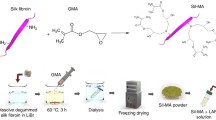
Abstract
Three-dimensional (3D) bioprinting has been a highly influential technology in the field of tissue engineering to enable speedy and precise spatial patterning of cells, growth factors, and biomaterials. Bioink is one of the main factors in 3D bioprinting, and hydrogels are excellent matrix type by means of bioinks for 3D bioprinting. Recently, stereolithographic bioprinting via digital light processing (DLP) that allows high spatial resolution and rapid printing time of complex structures has attracted many studies. However, a small number of bioinks have been applied to DLP bioprinting in comparison with bioinks for other bioprinters. We developed a novel bioink based on silk fibroin that has been extensively used in biomedical fields due to its positive biological and biochemical properties as biomaterials. In this chapter, we summarized the silk fibroin basics and various applications of silk fibroin as printing material. Also, fabrication and performance of silk-based bioink for DLP bioprinter were discussed.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
21 October 2020
Correction to: Chapter 4 in: H. J. Chun et al. (eds.), Bioinspired Biomaterials, Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology 1249, https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-3258-0_4
References
Derakhshanfar S, Mbeleck R, Xu K, Zhang X, Zhong W, Xing M (2018) 3D bioprinting for biomedical devices and tissue engineering: a review of recent trends and advances. Bioactive Mater 3(2):144–156
Liu F, Liu C, Chen Q, Ao Q, Tian X, Fan J, Tong H, Wang X (2018) Progress in organ 3D bioprinting. Int J Bioprint 4:1–15
Kačarević ŽP, Rider PM, Alkildani S, Retnasingh S, Smeets R, Jung O, Barbeck M (2018) An introduction to 3D bioprinting: possibilities, challenges and future aspects. Materials 11(11):2199
Lu Y, Mapili G, Suhali G, Chen S, Roy K (2006) A digital micro-mirror device-based system for the microfabrication of complex, spatially patterned tissue engineering scaffolds. J Biomed Mater Res Part A 77(2):396–405
Ju HW, Lee OJ, Moon BM, Sheikh FA, Lee JM, Kim JH, Park CH (2014) Silk fibroin based hydrogel for regeneration of burn induced wounds. Tissue Eng Regen Med 11(3):203–210
Melke J, Midha S, Ghosh S, Ito K, Hofmann S (2016) Silk fibroin as biomaterial for bone tissue engineering. Acta Biomater 31:1–16
Qi Y, Wang H, Wei K, Yang Y, Zheng RY, Kim IS, Zhang KQ (2017) A review of structure construction of silk fibroin biomaterials from single structures to multi-level structures. Int J Mol Sci 18(3):237
Das S, Pati F, Choi YJ, Rijal G, Shim JH, Kim SW, Ghosh S (2015) Bioprintable, cell-laden silk fibroin–gelatin hydrogel supporting multilineage differentiation of stem cells for fabrication of three-dimensional tissue constructs. Acta Biomater 11:233–246
Lee H, Yang GH, Kim M, Lee J, Huh J, Kim G (2018) Fabrication of micro/nanoporous collagen/dECM/silk-fibroin biocomposite scaffolds using a low temperature 3D printing process for bone tissue regeneration. Mater Sci Eng C 84:140–147
Shi W, Sun M, Hu X, Ren B, Cheng J, Li C, Ao Y (2017) Structurally and functionally optimized silk-fibroin–gelatin scaffold using 3D printing to repair cartilage injury in vitro and in vivo. Adv Mater 29(29):1701089
Miyaguchi Y, Hu J (2005) Physicochemical properties of silk fibroin after solubilization using calcium chloride with or without ethanol. Food Sci Technol Res 11(1):37–42
Zhang X, Reagan MR, Kaplan DL (2009) Electrospun silk biomaterial scaffolds for regenerative medicine. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 61(12):988–1006
Cao Z, Chen X, Yao J, Huang L, Shao Z (2007) The preparation of regenerated silk fibroin microspheres. Soft Matter 3(7):910–915
Lee J, Sultan M, Kim S, Kumar V, Yeon Y, Lee O, Park C (2017) Artificial auricular cartilage using silk fibroin and polyvinyl alcohol hydrogel. Int J Mol Sci 18(8):1707
Lee OJ, Lee JM, Kim JH, Kim J, Kweon H, Jo YY, Park CH (2012) Biodegradation behavior of silk fibroin membranes in repairing tympanic membrane perforations. J Biomed Mater Res A 100(8):2018–2026
