Abstract
Background
Heat shock protein family A member 5 (HSPA5), a recently identified suppressor of ferroptosis, was reported to potentially regulating osteoarthritis. However, the exact role of HSPA5 and how its expression was regulated in osteoarthritis are largely unclear.
Methods
Rat primary chondrocytes were treated with 10 ng/mL IL-1β for 24 h and incubated with ferrostatin-1 (a ferroptosis inhibitor). Cell viability, production of TNF-α, ROS and MDA, expression levels of collagen II, MMP13, GPX4, and SND1, and Fe2+ concentration were detected. Gain- and loss-of-function manipulations were performed to investigate the effect of HSPA5 on chondrocyte functions, and SND1 shRNA (sh-SND1) was transfected into IL-1β-treated primary chondrocytes alone or together with sh-HSPA5. Furthermore, the interaction between HSPA5 and GPX4 and the regulation of HSPA5 on GPX4 were explored. Finally, SND1 was knocked down in the rats with osteoarthritis, and the histopathology, expression of HSPA5-GPX4 axis, and levels of oxidative stress markers were evaluated.
Results
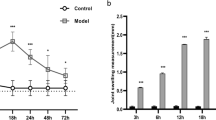
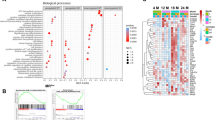
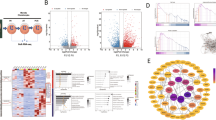
IL-1β treatment could enhance extracellular matrix (ECM) degradation (collagen II reduced and MMP13 increased), promote ferroptosis, manifested by decreased cell viability, increased levels of TNF-α, ROS, MDA, and Fe2+ concentrations, and decreased level of GPX4 protein, and increase SND1 expression in chondrocytes, which could be reversed by ferrostatin-1. Knockdown of SND1 enhanced ECM degradation and suppressed ferroptosis IL-1β-treated chondrocytes, which could be eliminated by knockdown of HSPA5. SND1 bound with HSPA5 at the 3’UTR and destabilized the HSPA5 mRNA. HSPA5 protein directly bound with GPX4 protein and positively regulate its expression. HSPA5 overexpression suppressed IL-1β-induced chondrocyte ferroptosis, while this effect was counteracted by GPX4 silencing. Knockdown of SND1 upregulated HSPA5 and GPX4 in rat cartilage, inhibited inflammatory damage and ferroptosis, and alleviated OA progression.
Conclusion
The RNA-binding protein SND1 promotes the degradation of GPX4 by destabilizing the HSPA5 mRNA and suppressing HSPA5 expression, promoting ferroptosis in osteoarthritis chondrocytes.






Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used during the present study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- OA:
-
Osteoarthritis
- SND1:
-
Staphylococcal nuclease domain containing 1
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- GPX4:
-
Glutathione peroxidase 4
- HSPA5:
-
Heat shock protein family a member 5
- IL-1β:
-
Interleukin-1β
- TNF-α:
-
Tumor necrosis factor-α
- MMP13:
-
Matrix metallopeptidase13
- OARSI:
-
Osteoarthritis Research Society International
- SDS-PAGE:
-
Sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
- PVDF:
-
Polyvinylidene difluoride
- HRP:
-
Horseradish peroxidase
References
Liu R, Yuan X, Yu J, Quan Q, Meng H, Wang C, et al. An updated meta-analysis of the asporin gene D-repeat in knee osteoarthritis: effects of gender and ethnicity. J Orthop Surg Res. 2017;12:148.
Showery JE, Kusnezov NA, Dunn JC, Bader JO, Belmont PJ Jr, Waterman BR. The rising incidence of degenerative and posttraumatic osteoarthritis of the knee in the United States Military. J Arthroplasty. 2016;31:2108–14.
Qin G, Song Y, Guo Y, Sun Y, Zeng W. LincRNA TINCR facilitates excessive proliferation and inflammation in post-burn skin fibroblasts by directly binding with SND1 protein and inducing SND1-mediated TGF-β1 expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019;509:903–10.
Zhao C, Cui X, Zhao Y, Qian B, Zhang N, Xin L, et al. Impact of hepatocyte-specific deletion of staphylococcal nuclease and tudor domain containing 1 (SND1) on liver insulin resistance and acute liver failure of mice. Bioengineered. 2021;12:7360–75.
Qin G, Sun Y, Guo Y, Song Y. PAX5 activates telomerase activity and proliferation in keloid fibroblasts by transcriptional regulation of SND1, thus promoting keloid growth in burn-injured skin. Inflamm Res. 2021;70:459–72.
Simão M, Cancela ML. Musculoskeletal complications associated with pathological iron toxicity and its molecular mechanisms. Biochem Soc Trans. 2021;49:747–59.
Delling U, Brehm W, Metzger M, Ludewig E, Winter K, Jülke H. In vivo tracking and fate of intra-articularly injected superparamagnetic iron oxide particle-labeled multipotent stromal cells in an ovine model of osteoarthritis. Cell Transplant. 2015;24:2379–90.
Hu Q, Zhang Y, Lou H, Ou Z, Liu J, Duan W, et al. GPX4 and vitamin E cooperatively protect hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells from lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis. Cell Death Dis. 2021;12:706.
Krümmel B, Plötz T, Jörns A, Lenzen S, Mehmeti I. The central role of glutathione peroxidase 4 in the regulation of ferroptosis and its implications for pro-inflammatory cytokine-mediated beta-cell death. Biochimica et biophysica acta Molecular basis of disease 2021; 1867:166114.
Yao X, Sun K, Yu S, Luo J, Guo J, Lin J, et al. Chondrocyte ferroptosis contribute to the progression of osteoarthritis. J Orthop Transl. 2021;27:33–43.
