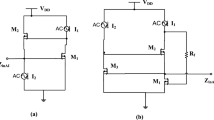
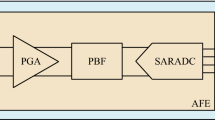
Abstract
Biomedical devices have enormous possibilities in health applications. A low-noise amplifier (LNA) is a crucial circuit in neural recording, ECG, and EEG systems. The performance of LNAs has to vary with the characteristics of their different components. This contribution presents an empirical comparison between the latest state-of-the-art LNAs in health applications. Using the specter tool of MOS technology, LNAs have implemented at 180, 90, and 65 nm and simulated at a wide supply voltage (1–1.8 V) range. There are 99.9% power variation, 103.7% bandwidth range, 93.18% gain range, 91.17% noise figure vary, and IIP3 97.5% area variation for different LNA designs. Different LNAs have used in analog front end (AFE) design/circuits. A comparison of AFE designs has shown that there are 85.07% power saving, 79.78% maximal bandwidth, and 93.54% best performance.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. Yang, J. Holleman, An ultralow-power low-noise CMOS biopotential amplifier for neural recording. IEEE Trans. Circ. Syst. II Express Briefs 62(10), 927–931 (2015)
T.Y. Wang, L.H. Liu, S.Y. Peng, A power-efficient highly linear reconfigurable biopotential sensing amplifier using gate-balanced pseudoresistors. IEEE Trans. Circ. Syst. II Express Briefs 62(2), 199–203 (2015)
R. Nagulapalli, K. Hayatleh, S. Barker, A.A. Tammam, N. Yassine, B. Yassine, M. Ben-Esmael, A Low noise amplifier suitable for biomedical recording analog front-end in 65 nm CMOS technology. J. Circ. Syst. Comput. 28(08), 1950137 (2019)
M. Meghdadi, M. Piri, A. Medi, A highly linear dual-gain CMOS low-noise amplifier for X-band. IEEE Trans. Circ. Syst. II Express Briefs 65(11), 1604–1608 (2017)
Y. Liu, T. Ma, P. Guan, L. Mao, B. Chi, A G-band wideband bidirectional transceiver front-end in 40-nm CMOS. IEEE Trans. Circ. Syst. II Express Briefs 66(5), 798–802 (2019)
L. Belostotski, E.A. Klumperink, Figures of merit for CMOS low-noise amplifiers and estimates for their theoretical limits (Express Briefs, IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II, 2021)
S. Dey, M. Pattanaik, G. Kaushal, A low power low noise analog front-end for ECG recording. Analog Integr. Circ. Sig. Proc. 109(2), 449–458 (2021)
T.Y. Wang, M.R. Lai, C.M. Twigg, S.Y. Peng. A fully reconfigurable low-noise biopotential sensing amplifier with 1.96 noise efficiency factor. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circ. Syst. 8(3), 411–422 (2013)
H.C. Hsieh, A.D. Nguyen, J.S. Lai, Low noise ZVS switch sharing multichannel switching amplifier for magnetic bearing applications. IEEE Trans. Circ. Syst. II Express Briefs 67(10), 1999–2003 (2019)
J. Elkind, E. Socher, Noise figure optimization tool for millimeter-wave receivers at Near- fmax frequencies. IEEE Trans. Circ. Syst. II Express Briefs 63(10), 914–918 (2016)
J.Y. Hsieh, K.Y. Lin. A 0.6-V low-power variable-gain LNA in 0.18-µm CMOS Technology. IEEE Trans. Circ. Syst. II: Express Briefs, 67(1), 23–26 (2019)
H. Yu, Y. Chen, C.C. Boon, C. Li, P.I. Mak, R.P. Martins. A 0.044-mm 2 0.5-to-7-GHz resistor-plus-source-follower-feedback noise-cancelling LNA achieving a flat NF of 3.3±0.45 dB. IEEE Trans. Circ. Syst. II: Express Briefs 66(1), 71–75 (2018)
Y. Yu, J. Zhu, Z. Zong, P. Tang, H. Liu, C. Zhao, Y. Wu, K. Kang, A 21-to-41-GHz high-gain low noise amplifier with triple-coupled technique for multiband wireless applications. IEEE Trans. Circ. Syst. II Express Briefs 68(6), 1857–1861 (2020)
S.S. Regulagadda, B.D. Sahoo, A. Dutta, K.Y. Varma, V.S. Rao, A packaged noise-canceling high-gain wideband low noise amplifier. IEEE Trans. Circ. Syst. II Express Briefs 66(1), 11–15 (2018)
T. Ma, F. Hu, A wideband flat gain low noise amplifier using active inductor for input matching. IEEE Trans. Circ. Syst. II Express Briefs 66(6), 904–908 (2018)