Yoshimizu H, Asakura T (1990) Preparation and characterization of silk fibroin powder and its application to enzyme immobilization. J Appl Polym Sci 40(1–2):127–134
Park YR, Ju HW, Lee JM, Kim DK, Lee OJ, Moon BM, Park CH (2016) Three-dimensional electrospun silk-fibroin nanofiber for skin tissue engineering. Int J Biol Macromol 93:1567–1574
Sheikh FA, Ju HW, Lee JM, Moon BM, Park HJ, Lee OJ, Park CH (2015) 3D electrospun silk fibroin nanofibers for fabrication of artificial skin. Nanomedicine 11(3):681–691
Park HJ, Lee OJ, Lee MC, Moon BM, Ju HW, min Lee J, Park CH (2015) Fabrication of 3D porous silk scaffolds by particulate (salt/sucrose) leaching for bone tissue reconstruction. Int J Biol Macromol 78:215–223
Irawan V, Sung TC, Higuchi A, Ikoma T (2018) Collagen scaffolds in cartilage tissue engineering and relevant approaches for future development. Tissue Eng Regen Med 15(6):673–697
Dickerson MB, Dennis PB, Tondiglia VP, Nadeau LJ, Singh KM, Drummy LF, Naik RR (2017) 3D printing of regenerated silk fibroin and antibody-containing microstructures via multiphoton lithography. ACS Biomater Sci Eng 3(9):2064–2075
Tao H, Kaplan DL, Omenetto FG (2012) Silk materials–a road to sustainable high technology. Adv Mater 24(21):2824–2837
Pereira RF, Silva MM, de Zea Bermudez V (2015) Bombyx mori silk fibers: an outstanding family of materials. Macromol Mater Eng 300(12):1171–1198
Rockwood DN, Preda RC, Yücel T, Wang X, Lovett ML, Kaplan DL (2011) Materials fabrication from Bombyx mori silk fibroin. Nat Protoc 6(10):1612
Wray LS, Hu X, Gallego J, Georgakoudi I, Omenetto FG, Schmidt D, Kaplan DL (2011) Effect of processing on silk-based biomaterials: reproducibility and biocompatibility. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater 99(1):89–101
Jung CS, Kim BK, Lee J, Min BH, Park SH (2018) Development of printable natural cartilage matrix bioink for 3D printing of irregular tissue shape. Tissue Eng Regen Med 15(2):155–162
Shera SS, Sahu S, Banik RM (2018) Preparation of drug eluting natural composite scaffold using response surface methodology and artificial neural network approach. Tissue Eng Regen Med 15(2):131–143
Seok H, Jo YY, Kweon H, Kim SG, Kim MK, Chae WS (2017) Comparison of bio-degradation for ridge preservation using silk fibroin-based grafts and a collagen plug. Tissue Eng Regen Med 14(3):221–231
Kashte S, Jaiswal AK, Kadam S (2017) Artificial bone via bone tissue engineering: current scenario and challenges. Tissue Eng Regen Med 14(1):1–14
Chen L, Hu J, Ran J, Shen X, Tong H (2014) Preparation and evaluation of collagen-silk fibroin/hydroxyapatite nanocomposites for bone tissue engineering. Int J Biol Macromol 65:1–7
Sanosh KP, Gervaso F, Sannino A, Licciulli A (2014) Preparation and characterization of collagen/hydroxyapatite microsphere composite scaffold for bone regeneration. Key Eng Mater 587:239–244. Trans Tech Publications
Paşcu EI, Stokes J, McGuinness GB (2013) Electrospun composites of PHBV, silk fibroin and nano-hydroxyapatite for bone tissue engineering. Mater Sci Eng C 33(8):4905–4916
Kim SH, Jeong JY, Park HJ, Moon BM, Park YR, Lee OJ, Park CH (2017) Application of a collagen patch derived from duck feet in acute tympanic membrane perforation. Tissue Eng Regen Med 14(3):233–241
Tavakoli J (2017) Tissue engineering of the intervertebral disc’s annulus fibrosus: a scaffold-based review study. Tissue Eng Regen Med 14(2):81–91
Lee JM, Chae T, Sheikh FA, Ju HW, Moon BM, Park HJ, Park CH (2016) Three dimensional poly (ε-caprolactone) and silk fibroin nanocomposite fibrous matrix for artificial dermis. Mater Sci Eng C 68:758–767
Lee OJ, Kim JH, Moon BM, Chao JR, Yoon J, Ju HW, Park HS (2016) Fabrication and characterization of hydrocolloid dressing with silk fibroin nanoparticles for wound healing. Tissue Eng Regen Med 13(3):218–226
Moon BM, Choi MJ, Sultan MT, Yang JW, Ju HW, Lee JM, Lee MC (2017) Novel fabrication method of the peritoneal dialysis filter using silk fibroin with urease fixation system. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater 105(7):2136–2144
