Abstract
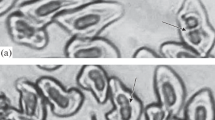
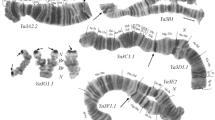
From electrophoretic ovidence of sex-linked inheritance of catalase in Plodia interpunctella it is suggested that the observed exceptional offspring are the result of an X-Y translocation which is proved to occur with a non negligible frequency. The rate of electrophoretically observed translocation was 1.8%. The existence of a Y chromosome in heterogametic females was proved by the finding of positive sex chromatin. The population sample examined was panmictic. The results favour the possibility that the translocation takes place randomly.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barry, E.G. (1960). Genetic analysis of an insertional translocation in Neurospora crassa (Abstr.) Genetica 45: 974.
Eicher, E.M. (1967). The genetic extent of the insertion involved in the flecked translocation in the mouse. Genetics 55: 203–212.
Frizzi, G. (1948). L'eteropicnosi come indice di riconoscimento dei sessi in Bombyx mori L. Ricerca scient. 18: 1–7.
Goldschmidt, R. (1955). Theoretical Genetics, Berkeley and Los Angeles. Univ. of California Press X: 563.
Lampropoulou, M.S. & H. Gelti-Douka (1975). Catalase in Plodia interpunctella. I. Genetic control and enzymatic patterns during development. Genetica 47: 49–52.
Perkins, D.D. (1972). An insertional translocation in Neurospora that generates duplications heterozygous for mating type. Genetics 71: 25–51.
Roberts, P.A. (1970). Screening for X-ray—induced crossover suppressors in D. melanogaster: prevalence and effectiveness of translocations. Genetics 65: 429–448.
Seiler, J. (1921). Geschlechtschromosomen. Untersuchungen an Psychiden. II. Die Chromosomenzyklen von Fumea castanea and Talaeporia tubulosa. Arch. Zellforsch. 16: 19–46.
Stewart, B.R. & J.R. Merrian (1974). Segmental aneuplody and enzyme activity as a method for cytogenetic localization in D. melanogaster. Genetics 76: 301–309.
Tazima, Y. (1964). The genetics of the silkworm. Logos Press, Acad. Press, London, p. 253.
Tobler, J., J.T. Bowman & J.R. Simmons (1971). Gene modulation in Drosophila: dosage compensation and relocated v* gene. Biochem. Genet. 5: 111–117.
Traut, W. & G.C. Mosbacher (1968). Geschlechtschromatin bei Lepidopteren. Chromosoma 25: 343–356.
Upadya, M.D. (1968). Peroxydase isoenzymes associated with the Aegilops um bellulata chromosome segment transferred to Chinese Spring (Triticum aestivum). Experientia 24: 613–614.
Van Breugel, F.M.A. (1971). X-Y exchanges in males of D. hydei carrying the Wm Go duplication. Genetica 42: 1–12.
Zouros, E. & C.B. Krimbas (1970). A case of duplication of an Esterase locus in the olive fruit fly Dacus oleae. Isozyme Bull. 3: 44.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lampropoulou, M.S., Gelti-Douka, H. Catalase in Plodia interpunctella II. Biochemical variation associated with an X-Y translocation. Genetica 47, 53–58 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00122439
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00122439