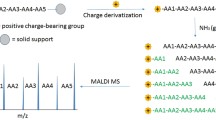
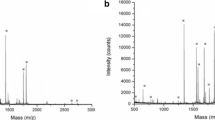
Summary
In the last few years the development of new mass spectrometric techniques enabled fast and sensitive protein analysis by the introduction of mass spectrometry (MS) fingerprinting and MS/MS sequencing. For these methods mixtures of peptide fragments of the proteins can be employed, whereas the Edman degradation method requests purified peptides. On the other hand, Edman sequencing has the advantages that interpretation of the data is more simple, extended sequences can be derived, and reliable sequence information on unknown proteins is possible. Hence, Edman chemistry as an alternative technique to MS is still valuable. But higher sensitivity of the sequencers is needed in order to meet modern demands, e.g. in proteomics research. We designed a wafer-based chip sequencer for protein and peptide sequencing in the femto-to attomole range. The main advantage of our new design is the complete integration of dead volume free valves together with reactor and converter and volume-measuring loops within one wafer-based system. In this system aggressive chemicals and solvents for the Edman degradation can be delivered in sub-microliter amounts, which allows a considerable shortening of the degradation cycles. Further, we developed sensitive maintenance and tightness tests to prove a precise and reproducible delivery of the chemicals and the reduction of drying times as compared with conventional sequencers. Real parallel processing of several samples can easily be implemented. The system is designed to serve future needs in protein research.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kahn K (1995) From genome to proteome: looking at a cell’s proteins. Science 270: 369–370
Edman P, Begg G (1967) A protein sequenator. Eur J Biochem 1: 80–97
Wittmann-Liebold B, Graffunder H, Kohls H (1976) A device coupled to a modified sequenator for the automated conversion of anilinothiazolinones into PTH-amino acids. Anal Biochem 75: 621–633
Hewick RM, Hunkapiller MW, Hood LE, Dreyer WJ (1981) A gas-liquid solid phase peptide and protein sequenator. J Biol Chem 256: 7990–7997
Wittmann-Liebold B, Ashman K (1985) On-line detection of amino acid derivatives released by automatic Edman degradation of polypeptides. In: Tschesche H (ed): Modern methods in protein chemistry. Walter de Gruyter, Berlin, 303–327
Wittmann-Liebold B (1986) Design of a multipurpose sequencer. In: JE Shively (ed): Methods in protein microcharacterisation. Humana Press, Clifton, NJ, 249–277
Wittmann-Liebold B (1992) High sensitive protein analysis. Pure Appl Chem 64: 537–543
Klose J, Kobalz U (1995) Two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins: an updated protocol and implications for a functional analysis of the genome. Electrophoresis 16: 1034–1059
Otto A, Thiede B, Muller E-C, Scheler C, Wittmann-Liebold B, Jungblut P (1996) Identification of human myocardial proteins separated by two-dimensional electrophoresis using an effective sample preparation for mass spectrometry. Electrophoresis 17: 1643–1650
Brockstedt E, Rickers A, Kostka S, Laubersheimer A, Dorken B, Wittmann-Liebold B, Bommert K, Otto A (1998) Identification of apoptosis-associated proteins in a human Burkitt Lymphoma cell line, cleavage of hnRNP AI by caspase 3. J Biol Chem 273: 28057–28064
Karas M, Hillenkamp F (1988) Laser desorption ionization of proteins with molecular masses exeeding 10,000 dalton. Anal Chem 60: 2299
Fenn JB, Mann M, Meng CK, Wong SF, Whitehouse CM (1989) Electrospray ionization for mass spectrometry of large biomolecules. Science 246: 64–71
Hunt DF, Yates JR III, Shabanowitz J, Winston S, Hauer CR (1986) Protein sequencing by tandem mass spectrometry. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83: 6233–6237
Spengler B, Kirsch D, Kaufmann R, Jaeger E (1992) Peptide sequencing by matrix-assisted laser-desorption mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 6: 105–108
Mann M, Wilm M (1994) Error-tolerant identification of peptides in sequence databases by peptide sequence tags. Anal Chem 66, 4390–4399
