Abstract
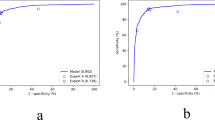
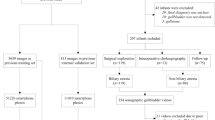
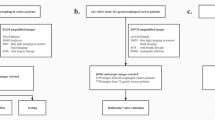
The diagnosis of Biliary Atresia (BA) is still complicated and high resource consumed. Though sonographic gallbladder images can be used as an initial detection tool, lack of experienced experts limits BA infants to be treated timely, resulting in liver transplantation or even death. We developed a diagnosis tool by ViT-CNN ensemble model to help doctors in underdeveloped area to diagnose BA. It performs better than human expert (with 88.1% accuracy versus 87.4%, 0.921 AUC versus 0.837), and still has an acceptable performance on severely noised images photographed by smartphone, providing doctors in clinical facilities with outdated Ultrasound instruments a simple and feasible solution to diagnose BA with our online tool
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang, J., et al.: Liver immune profiling reveals pathogenesis and therapeutics for biliary atresia. Cell. 183(7), pp. 1867–1883.e26 (2020). https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0092867420314550
Asai, A., Miethke, A., Bezerra, J.: Pathogenesis of biliary atresia: defining biology to understand clinical phenotypes. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 12, 05 (2015)
Hartley, J.L., Davenport, M., Kelly, D.A.: Biliary atresia. The Lancet 374(9702), 1704–1713 (2009)
Hsiao, C.-H., et al.: Universal screening for biliary atresia using an infant stool color card in Taiwan. Hepatology 47(4), 1233–1240 (2008)
Ohi, R.: Surgical treatment of biliary atresia in the liver transplantation era, pp. 1229–1232 (1998)
Serinet, M.-O., et al.: Impact of age at Kasai operation on its results in late childhood and adolescence: a rational basis for biliary atresia screening. Pediatrics 123(5), 1280–1286 (2009)
Lertudomphonwanit, C., et al.: Large-scale proteomics identifies MMP-7 as a sentinel of epithelial injury and of biliary atresia. Sci. Transl. Med. 9(417), eaan8462 (2017)
Harpavat, S., et al.: Diagnostic yield of newborn screening for biliary atresia using direct or conjugated bilirubin measurements. Jama 323(12), 1141–1150 (2020)
Humphrey, T.M., Stringer, M.D.: Biliary atresia: US diagnosis. Radiology 244(3), 845–851 (2007)
Qi, X., et al.: Machine learning-based CT radiomics model for predicting hospital stay in patients with pneumonia associated with SARS-COV-2 infection: a multicenter study. MedRxiv (2020)
Ardila, D., et al.: End-to-end lung cancer screening with three-dimensional deep learning on low-dose chest computed tomography. Nat. Med. 25(6), 954–961 (2019)
Zhou, W., et al.: Ensembled deep learning model outperforms human experts in diagnosing biliary atresia from sonographic gallbladder images. Nat. Commun. 12(1), 1–14 (2021)
Zhang, K., Zuo, W., Chen, Y., Meng, D., Zhang, L.: Beyond a gaussian denoiser: Residual learning of deep CNN for image denoising. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 26(7), 3142–3155 (2017)
Sun, Y., Yu, Y., Wang, W.: Moiré photo restoration using multiresolution convolutional neural networks. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 27(8), 4160–4172 (2018)
Dosovitskiy, A., et al.: An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv:2010.11929 (2021)
Gu, Y., Piao, Z., Yoo, S.J.: STHardNet: Swin transformer with HardNet for MRI segmentation. Appl. Sci. 12(1), 468 (2022)
Zhang, L., Wen, Y.: A transformer-based framework for automatic covid19 diagnosis in chest CTS. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 513–518 (2021)
Harpavat, S., Garcia-Prats, J.A., Shneider, B.L.: Newborn bilirubin screening for biliary atresia. N. Engl. J. Med. 375(6), 605–606 (2016)
Feldman, A.G., Sokol, R.J.: Recent developments in diagnostics and treatment of neonatal cholestasis. In: Seminars in Pediatric Surgery, vol. 29, no. 4, p. 150945. Elsevier (2020)
Zhou, L., Shan, Q., Tian, W., Wang, Z., Liang, J., Xie, X.: Ultrasound for the diagnosis of biliary atresia: a meta-analysis. Am. J. Roentgenol. 206(5), W73–W82 (2016)
Kim, M.-J., et al.: Biliary atresia in neonates and infants: triangular area of high signal intensity in the porta hepatis at t2-weighted MR cholangiography with us and histopathologic correlation. Radiology 215(2), 395–401 (2000)
Farrant, P., Meire, H., Mieli-Vergani, G.: Ultrasound features of the gall bladder in infants presenting with conjugated hyperbilirubinaemia. Br. J. Radiol. 73(875), 1154–1158 (2000)
Lee, H.-J., Lee, S.-M., Park, W.-H., Choi, S.-O.: Objective criteria of triangular cord sign in biliary atresia on us scans. Radiology 229(2), 395–400 (2003)
Park, W.-H., Choi, S.-O., Lee, H.-J., Kim, S.-P., Zeon, S.-K., Lee, S.-L.: A new diagnostic approach to biliary atresia with emphasis on the ultrasonographic triangular cord sign: comparison of ultrasonography, hepatobiliary scintigraphy, and liver needle biopsy in the evaluation of infantile cholestasis. J. Pediat. Surg. 32(11), 1555–1559 (1997)
