Summary
Background: Until recently intraductal carcinomas (DCIS) were thought to be a single entity of disease. In order to examine this theory we examined DCIS with respect to several morphological parameters.
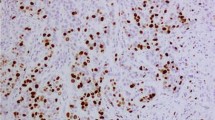
Methods: 88 DCIS were investigated by steroid hormone receptors, p53 and cellular proliferation determined by MIB1. DCIS were classified according to the new suggestion by EORTC. This classification is based mainly on nuclear pleomorphism and architectural pattern.
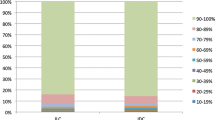
Results: All prognostic factors showed direct or inverse correlation, respectively, with subclassification of DCIS. There existed a significant correlation between steroid hormone receptor positivity and low proliferative activity in low grade DCIS subgroup compared to high grade DCIS. In contrast p53 expression was high in high grade DCIS and showed only little positivity in low grade DCIS.
Conclusions: It is concluded that DCIS classification based on nuclear pleomorphism may become an important prognosticator in the future.
Zusammenfassung
Grundlagen: Bis vor kurzer Zeit wurde das intraduktale Mammakarzinom (DCIS) als eine Krankheitsentität aufgefaßt. Um diese Theorie zu überprüfen, untersuchten wir mehrere morphologische Parameter bei DCIS.
Methodik: 88 DCIS wurden hinsichtlich des Steroidhormonrezeptorstatus, p53 und der zellulären Proliferation mittels MIB1 untersucht. Die DCIS wurden entsprechend dem neuen Klassifikationsvorschlag der EORTC klassifiziert. Diese Klassifikation beruht vor allem auf nukleären Merkmalen und auf architektonischen Faktoren.
Ergebnisse: Alle untersuchten prognostischen Faktoren zeigten eine direkte oder eine inverse Korrelation mit den Subgruppen des DCIS. Es fand sich eine statistisch signifikante Korrelation zwischen positiven Steroidhormonrezeptoren, niedriger proliferativer Aktivität und niedrigem Malignitätsgrad der DCIS im Vergleich zu DCIS hohen Malignitätsgrades. Im Gegensatz dazu war p53 deutlich häufiger bei DCIS hohen Malignitätsgrades exprimiert und zeigte bei DCIS niedriger Malignität nur selten eine Expression.
Schlußfolgerungen: Aus diesen Ergebnissen wird geschlossen, daß in Zukunft Klassifikationen für DCIS prognostische Bedeutung erlangen könnten, die nukleäre Polymorphie als wesentliches Merkmal berücksichtigen.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Patchefsky AS, Schwartz GF, Finkelstein SD: Heterogeneity of intraductal carcinoma of the breast. Cancer 1989;63:731–741.
Posner MC, Wolmark N: Non-invasive breast carcinoma. Breast Cancer Res Treat 1992;21:155–164.
Lagios MD: Heterogeneity of ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast. J Cell Biochem Suppl 1993;17G:49–52.
Recht A, van Dongen JA, Fentiman IS: Third meeting of the DCIS working party of the EORTC (Fondazione Cini, Isola S. Giorgio, Venezia, 28 February 1994) — Conference report. Eur J Cancer 1994;30A:1895–1901.
Holland R, Peterse JL, Millis RR: Ductal carcinoma in situ: a proposal for a new classification. Semin Diagnostic Pathol 1994;11:167–180.
Tavassoli FA: Pathology of the breast. Norwalk/Connecticut, Appleton & Lange, 1992, pp 298–300.
Key G, Becker MHG, Baron B: New Ki-67 equivalent murine monoclonal antibodies (MIB 1–3) generated against bacterially expressed parts of the Ki-67 cDNA containing three 62 base pair repetitive elements encoding for the Ki-67 epitope. Lab Invest 1993;68:629–636.
Banks L, Matlashewski G, Crawford L: Isolation of human p53 specific antibodies and their use in the study of human p53 expression. Eur J Biochem 1986;159:529–534.
Davidoff AM, Kerns B-JM, Iglehart JD: Maintenance of p53 alterations throughout breast cancer progression. Cancer Res 1991;51:2605–2610.
Thor AD, Moore DH, Edgerton SM: Accumulation of p53 tumor suppressor gene protein: an independent marker of prognosis in breast cancers. J Natl Cancer Inst 1992;84:845–855.
Poller DN, Roberts EC, Bell JA: p53 expression in mammary ductal carcinoma in situ: relationship to immunohistochemical expression of estrogen receptor and c-erbB-2 protein. Hum Pathol 1993;24:463–468.
Barbareschi M, Leonardi E, Mauri FA: p53 and c-erbB2-expression in breast carcinomas: an immunohistochemical study including correlations with receptor status, proliferation markers, and clinical stage in human breast cancer. Am J Clin Pathol 1992;98:408–418.
Davidoff AM, Herndon JE, Glover NS: Relation between p53 overexpression and established prognostic factors in breast cancer. Surgery 1991;110:259–264.
Cattoretti G, Rilke F, Andreola S: p53 expression in breast cancer. Int J Cancer 1988;41:178–183.
Martinazzi M, Crivelli F, Zampatti C: Relationship between p53 expression and other prognostic factors in human breast carcinoma: an immunohistochemical study. Am J Clin Pathol 1993;100:213–217.
Meyer JS: Cell kinetics of histologic variants of in situ breast carcinoma. Breast Cancer Res Treat 1986;7:171–180.
Rudas M, Gnant MFX, Mittlböck M: Thymidine labeling index and Ki-67 growth fraction in breast cancer: comparison and correlation with prognosis. Breast Cancer Res Treat 1994;32:165–175.
Pallis L, Wilking N, Cedermark B: Receptors for estrogen and progesterone in breast carcinoma in situ. Anticancer Res 1992;12:2113–2116.
Bur ME, Zimarovsy MJ, Schnitt SJ: Estrogen receptor immunohistochemistry in carcinoma in situ of the breast. Cancer 1992;69:1174–1181.
Giri DD, Dundas SAC, Nottingham JF: Oestrogen receptors in benign epithelial lesions and intraduct carcinomas of the breast: an immunohistochemical study. Histopathology 1989;15:575–584.
Poller DN, Snead DRJ, Roberts EC: Oestrogen receptor expression in ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast: relationship to flow cytometric analysis of DNA and expression of the c-erbB-2 oncoprotein. Br J Cancer 1993;68:156–161.
Reiner A, Reiner G, Spona J: Histopathologic characterization of human breast cancer in correlation with estrogen receptor status: a comparison of immunocytochemical and biochemical analysis. Cancer 1988;61:1149–1154.
Bloom HJ, Richardson WW: Histological grading and prognosis in breast cancer. Br J Cancer 1957;11:359–377.
le Doussal V, Tubiana-Hulin M, Friedman S: Prognostic value of histologic grade nuclear components of Scarff-Bloom-Richardson (SBR): an improved score modification based on a multivariate analysis of 1262 invasive ductal breast cancers. Cancer 1989;64:1914–1921.
Schumacher M, Schmoor C, Sauerbrei W: The prognostic effect of histologic tumor grade in node-negative breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res Treat 1993;25:235–245.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reiner, A., Rudas, M., Neumayer, R. et al. Protein p53 expression, cell proliferation and steroid hormone receptors in ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast. Acta Chir Austriaca 29, 123–125 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02619764
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02619764