Abstract
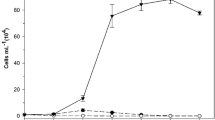
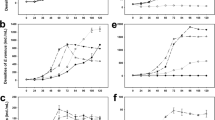
Growth inhibition effect of different concentration of distilled water extract and four polar organic solvent (methanol, acetone, ether and chloroform) extracts ofUlva pertusa on three typical red tide microalgae (Heterosigma akashiwo, Alexandrium tamarense andProrocentrum micans) were investigated. Liquid-liquid fractionation and HPLC analysis for methanol extract ofU. pertusa were carried out. Growth of the three microalgae was significantly inhibited by the distilled water extract ofU. pertusa at relatively higher concentration. However, the cells of the three microalgae did not die completely even at high concentration. Methanol extract ofU. pertusa showed the highest growth inhibition on the three microalgae, and all the cells of the three microalgae were killed at relatively high concentration. The other three organic solvent extracts ofU. pertusa had no apparent effect on the three microalgae. The results of bioassays and HPLC analysis suggested that the inhibitory substances inU. pertusa to the microalgal growth had relatively high polarities.H. akashiwo was the most sensitive one whileA. tamarense was the most tolerant one to the growth inhibitory substances.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Guillard, R. R. L. and J. H. Ryther, 1962. Studies on marine planktonic diatoms. I.Cyclotella nana (Hustedt) andDetonula confervaceae (Cleve).Can. J. Microbiol. 8: 229–239.
Guo, Y., 1994. Studies onHeterosigma akashiwo (Hada) Hada in the Dalian Bight, Liaoning, China.Oceanol. Limnol. Sin. 25 (2): 211–215. (in Chinese)
Horner, R. A., D. L. Garrison and F. G. Plumley, 1997. Harmful algal blooms and red tide problems on the U. S. west coast.Limnol. Oceanogr. 42: 1076–1088.
Imai, I., Y. Ishida and Y. Hata, 1993. Killing of marine phytoplankton by a gliding bacteriumCytophaga sp., isolated from the coastal sea of Japan.Mar. Biol. 116: 527–532.
Jeong, J. H., H. J. Jin, C. H. Sohn, K. H. Suh and Y. K. Hong, 2000. Algicidal activity of the seaweedCorallina pilulifera against red tide microalgae.J. Appl. Phycol. 12: 37–43.
Jin, Q. and S. Dong, 2003. Comparative studies on the allelopathic effects of two different strains ofUlva pertusa onHeterosigma akashiwo andAlexandrium tamarense.J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 293(1): 41–55.
Kakisawa, H., F. Asari, T. Kusumi, T. Toma, T. Sakurai, T. Oohusa, Y. Hara and M. Chihara, 1988. An allelopathic fatty acid from the brown algaCladosiphon okamuranus.Phytochemistry 27: 731–735.
Qi, Y. and F. Qian, 1994. Taxonomic studies on red tide causative dinoflagellates in Dapeng Bay, South China Sea.Oceanol. Limnol. Sin. 25 (2): 206–211. (in Chinese)
Qi, Y., Z. Zhang, Y. Hong, S. Lu, C. Zhu and Y. Li, 1993. Occurrence of red tides on the coasts of China.Toxic Phytoplankton Blooms Sea 3: 43–46.
Steidinger, K. A., 1983. A re-evaluation of toxic dinoflagellate biology and ecology.Prog. Phycol. Res. 2: 147–188.
Sun, X., X. Song, B. Zhang and Z. Yu. 1999. A study on the coagulation of clay-MMH system with red tide organisms.Mar. Sci. 2: 46–49. (in Chinese).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This research supported by the Open Research Fund Program of Key Laboratory of Marine Drugs (Ocean University of China), the Ministry of Education of China: also by NSFC for Talented Youths (No. 397250239) and the Project under Major State Basic Research of China (No. G1999012011).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qiu, J., Shuanglin, D. & Changyun, W. Growth inhibition to three red tide microalgae by extracts ofUlva pertusa . Chin. J. Ocean. Limnol. 24, 147–153 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02842814
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02842814