Abstract
Objective
This study aimed to investigate the relationship between miR-21 and lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced myocardial injury and its molecular and regulatory mechanisms.
Methods
We constructed LPS-mediated myocardial injury model using C57BL/6J mice and H9c2 cells. In-vivo, in-vitro, RIP and dual-luciferase reporter assays were used to determine the effect of miR-21 on myocardial injury.
Results
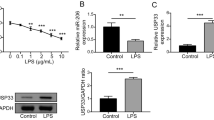
In-vivo and in-vitro results showed that the expression of miR-21 was increased in LPS-treated H9c2 cells and myocardial tissues of mice, and the pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8 and TNF-α) and NF-κB pathway were activated in LPS-treated H9c2 cells. Besides, the B-cell lymphoma-2 (Bcl-2) and cyclin-dependent kinase 6 (CDK6) expression levels decreased, while Bax and cleaved caspase 9 levels increased in LPS-treated H9c2 cells. Inhibition of miR-21 could suppress LPS-induced apoptosis, inflammatory reactions and NF-κB activation to attenuate LPS-induced myocardial injury in H9c2 cells, and effectively improve survival of mice with sepsis. Most importantly, Bcl-2 and CDK6 were found to be the direct target of miR-21 using dual-luciferase reporter and RNA immunoprecipitation assays. Further gain-of-function assay demonstrated that Bcl-2 or CDK6 over-expression promoted the protective effects of miR-21 inhibitor on LPS-mediated myocardial cells.
Conclusion
Our findings revealed that the down-regulation or antagonism of miR-21 protects myocardial cells against LPS-induced apoptosis and inflammation through up-regulating Bcl-2 and CDK6 expression, which provided a new insight for prevention and treatment of myocardial injury.





Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
Please contact the corresponding author.
Abbreviations
- Bcl-2:
-
B-cell lymphoma 2
- CDK6:
-
Cyclin-dependent kinase 6
- ELISA:
-
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
- LPS:
-
Lipopolysaccharide
- miR-21:
-
MiRNA-21
- PBS:
-
Phosphate-buffered saline
- RT-qPCR:
-
Real-time quantitative PCR
- RIP:
-
Immunoprecipitation
References
Fernández-Avilés F, Sanz-Ruiz R, Bogaert J, Casado Plasencia A, Gilaberte I, Belmans A, et al. Safety and efficacy of intracoronary infusion of allogeneic human cardiac stem cells in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction and left ventricular dysfunction. Circ Res. 2018;123:579–89.
Tissier S, Lancel S, Marechal X, Mordon S, Depontieu F, Scherpereel A, et al. Calpain inhibitors improve myocardial dysfunction and inflammation induced by endotoxin in rats. Shock. 2004;21:352–7.
McDiarmid AK, Swoboda PP, Erhayiem B, Bounford KA, Bijsterveld P, Tyndall K, et al. Myocardial effects of aldosterone antagonism in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. J Am Heart Assoc. 2020;9:11521.
Tahir E, Starekova J, Muellerleile K, Freiwald E, von Stritzky A, Münch J, et al. Impact of myocardial fibrosis on left ventricular function evaluated by feature-tracking myocardial strain cardiac magnetic resonance in competitive male triathletes with normal ejection fraction. Circ J. 2019;83:1553–62.
Ye Y, Perez-Polo JR, Qian J, Birnbaum Y. The role of microRNA in modulating myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. Physiol Genomics. 2011;43:534–42.
Wang J, Liu H, Tian L, Wang F, Han L, Zhang W, et al. miR-15b inhibits the progression of glioblastoma cells through targeting insulin-like growth factor receptor 1. Horm Cancer. 2017;8:49–57.
Specjalski K, Jassem E. MicroRNAs: potential biomarkers and targets of therapy in allergic diseases? Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2019;67:213–23.
Zhu S, Song W, Sun Y, Zhou Y, Kong F. MiR-342 attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury via inhibiting MAPK1 expression. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2020;47:1448–54.
Haneklaus M, Gerlic M, O’Neill LA, Masters SL. miR-223: infection, inflammation and cancer. J Intern Med. 2013;274:215–26.
Ma Y, Liu Y, Hou H, Yao Y, Meng H. MiR-150 predicts survival in patients with sepsis and inhibits LPS-induced inflammatory factors and apoptosis by targeting NF-κB1 in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;500:828–37.
Zhao Z, Hao J, Li X, Chen Y, Qi X. MiR-21-5p regulates mycobacterial survival and inflammatory responses by targeting Bcl-2 and TLR4 in Mycobacterium tuberculosis-infected macrophages. FEBS Lett. 2019;593:1326–35.
Li G, Yang Y, Xu S, He M, Zhang Z. mir-21–5p inhibits the progression of human chondrosarcoma by regulating CCR7/STAT3/NF-κB pathway. Connect Tissue Res. 2019;62:1–12.
Hayden MS, Ghosh S. Shared principles in NF-kappaB signaling. Cell. 2008;132:344–62.
Feng J, Li A, Deng J, Yang Y, Dang L, Ye Y, et al. miR-21 attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced lipid accumulation and inflammatory response: potential role in cerebrovascular disease. Lipids Health Dis. 2014;13:27.
Wang H, Bei Y, Shen S, Huang P, Shi J, Zhang J, et al. miR-21-3p controls sepsis-associated cardiac dysfunction via regulating SORBS2. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2016;94:43–53.
Ge J, Yao Y, Jia H, Li P, Sun W. Inhibition of miR-21 ameliorates LPS-induced acute lung injury through increasing B cell lymphoma-2 expression. Innate Immun. 2020;26:693–702.
Zhuang D, Liang L, Zhang H, Feng X. miR-202 suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma progression via downregulating BCL2 expression. Oncol Res. 2020;28:399–408.
Guo Z, Lv X, Jia H. MiR-186 represses progression of renal cell cancer by directly targeting CDK6. Hum Cell. 2020;33:759–67.
Handschick K, Beuerlein K, Jurida L, Bartkuhn M, Müller H, Soelch J, et al. Cyclin-dependent kinase 6 is a chromatin-bound cofactor for NF-κB-dependent gene expression. Mol Cell. 2014;53:193–208.
Schmitz ML, Kracht M. Cyclin-dependent kinases as coregulators of inflammatory gene expression. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2016;37:101–13.
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All experimental animal procedures in this study conformed to the National Institutes of Health Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals, and were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Sunshine Union Hospital.
Consent for publication
Yes from all authors.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: John Di Battista.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Sun, G. & Wang, L. MiR-21 participates in LPS-induced myocardial injury by targeting Bcl-2 and CDK6. Inflamm. Res. 71, 205–214 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-021-01535-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-021-01535-1