Summary
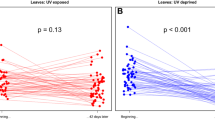
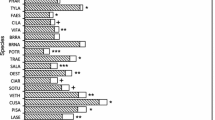
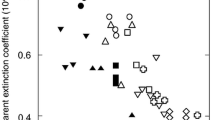
Leaf epidermal transmittance of ultraviolet radiation (280–400 nm) was examined in several plant species to determine the capability of the epidermis to attenuate solar ultraviolet radiation. Epidermal samples were mechanically isolated and examined with a spectroradiometer/integrating sphere for transmittance. A survey of 25 species exposed to natural insolation was conducted. Although the species differed in life form, habitat type, and epidermal characteristics, epidermal transmittance was generally less than 10%. Ultraviolet radiation was attenuated 95 to 99% in more than half of the species. In 16 species, flavonoid and related pigments in the epidermis accounted for 20 to 57% of the attenuation. Several species exposed to supplemental ultraviolet irradiation (288–315 nm) in a greenhouse exhibited significant (P≦0.05) depressions in epidermal transmittance of 31 to 47%, apparently resulting from an increase in ultraviolet-absorbing pigments.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Biggs, R.H., Sisson, W.B., Caldwell, M.M.: Response of higher terrestrial plants to elevated UV-B irradiance. In. Impacts of climatic change on the biosphere, CIAP Monog. 5, Part 1: Ultraviolet radiation effects (D.S. Nachtwey, M.M. Caldwell, R.H. Biggs, eds.), pp. 4-34–4-50. Springfield, Va, U.S. Dept. Transportation, Report No. DOT-TST-75-55 (1975)
Brabham, D.E., Biggs, R.H.: Opical properties: penetration of UV-B radiation into higher plant tissues. In: Impacts of climatic change on the biosphere, CIAP Monog. 5, Part 1: Ultraviolet radiation effects (D.S. Nachtwey, M.M. Caldwell, R.H. Biggs, eds.), pp. 4–3 to 4–14. Springfield, Va., U.S. Dept. Transportation, Report No. DOT-TST-75-55 (1975)
Brandle, J.R., Campbell, W.F., Sisson, W.B., Caldwell, M.M.: Net photosynthesis, electron transport capacity, and ultrastructure of Pisum sativum L. exposed to ultraviolet-B radiation. Plant Physiol. 60, 165–169 (1977)
Caldwell, M.M.: Solar ultraviolet radiation as an ecological factor for alpine plants. Ecol. Monog. 38, 243–268 (1968)
Caldwell, M.M.: Solar UV irradiance and the growth and development of higher plants. In: Photophysiology, Vol. VI (A.C. Giese, ed.), pp. 137–177. New York-London: Academic Press 1971
Cicerone, R.J., Stolarski, R.S., Walters, S.: Stratospheric ozone destruction by man-made chlorofluoromethanes. Science 185, 1165–1167 (1974)
Cine, M.G., Salisbury, F.B.: Effects of ultraviolet radiation on the leaves of higher plants. Radiat. Bot. 6, 151–163 (1966)
Cronquist, A., Holmgren, A.H., Holmgren, N.H., Reveal, J.L.: Intermoutain flora, Vol. I, 270 pp. New York-London: Hafner 1972
Gausman, H.W., Rodriguez, R.R., Escobar, D.E.: Ultraviolet radiation reflectance, transmittance, and absorptance by plant leaf epidermises. Agron. J. 67, 719–724 (1975)
Giese, A.C.: Studies on ultraviolet radiation action upon animal cells. In: Photophysiology, vol. II (A.C. Giese, ed.), pp. 203–245. New York-London: Academic Press 1964
Green, A.E.S., Sawada, T., Shettle, E.P.: The middle ultraviolet reaching the ground. Photochem. Photobiol. 19, 251–259 (1974)
Grobecker, A.J., Coroniti, S.C., Cannon, R.H., Jr.: The effects of stratospheric pollution by aircraft. Climatic Impact Assessment Program, Springfield, Va., U.S. Dept. Transportation, Report No. DOT-TST-75-50 (1974)
Holmgren, A.H., Reveal, J.L.: Checklist of the vascular plants of the intermoutain region. U.S. Forest Service Research Paper INT-32 (1966)
Hultén, E.: Flora of Alaska and neighboring territories, 1008 pp. Stanford: Stanford Univ. Press 1968
Johnston, H.: Reduction of stratospheric ozone by nitrogen oxide catalysts from supersonic transport exhaust. Science 173, 517–522 (1971)
Koller, L.R.: Ultraviolet radiation, 2nd ed., 311 pp. New York-London-Sydney: Wiley 1965
Lautenschlager-Fleury, D.: Über die Ultraviolettdurchlässigkeit von Blattepidermen. Ber. Schweiz. Bot. Ges. 65, 343–386 (1955)
Murphy, T.M.: Effects of UV radiation on nucleic acids. In: Impacts of climatic change on the biosphere, CIAP Monog. 5, Part 1: Ultraviolet radiation effects (D.S. Nachtwey, M.M. Caldwell, R.H. Biggs, eds.), pp. 3-21–3-44. Springfield, Va., U.S. Dept. Transportation, Report No. DOT-TST-75-55 (1975)
Ram, H.Y.M., Nayyar, V.L.: A rapid method obtaining epidermal peels in plants by treatment with cupric sulphate and hydrochloric acid. Stain Tech. 49, 114–116 (1974)
Sisson, W.B., Caldwell, M.M.: Lamp/filter systems for simulation of solar UV irradiance under reduced atmospheric ozone. Photochem. Photobiol. 21, 453–456 (1975)
Sisson, W.B., Caldwell, M.M.: Photosynthesis, dark respiration, and growth of Rumex patientia L., exposed to ultraviolet irradiance (288 to 315 nanometers) simulating a reduced atmospheric ozone column. Plant Physiol. 58, 563–568 (1976)
Sisson, W.B., Caldwell, M.M.: Atmospheric ozone depletion: reduction of photosynthesis and growth of a sensitive higher plant exposed to enhanced UV-B radiation. J. Exptl. Bot. 28, 691–705 (1977)
Venable, W.H., Jr., Koskowski, H.J.: Reflectance of coatings made from Halon powder. Report, National Bureau of Standards (1975)
Wellmann, E.: UV dose-dependent induction of enzymes related to flavonoid biosynthesis in cell suspension cultures of parsley. FEBS Letters 51, 105–107 (1975)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Robberecht, R., Caldwell, M.M. Leaf epidermal transmittance of ultraviolet radiation and its implications for plant sensitivity to ulraviolet-radiation induced injury. Oecologia 32, 277–287 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00345107
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00345107