L. Ma, Z.G. Wang, J. Xu, N.M. Amin, A high-linearity wideband common-gate LNA with a differential active inductor. IEEE Trans. Circ. Syst. II Express Briefs 64(4), 402–406 (2016)
F.D. Baumgratz, C. Saavedra, M. Steyaert, F. Tavernier, S. Bampi. A wideband low-noise variable-gain amplifier with a 3.4 dB NF and up to 45 dB gain tuning range in 130-nm CMOS. IEEE Trans. Circ. Syst. II: Express Briefs, 66(7), 1104–1108 (2018)
M. Davulcu, C. Çalışkan, İ Kalyoncu, Y. Gurbuz, An X-Band SiGe BiCMOS Triple-Cascode LNA with boosted gain and P 1dB. IEEE Trans. Circ. Syst. II Express Briefs 65(8), 994–998 (2018)
J. Hu, K. Ma, S. Mou, F. Meng. Analysis and design of a 0.1–23 GHz LNA MMIC using frequency-dependent feedback. IEEE Trans. Circ. Syst. II: Express Briefs 66(9), 1517–1521 (2019)
M.K. Hedayati, A. Abdipour, R.S. Shirazi, C. Cetintepe, R.B. Staszewski, A 33-GHz LNA for 5G wireless systems in 28-nm bulk CMOS. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 65(10), 1460–1464 (2018)
S.J. Jung, S.K. Hong, O.K. Kwon, Low-power low-noise amplifier using attenuation-adaptive noise control for ultrasound imaging systems. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 11(1), 108–116 (2016)
A.A. Kumar, B.D. Sahoo, A. Dutta, A wideband 2–5 GHz noise canceling subthreshold low noise amplifier. IEEE Trans. Circ. Syst. II Express Briefs 65(7), 834–838 (2017)
C.H. Chang, A forward-body-bias CMOS LNA with ultra-low device junction leakage using intrinsic self-balanced pseudo resistor. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 66(4), 697–701 (2018)
D. Lee, C. Nguyen, Dual Q/V-band SiGe BiCMOS low noise amplifiers using Q-enhanced metamaterial transmission lines. IEEE Trans. Circ. Syst. II Express Briefs 68(3), 898–902 (2020)
G. Nikandish, A. Medi, A 40-GHz bandwidth tapered distributed LNA. IEEE Trans. Circ. Syst. II Express Briefs 65(11), 1614–1618 (2017)
R.A. Shaheen, T. Rahkonen, A. Pärssinen, Millimeter-wave frequency reconfigurable low noise amplifiers for 5G. IEEE Trans. Circ. Syst. II Express Briefs 68(2), 642–646 (2020)
C. Zhao, Y. Yu. A K-/Ka-band broadband low-noise amplifier based on the multiple resonant frequency technique. IEEE CAS-I: Regular Papers 69(8) (2022)
L. Lyu, D. Ye, C.J.R. Shi, A 340 nW/Channel 110 dB PSRR neural recording analog front-end using replica-biasing LNA, level-shifter assisted PGA, and averaged LFP servo loop in 65 nm CMOS. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 14(4), 811–824 (2020)
S.-Y. Lee , P.-H. Cheng, C.-F. Tsou, C.-C. Lin, G.-S. Shieh. A 2.4 GHz ISM band OOK transceiver with high energy efficiency for biomedical implantable applications. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circ. Syst. 14(1) (2020)
B. Liu, Y. Zhang, J. Qiu, W. Deng, Z. Xu, H. Zhang, J. Pang, Y. Wang , R. Wu, T. Someya, A. Shirane, K. Okada, An HDL-described Fully-synthesizable Sub-GHz IoT transceiver with ring oscillator based frequency synthesizer and digital background EVM calibration, in IEEE Custom Integrated Circuits Conference, pp. 2152–3630 (2019)
D. Martinez-Perez, F. Aznar et al. Design-Window Methodology for Inductorless Noise-Cncelling CMOS LNAs. IEEE Access 10 (2022)
R. Wang, C. Li, et al. A 18–44 GHz low noise amplifier with input matching and bandwidth extension techniques. IEEE Microwave Wireless Components Lett. (2022)
H.-H. Chen, W.-C. Cheng, C.-H. Hsieh, Design and analysis of high-gain and compact single-input differential-output low noise amplifier for 5G applications. IEEE Microw. Wireless Comp. Lett. 32(6) (2022)
Pritty, M. Jhamb. High-performance current mirror-based voltage-controlled oscillator for implantable devices, in Micro and Nanoelectronics Devices, Circuits and Systems Select Proceedings of MNDCS 2021, vol. 32 (Springer, 2021).