Koob, M., Pariente, D., Habes, D., Ducot, B., Adamsbaum, C., Franchi-Abella, S.: The porta hepatis microcyst: an additional sonographic sign for the diagnosis of biliary atresia. Eur. Radiol. 27(5), 1812–1821 (2017)
Caponcelli, E., Knisely, A.S., Davenport, M.: Cystic biliary atresia: an etiologic and prognostic subgroup. J. Pediat. Surg. 43(9), 1619–1624 (2008)
Zhou, L.-Y., et al.: Percutaneous us-guided cholecystocholangiography with microbubbles for assessment of infants with us findings equivocal for biliary atresia and gallbladder longer than 1.5 cm: a pilot study. Radiology 286(3), 1033–1039 (2018)
Zhou, W., Zhou, L.: Ultrasound for the diagnosis of biliary atresia: from conventional ultrasound to artificial intelligence. Diagnostics 12(1), 51 (2021)
Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I., Hinton, G.E.: Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 25 (2012)
LeCun, Y., Bottou, L., Bengio, Y., Haffner, P.: Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. Proc. IEEE 86(11), 2278–2324 (1998)
Simonyan, K., Zisserman, A.: Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. CoRR, abs/1409.1556 (2015)
Szegedy, C., et al.: Going deeper with convolutions. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp. 1–9 (2015)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 770–778 (2016)
Huang, G., Liu, Z., Van Der Maaten, L., Weinberger, K.Q.: Densely connected convolutional networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 4700–4708 (2017)
Liu, C., Zoph, B., Neumann, M., Shlens, J., Hua, W., Li, L.-J., Fei-Fei, L., Yuille, A., Huang, J., Murphy, K.: Progressive neural architecture search. In: Ferrari, V., Hebert, M., Sminchisescu, C., Weiss, Y. (eds.) ECCV 2018. LNCS, vol. 11205, pp. 19–35. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01246-5_2
Tan, M., Le, Q.: Efficientnet: rethinking model scaling for convolutional neural networks. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 6105–6114. PMLR (2019)
Hu, J., Shen, L., Sun, G.: Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 7132–7141 (2018)
Vaswani, A., et al.: Attention is all you need. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 30 (2017)
Kenton, J. D. M.-W. C., Toutanova, L.K.: BERT: pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. In: Proceedings of NAACL-HLT, pp. 4171–4186 (2019)
Radford, A., et al.: Language models are unsupervised multitask learners. OpenAI Blog 1(8), 9 (2019)
Dong, L., et al.: Unified language model pre-training for natural language understanding and generation. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 32 (2019)
Wang, X., Girshick, R., Gupta, A., He, K.: Non-local neural networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 7794–7803 (2018)
Touvron, H., Cord, M., Douze, M., Massa, F., Sablayrolles, A., Jégou, H.: Training data-efficient image transformers & distillation through attention. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 10:347–10:357. PMLR (2021)
Liu, Z., et al.: Swin transformer: hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 10:012–10:022 (2021)
Wu, H., et al.: CVT: introducing convolutions to vision transformers. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 22–31 (2021)
Dong, X., et al.: CSwin transformer: a general vision transformer backbone with cross-shaped windows. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 12:124–12:134 (2022)
Boland, P.J.: Majority systems and the condorcet jury theorem. J. R. Statist. Soc. Ser. D (The Statist.) 38(3), 181–189 (1989)
Ardabili, S., Mosavi, A., Várkonyi-Kóczy, A.R.: Advances in machine learning modeling reviewing hybrid and ensemble methods. In: Várkonyi-Kóczy, A.R. (ed.) INTER-ACADEMIA 2019. LNNS, vol. 101, pp. 215–227. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-36841-8_21
Ho, T.K.: Random decision forests. In: Proceedings of 3rd International Conference on Document Analysis and Recognition, vol. 1, pp. 278–282. IEEE (1995)
Breiman, L.: Bagging predictors. Mach. Learn. 24(2), 123–140 (1996)
Kaniovski, S., Zaigraev, A.: Optimal jury design for homogeneous juries with correlated votes. Theory Decis. 71(4), 439–459 (2011)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Wei, Z. (2023). Ensemble Model of Visual Transformer and CNN Helps BA Diagnosis for Doctors in Underdeveloped Areas. In: Zheng, Y., Keleş, H.Y., Koniusz, P. (eds) Computer Vision – ACCV 2022 Workshops. ACCV 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 13848. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-27066-6_6
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-27066-6_6
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-27065-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-27066-6
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)