Dal Pra I, Freddi G, Minic J, Chiarini A, Armato U (2005) De novo engineering of reticular connective tissue in vivo by silk fibroin nonwoven materials. Biomaterials 26(14):1987–1999
Gopinathan J, Noh I (2018) Recent trends in bioinks for 3D printing. Biomater Res 22(1):11
Tao H, Marelli B, Yang M, An B, Onses MS, Rogers JA, Omenetto FG (2015) Inkjet printing of regenerated silk fibroin: from printable forms to printable functions. Adv Mater 27(29):4273–4279
Li X, Zhang Q, Feng Y, Yan S, Qu J, You R (2016) Preparation of Antheraea pernyi silk fibroin microparticles through a facile electrospinning method. Adv Mater Sci Eng 2016:1–7
Kim HH, Kim MK, Lee KH, Park YH, Um IC (2015) Effects of different Bombyx mori silkworm varieties on the structural characteristics and properties of silk. Int J Biol Macromol 79:943–951
Ghosh S, Parker ST, Wang X, Kaplan DL, Lewis JA (2008) Direct-write assembly of microperiodic silk fibroin scaffolds for tissue engineering applications. Adv Funct Mater 18(13):1883–1889
Wang X, Kluge JA, Leisk GG, Kaplan DL (2008) Sonication-induced gelation of silk fibroin for cell encapsulation. Biomaterials 29(8):1054–1064
Kim SH, Yeon YK, Lee JM, Chao JR, Lee YJ, Seo YB, Hong IS (2018) Precisely printable and biocompatible silk fibroin bioink for digital light processing 3D printing. Nat Commun 9(1):1620
Compaan AM, Christensen K, Huang Y (2016) Inkjet bioprinting of 3D silk fibroin cellular constructs using sacrificial alginate. ACS Biomater Sci Eng 3(8):1519–1526
Mandrycky C, Wang Z, Kim K, Kim DH (2016) 3D bioprinting for engineering complex tissues. Biotechnol Adv 34(4):422–434
Zhong N, Dong T, Chen Z, Guo Y, Shao Z, Zhao X (2019) A novel 3D-printed silk fibroin-based scaffold facilitates tracheal epithelium proliferation in vitro. J Biomater Appl 34(1):3–11. 0885328219845092
Rodriguez MJ, Dixon TA, Cohen E, Huang W, Omenetto FG, Kaplan DL (2018) 3D freeform printing of silk fibroin. Acta Biomater 71:379–387
Yeon YK, Park HS, Lee JM, Lee JS, Lee YJ, Sultan MT, Park CH (2018) New concept of 3D printed bone clip (polylactic acid/hydroxyapatite/silk composite) for internal fixation of bone fractures. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed 29(7–9):894–906
Zhou M, Lee BH, Tan LP (2017) A dual crosslinking strategy to tailor rheological properties of gelatin methacryloyl. Int J Bioprint 3(2):130–137
Billiet T, Vandenhaute M, Schelfhout J, Van Vlierberghe S, Dubruel P (2012) A review of trends and limitations in hydrogel-rapid prototyping for tissue engineering. Biomaterials 33(26):6020–6041
Shin S, Kwak H, Hyun J (2018) Melanin nanoparticle-incorporated silk fibroin hydrogels for the enhancement of printing resolution in 3D-projection Stereolithography of poly (ethylene glycol)-Tetraacrylate bio-ink. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 10(28):23573–23582
Zhao YH, Niu CM, Shi JQ, Wang YY, Yang YM, Wang HB (2018) Novel conductive polypyrrole/silk fibroin scaffold for neural tissue repair. Neural Regen Res 13(8):1455
Na K, Shin S, Lee H, Shin D, Baek J, Kwak H, Hyun J (2018) Effect of solution viscosity on retardation of cell sedimentation in DLP 3D printing of gelatin methacrylate/silk fibroin bioink. J Ind Eng Chem 61:340–347
Kim DK, Lee JM, Jeong JY, Park HJ, Lee OJ, Chao J, Park CH (2018) New fabrication method of silk fibroin plate and screw based on a centrifugal casting technique. J Tissue Eng Regen Med 12(11):2221–2229
Salamon A, Van Vlierberghe S, Van Nieuwenhove I, Baudisch F, Graulus GJ, Benecke V, Dubruel P (2014) Gelatin-based hydrogels promote chondrogenic differentiation of human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells in vitro. Materials 7(2):1342–1359
West DC, Hampson IN, Arnold F, Kumar S (1985) Angiogenesis induced by degradation products of hyaluronic acid. Science 228(4705):1324–1326
Chen WJ, Abatangelo G (1999) Functions of hyaluronan in wound repair. Wound Repair Regen 7(2):79–89
Majima T, Irie T, Sawaguchi N, Funakoshi T, Iwasaki N, Harada K, Nishimura SI (2007) Chitosan-based hyaluronan hybrid polymer fibre scaffold for ligament and tendon tissue engineering. Proc Inst Mech Eng H J Eng Med 221(5):537–546