Z. Liu, C.C. Boon, A 0.092-mm2 2–12-GHz Noise-cancelling low-noise amplifier with gain improvement and noise reduction. IEEE TCAS-II: Express Briefs 69, 4013–4017 (2022)
M. Tarkhan, M. Sawan, A novel current density based design approach of low noise amplifiers. IEEE Access 10 (2022)
L. Qiu, J. Liu et al., Ultra low power E-band Low noise amplifier with three stacked current-sharing amplification stages in 28-nm CMOS. IEEE Microwave Wirel. Compon. Lett. 32(6), 732–735 (2022)
G. Atzeni, et. al. An impedance-boosted switched-capacitor low-noise amplifier achieving 0.4 NEF, in 2022 IEEE Symposium on VLSI Technology and Circuits (2022), pp. 116–117
J. Zhang, H. Zhang, Q. Sun, R. Zhang, A low-noise, low-power amplifier with current-reused OTA for ECG recordings. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 12(3), 700–708 (2018)
L. Liu, D. Gao, Y. Tain, Y. Yu, Z. Qin, A low mismatch and high input impedance multi-channel Tine-division multiplexing analog front end for bio-sensors. IEEE Sens. J. 22(7), 6755–6763 (2022)
Y. Wang, F. Miao, Qi An, Z. Liu, C. Chen, Y. Li. Wearable multimodal vital sign monitoring sensor with fully integrated analog front end. IEEE Sens. J. 22(3) 13462–13471 (2022)
Y. Chen, H. Tang, Z. Wang, P. Xu Y. Zhuang. A programmable analog front-end IC applied for Biomedical signal monitoring systems. Circ. Syst. Sig. Proc. 1–25 (2022)
B.G. Perumana, J.H.C. Zhan, S.S. Taylor, B.R. Carlton, J. Laskar, Resistive-feedback CMOS low-noise amplifiers for multiband applications. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Techn. 56(5), 1218–1225 (2008)
T. Chang, J. Chen, L.A. Rigge, J. Lin, ESD-protected wideband CMOS LNAs using modified resistive feedback techniques with chipon- board packaging. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Techn. 56(8), 1817–1826 (2008)
Y. Wang, B. Afshar, T.-Y. Cheng, V. Gaudet, and A. M. Niknejad. A 2.5mW inductor less wideband VGA with dual feedback DC-offset correction in 90 nm CMOS technology in Proceeding IEEE Radio Frequency Integrated Circuits Symposium (RFIC), pp 91–94 (2008)
T. Chang, J. Chen, L. Rigge, J. Lin, A packaged and ESD protected inductorless 0.1–8 GHz wideband CMOS LNA. IEEE Microw. Compon. Lett. 18(6), 416–418 (2008)
Pritty, M. Jhamb, Low power and highly reliable 8-Bit carry select adder, in Innovations in Elect and Electronic Engineering (Springer, Singapore, 2021), pp. 537–549
Pritty, M. Jhamb. Ultra low power current mirror design with enhanced bandwidth. Microelectronics J. 113, 105063 (2021)
M. El-Nozahi, A.A. Helmy, E. Sanchez-Sinencio, K. Entesari, An inductor-less noise-canceling broadband low noise amplifier with composite transistor pair in 90 nm CMOS technology. IEEE J. Solid-State Circ. 46(5), 1111–1122 (2011)
K.-W. Cheng, W.-W. Chen, S.-D. Yang, A low power sub-GHz wideband LNA employing current-reuse and device-reuse positive shunt-feedback technique. IEEE Microw. Wireless Components Lett. (2022)
Acknowledgements
Authors are grateful for IP research fellowship from USIC&T, Guru Gobind Singh Indraprastha University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Pritty, Jhamb, M. (2024). Low-Power LNA in Analog Front End for Biomedical Applications. In: Lenka, T.R., Saha, S.K., Fu, L. (eds) Micro and Nanoelectronics Devices, Circuits and Systems. MNDCS 2023. Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering, vol 1067. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-4495-8_25
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-4495-8_25
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-99-4494-1
Online ISBN: 978-981-99-4495-8
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)