stenosis by pressure ratio measurements. Heliyon. 2023;9(2):e13527.
Liu J, Yan Z, Pu Y, Shiu WS, Wu J, Chen R, Leng X, Qin H, Liu X, Jia B, Song L, Wang Y, Miao Z, Wang Y, Liu L, Cai XC. Functional assessment of cerebral artery stenosis: A pilot study based on computational fluid dynamics. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2017;37(7):2567–76.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the ORDOS Industrial Innovation Talent Team Award, ORDOS science and technology Innovation Leaders, the Inner Mongolia Science and Technology Program (No. 2022YFSH0131) as well as Beijing Natural Science Foundation (No. Z220016).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Y. Wu, F. Gao and H. Feng declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical standards
All investigations described in this manuscript were carried out with the approval of the responsible ethics committee and in accordance with national law and the Helsinki Declaration of 1975 (in its current revised form). Written informed consent was waived by the Institutional Review Board.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Y., Gao, F. & Feng, H. Hemodynamic Impairments of Evaluating Symptomatic Intracranial Atherosclerotic Stenosis using Quantitative Flow Ratio on Digital Subtraction Angiography. Clin Neuroradiol (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00062-024-01395-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00062-024-01395-2