Kim TH, Yun YP, Shim KS, Kim HJ, Kim SE, Park K, Song HR (2018) In vitro anti-inflammation and Chondrogenic differentiation effects of inclusion Nanocomplexes of hyaluronic acid-Beta Cyclodextrin and simvastatin. Tissue Eng Regen Med 15(3):263–274
Kang SW, Bada LP, Kang CS, Lee JS, Kim CH, Park JH, Kim BS (2008) Articular cartilage regeneration with microfracture and hyaluronic acid. Biotechnol Lett 30(3):435–439
Leach JB, Schmidt CE (2005) Characterization of protein release from photocrosslinkable hyaluronic acid-polyethylene glycol hydrogel tissue engineering scaffolds. Biomaterials 26(2):125–135
Masters KS, Shah DN, Leinwand LA, Anseth KS (2005) Crosslinked hyaluronan scaffolds as a biologically active carrier for valvular interstitial cells. Biomaterials 26(15):2517–2525
Perale G, Hilborn J (eds) (2016) Bioresorbable polymers for biomedical applications: from fundamentals to translational medicine. Woodhead Publishing, Sawston
Van Den Bulcke AI, Bogdanov B, De Rooze N, Schacht EH, Cornelissen M, Berghmans H (2000) Structural and rheological properties of methacrylamide modified gelatin hydrogels. Biomacromolecules 1(1):31–38
Smeds KA, Grinstaff MW (2001) Photocrosslinkable polysaccharides for in situ hydrogel formation. J Biomed Mater Res 54(1):115–121
Hospodiuk M, Dey M, Sosnoski D, Ozbolat IT (2017) The bioink: a comprehensive review on bioprintable materials. Biotechnol Adv 35(2):217–239
Wang Z, Abdulla R, Parker B, Samanipour R, Ghosh S, Kim K (2015) A simple and high-resolution stereolithography-based 3D bioprinting system using visible light crosslinkable bioinks. Biofabrication 7(4):045009
Shanjani Y, Pan CC, Elomaa L, Yang Y (2015) A novel bioprinting method and system for forming hybrid tissue engineering constructs. Biofabrication 7(4):045008
Zhang AP, Qu X, Soman P, Hribar KC, Lee JW, Chen S, He S (2012) Rapid fabrication of complex 3D extracellular microenvironments by dynamic optical projection stereolithography. Adv Mater 24(31):4266–4270
Soman P, Chung PH, Zhang AP, Chen S (2013) Digital microfabrication of user-defined 3D microstructures in cell-laden hydrogels. Biotechnol Bioeng 110(11):3038–3047
Bertlein S, Brown G, Lim KS, Jungst T, Boeck T, Blunk T, Groll J (2017) Thiol–ene clickable gelatin: a platform bioink for multiple 3D biofabrication technologies. Adv Mater 29(44):1703404
Lim KS, Levato R, Costa PF, Castilho MD, Alcala-Orozco CR, van Dorenmalen KM, Woodfield TB (2018) Bio-resin for high resolution lithography-based biofabrication of complex cell-laden constructs. Biofabrication 10(3):034101
Yu C, Ma X, Zhu W, Wang P, Miller KL, Stupin J, Chen S (2019) Scanningless and continuous 3D bioprinting of human tissues with decellularized extracellular matrix. Biomaterials 194:1–13
Anada T, Pan CC, Stahl AM, Mori S, Fukuda J, Suzuki O, Yang Y (2019) Vascularized bone-mimetic hydrogel constructs by 3D bioprinting to promote osteogenesis and angiogenesis. Int J Mol Sci 20(5):1096
Miri AK, Nieto D, Iglesias L, Goodarzi Hosseinabadi H, Maharjan S, Ruiz-Esparza GU, Shin SR (2018) Microfluidics-enabled multimaterial Maskless stereolithographic bioprinting. Adv Mater 30(27):1800242
Lam T, Dehne T, Krüger JP, Hondke S, Endres M, Thomas A, Kloke L (2019) Photopolymerizable gelatin and hyaluronic acid for stereolithographic 3D bioprinting of tissue-engineered cartilage. J Biomed Mater Res Part B Appl Biomater 107(8):2649–2657
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIP) (grant No.: 2016R1E1A1A01942120), Republic of Korea and by the Hallym University Research Fund.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Kim, S.H., Kim, D.Y., Lim, T.H., Park, C.H. (2020). Silk Fibroin Bioinks for Digital Light Processing (DLP) 3D Bioprinting. In: Chun, H.J., Reis, R.L., Motta, A., Khang, G. (eds) Bioinspired Biomaterials. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, vol 1249 . Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-3258-0_4
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-3258-0_4
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-15-3257-3
Online ISBN: 978-981-15-3258-0
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)