Geng Y, Chen J, Alahdal M, Chang C, Duan L, Zhu W, et al. Intra-articular injection of hUC-MSCs expressing miR-140-5p induces cartilage self-repairing in the rat osteoarthritis. J Bone Miner Metab. 2020;38:277–88.
Hu S, Sechi M, Singh PK, Dai L, McCann S, Sun D, et al. A novel redox modulator induces a GPX4-mediated cell death that is dependent on iron and reactive oxygen species. J Med Chem. 2020;63:9838–55.
Rakshit J, Mallick A, Roy S, Sarbajna A, Dutta M, Bandyopadhyay J. Iron-induced apoptotic cell death and autophagy dysfunction in human neuroblastoma cell line SH-SY5Y. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2020;193:138–51.
Tang HM, Cheung PCK. Gallic acid triggers iron-dependent cell death with apoptotic, ferroptotic, and necroptotic features. Toxins. 2019;11:492.
Zhou X, Zheng Y, Sun W, Zhang Z, Liu J, Yang W, et al. D-mannose alleviates osteoarthritis progression by inhibiting chondrocyte ferroptosis in a HIF-2α-dependent manner. Cell Prolif. 2021;54:e13134.
Luo H, Zhang R. Icariin enhances cell survival in lipopolysaccharide-induced synoviocytes by suppressing ferroptosis via the Xc-/GPX4 axis. Exp Ther Med. 2021;21:72.
Zhou M, Wang A, Yin B, Wu D, Han S, Zhang W, et al. SND1 promotes the proliferation of osteosarcoma cells by upregulating COX-2/PGE2 expression via activation of NF-κB. Oncol Rep. 2019;41:579–89.
Huang YZ, Zhang J, Shen JJ, Zhao TX, Xu YJ. miRNA-296-5p functions as a potential tumor suppressor in human osteosarcoma by targeting SND1. Chin Med J. 2021;134:564–72.
Navarro-Imaz H, Ochoa B, García-Arcos I, Martínez MJ, Chico Y, Fresnedo O, et al. Molecular and cellular insights into the role of SND1 in lipid metabolism. Biochim biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2020;1865:158589.
Ochoa B, Chico Y, Martínez MJ. Insights into SND1 oncogene promoter regulation. Front Oncol. 2018;8:606.
Tsuchiya N, Ochiai M, Nakashima K, Ubagai T, Sugimura T, Nakagama H. SND1, a component of RNA-induced silencing complex, is up-regulated in human colon cancers and implicated in early stage colon carcinogenesis. Can Res. 2007;67:9568–76.
Shao J, Gao F, Zhang B, Zhao M, Zhou Y, He J, et al. Aggregation of SND1 in stress granules is associated with the microtubule cytoskeleton during heat shock stimulus. Anatomical Rec (Hoboken, NJ: 2007). 2017;300:2192–9.
Baquero-Perez B, Antanaviciute A, Yonchev ID, Carr IM, Wilson SA, Whitehouse A. The Tudor SND1 protein is an m(6)A RNA reader essential for replication of Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus. Elife. 2019. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.47261.
Han C, Xie K, Yang C, Zhang F, Liang Q, Lan C, et al. HA15 alleviates bone loss in ovariectomy-induced osteoporosis by targeting HSPA5. Exp Cell Res. 2021;406:112781.
Duangchan T, Tawonsawatruk T, Angsanuntsukh C, Trachoo O, Hongeng S, Kitiyanant N, et al. Amelioration of osteogenesis in iPSC-derived mesenchymal stem cells from osteogenesis imperfecta patients by endoplasmic reticulum stress inhibitor. Life Sci. 2021;278:119628.
de Seny D, Bianchi E, Baiwir D, Cobraiville G, Collin C, Deliège M, et al. Proteins involved in the endoplasmic reticulum stress are modulated in synovitis of osteoarthritis, chronic pyrophosphate arthropathy and rheumatoid arthritis, and correlate with the histological inflammatory score. Sci Rep. 2020;10:14159.
Yang H, Wen Y, Zhang M, Liu Q, Zhang H, Zhang J, et al. MTORC1 coordinates the autophagy and apoptosis signaling in articular chondrocytes in osteoarthritic temporomandibular joint. Autophagy. 2020;16:271–88.
Chen Y, Mi Y, Zhang X, Ma Q, Song Y, Zhang L, et al. Dihydroartemisinin-induced unfolded protein response feedback attenuates ferroptosis via PERK/ATF4/HSPA5 pathway in glioma cells. J Exp Clin Cancer Res CR. 2019;38:402.
Huang Y, Xie Z, Li X, Chen W, He Y, Wu S, et al. Development and validation of a ferroptosis-related prognostic model for the prediction of progression-free survival and immune microenvironment in patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma. Int Immunopharmaco. 2021;101:108156.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LL: conceptualization and supervision; ML: supervision and writing-original draft; YC: methodology and writing—original draft; WH: resources, data curation; KP: formal analysis and software; KX: formal analysis and data curation; CL: writing—original draft and data curation; WY: resources; WZ: software.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No conflict of interest exits in the submission of this manuscript.
Ethics approval
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Xi’an Jiaotong University (No. XJTULAC-2018-096).
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Jason J. McDougall.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lv, M., Cai, Y., Hou, W. et al. The RNA-binding protein SND1 promotes the degradation of GPX4 by destabilizing the HSPA5 mRNA and suppressing HSPA5 expression, promoting ferroptosis in osteoarthritis chondrocytes. Inflamm. Res. 71, 461–472 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-022-01547-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-022-01547-5