Gevaert K, Demol H, Puype M, Broekaert D, De Boeck S, Houthaeve T, Vandekerckhove J (1997) Peptides adsorbed on reverse-phase chromatographic beads as targets for femtomole sequencing by post-source decay matrix assisted laser desorption ionization-reflectron time of flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-RETOF-MS). Electrophoresis 18: 2950–2960
Katta V, Chow DT, Rohde MF (1998) Applications of in-source fragmentation of protein ions for direct sequence analysis by delayed extraction MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. Anal Chem 70: 4410–4416
O’Neill SA, Zieske LR, Hsi K-L, Grimley C, Kochersperger ML, Yuan P-M (1996) An integrated approach for sub-picomole protein/peptide sequencing. Application note PE Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA
Chen M, Waldron KC, Zhao YW, Dovichi NJ (1994) Micellar capillary electrophoresis separation and thermo-optical absorbance detection of products from manual peptide sequencing. Electrophoresis 15: 1290–1294
Li XF, Waldron KC, Black J, Lewis D, Ireland I, Dovichi NJ (1997) Miniaturized protein microsequencer with PTH identification by capillary electrophoresis II. A syringe-pumpbased system for covalent sequencing. Talanta 44: 401–411
Wu S, Dovichi NJ (1992) Capillary zone electrophoresis separation and laser-induced fluorescence detection of zeptomole quantities of fluorescein thiohydantoin derivatives of amino acids. Talanta 39: 173–178
Chang JY, Brauer D, Wittmann-Liebold B (1978) Micro-sequence analysis of peptides and proteins using 4-N,N-dimethylaminoazobenzene 4’-isothiocyanate/phenylisothiocyanate double coupling method. FEBS Lett 93: 205–214
Ireland ID, Lewis DF, Li XF, Renborg A, Kwong S, Chen M, Dovichi NJ (1997) Double coupling Edman chemistry for high-sensitivity automated protein sequencing. J Prot Chem 16: 491–495
Schulten H-R, Wittmann-Liebold B (1976) High resolution field desorption mass spectrometry V: mixtures of amino acid phenylthiohydantoins and Edman degradation products. Anal Biochem 76: 300–310
Zhou J, Hefta S, Lee TD (1997) High sensitive analysis of phenylthiohydantoin amino acid derivatives by electrospray mass spectrometry. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom 8: 1165–1174
Hess D, Nika H, Chow DT, Bures EJ, Morrison HD, Aebersold R (1995) Liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization mass spectrometry of 4-(3-pyridinylmethylaminocarboxypropyl) phenylthiohydantoins. Anal Biochem 224: 373–381
Becker EW, Ehrfeld W, Hagmann P, Manner A, Munchmeyer D (1986) Fabrication of microstructures with high aspect ratios and great structural heights by synchrotron radiation lithography, galvanoforming and plastic molding (LIGA process). Microelectron Eng 4: 35–36
Ehrfeld W (ed) (1995) Microsystem technology for chemical and biochemical micro-reactors. DECHEMA Monographs, vol. 132. VCH, Weinheim
Ehrfeld W (ed) (1998) Microreaction technology: Proceedings of the First International Conference on Microreaction Technology. Springer, Berlin
van der Schoot BH, Jeanneret van den Berg A, de Rooij NF (1992) A silicon integrated miniature chemical analysis system. Sensors Actuators Bl: 254–248
Manz A, Graber N, Widmer HM (1990) Miniaturized total chemical analysis system: a novel concept for chemical sensing. Sensors Actuators B6: 57–60
Ramsey JM, Jacobson SC, Foote RS (1998) Microfabricated device for performing chemical and biochemical analysis. In: [29], 204–218
Figeys D, Ning Y, Aebersold R (1997) A micro fabricated device for rapid protein iden-tification by microelectrospray ion trap mass spectrometry. Anal Chem 69: 3153–3160
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2000 Springer Basel AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Wurzel, C., Wittmann-Liebold, B. (2000). New approaches for innovations in sensitive Edman sequence analysis by design of a wafer-based chip sequencer. In: Jollès, P., Jörnvall, H. (eds) Proteomics in Functional Genomics. EXS, vol 88. Birkhäuser, Basel. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-0348-8458-7_10
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-0348-8458-7_10
Publisher Name: Birkhäuser, Basel
Print ISBN: 978-3-0348-9576-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-0348-8458-7
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive