Abstract
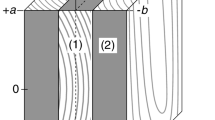
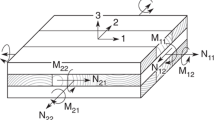
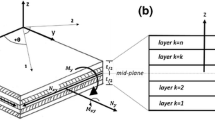
This chapter focuses on moisture-induced deformations in three-layered cross-laminated timber with a symmetrical build-up, where the fibre direction of the middle layer is oriented perpendicular to that of the outer layers. Dimensional stability, i.e. the ability to resist warping, is of main interest for the application of such wood panels. The cross lamination of the layers is advantageous to warping. The moisture-induced expansion/contraction of each single layer is partly restrained by the adjacent layers. The free swelling and shrinkage of adjacent layers differ approximately by a factor of 10 (radial/longitudinal) to 20 (tangential/longitudinal). As a consequence of this difference, stresses and even cracks may occur. In large-scale panels warping was observed. This reduces the serviceability in the practice. Due to a climate gradient considerable distortions (warp) in the form of cup and twist may occur. Models to calculate the moisture and stress fields are provided and validated to experimental tests.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
DIN EN ISO 12572 (2001) Hygrothermal performance of building materials and products – Determination of water vapour transmission properties
Bodig J, Jayne A (1982) Mechanics of wood and wood composites. Van Nostrand Reinhold Company, New York, NY
Dahlblom O, Persson K, Petersson H, Ormarsson S (1999) Investigation of variation of engineering properties of spruce. 6th international IUFRO wood drying conference: Wood Drying Research & Technology for Sustainable Forestry Beyond 2000. University of Stellenbosch, South Africa
Frandsen HL, Damkilde L, Svensson S (2007) A revised multi-Fickian moisture transport model to describe non-Fickian effects in wood. Holzforschung 61:563–572
Gereke T (2009) Moisture-induced stresses in cross-laminated wood panels. PhD thesis, ETH Zurich
Gereke T, Schnider T, Hurst A, Niemz P (2009a) Identification of moisture-induced stresses in cross-laminated wood panels from beech wood (Fagus sylvatica L.) Wood Sci. Techn 43(3-4): 301–315. Published on line: September 23, 2008
Gereke T, Gustafsson PJ, Persson K, Niemz P (2009b) Experimental and numerical determination of the hygroscopic warping of cross-laminated solid wood panels Holzforschung 63(3):340–347
Hanhijärvi A (1995) Modelling of creep deformation mechanisms in wood. Technical Research Centre of Finland, Espoo
Hukka A (1999) The effective diffusion coefficient and mass transfer coefficient of nordic softwood as calculated from direct drying experiments. Holzforschung 53:534–540
Keunecke D, Hering S, Niemz P (2008) Three-dimensional elastic behaviour of common yew and Norway spruce. Wood Sci Technol 42:633–647
Konnerth J, Gindl W, Müller U (2007) Elastic properties of adhesive polymers. Part I: Polymer films by means of electronic speckle pattern interferometry. J Appl Polym Sci 103:3936–3939
Konnerth J, Jäger A, Eberhardsteiner J, Müller U, Gindl W (2006) Elastic properties of adhesive polymers. Part II. Polymer films and bond lines by means of nanoindentation. J Appl Polym Sci 102:1234–1239
Leicester RM (1971) A rheological model for mechano-sorptive deflections of beams. Wood Sci Technol 5:211–220
Mårtensson A (1992) Mechanical behaviour of wood exposed to humidity variations. Report TVBK-1006, Lund University, Lund, Sweden
Neuhaus F.-H (1981) Elastizitätszahlen von Fichtenholz in Abhängigkeit von der Holzfeuchtigkeit. Ruhr-University Bochum
Ormarsson S (1999) Numerical analysis of moisture-related distortions in sawn timber. Phd thesis, Chalmers University of Technology, Göteborg, Sweden,
Ranta-Maunus A (1990) Impact of mechano-sorptive creep to the long-term strength of timber. Holz als Roh- und Werkstoff 48:67–71
Santaoja K, Leino T, Ranta-Maunus A, Hanhijärvi A (1991) Mechano-sorptive structural analysis of wood by the ABAQUS finite element program. Research Notes 1276, Technical Research Center of Finland, Espoo
Sell J (1997) Eigenschaften und Kenngrössen von Holzarten. Baufachverlag AG, Dietikon
Siau JF (1995) Wood: Influence of moisture on physical properties. Department of Wood Science and Forest Products, Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University, Blacksburg, USA
Takemura T (1967) Plastic properties of wood in relation to the non equilibrium states of moisture content. Part II. Mokuzai Gakkaishi 13(3):77–81
Teischinger A, Vanek M (1987) Eignung verschiedener Auftrennmethoden zur Bestimmung eines Feuchtegradienten im Holz nach der Darrmethode. Holzforschung und Holzverwertung 39:5–8
Toratti T (1992) Creep of timber beams in a variable environment. Helsinki University of Technology, Espoo
Vanek M, Teischinger A (1989) Diffusionskoeffizienten und Diffusionswiderstandszahlen von verschiedenen Holzarten. Holzforschung und Holzverwertung 1:3–6
Acknowledgements
Financial support from the European Cooperation in Science and Technology (COST, Action E49) is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2010 Springer Science+Business Media B.V.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Gereke, T., Gustafsson, P.J., Persson, K., Niemz, P. (2010). The Hygroscopic Warping of Cross-Laminated Timber. In: Bucur, V. (eds) Delamination in Wood, Wood Products and Wood-Based Composites. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-90-481-9550-3_14
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-90-481-9550-3_14
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Dordrecht
Print ISBN: 978-90-481-9549-7
Online ISBN: 978-90-481-9550-3
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)