Abstract
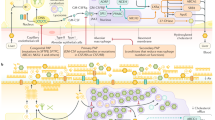
Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis (PAP) is a syndrome characterized by the accumulation of pulmonary surfactant resulting in reduced oxygen uptake. It affects men, women, and children without predilection for socioeconomic status, geographic location, or race but occurs more commonly in smokers. Prevalence has been reported at 7–26 per million in the general population. Symptoms include dyspnea, cough, and fatigue. The clinical course includes progressive dyspnea, failure and, in some patients, serious secondary infections, pulmonary fibrosis, hypoxemic respiratory failure, and death. PAP is classified as primary (mediated by disruption of GM-CSF signaling), secondary (mediated by reduced alveolar macrophage functions due to an underlying clinical condition), or congenital (caused by mutations in genes involved in surfactant production). In primary PAP the most common cause is autoimmune PAP, which accounts for over 90% of all PAP syndrome. Pathogenesis is driven by impaired GM-CSF signaling to alveolar macrophages which require GM-CSF stimulation to stimulate surfactant clearance. The diagnosis of autoimmune PAP can be made by testing for an increased level of serum GM-CSF autoantibodies without a requirement for a lung biopsy. Whole-lung lavage is the main current treatment approach designed to remove excess surfactant by physically washing it out of the lungs but a pharmacotherapeutic approaches, inhaled GM-CSF is currently under evaluation.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Trapnell BC, Whitsett JA, Nakata K. Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. N Engl J Med. 2003;349(26):2527–39.
Seymour JF, Presneill JJ. Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis: progress in the first 44 years. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002;166(2):215–35.
Carey B, Trapnell BC. The molecular basis of pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. Clin Immunol. 2010;135(2):223–35.
Xu Z, Jing J, Wang H, Xu F, Wang J. Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis in China: a systematic review of 241 cases. Respirology. 2009;14(5):761–6.
Bonella F, Bauer PC, Griese M, Ohshimo S, Guzman J, Costabel U. Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis: new insights from a single-center cohort of 70 patients. Respir Med. 2011;105(12):1908–16.
Campo I, Mariani F, Rodi G, Paracchini E, Tsana E, Piloni D, et al. Assessment and management of pulmonary alveolar proteinosis in a reference center. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2013;8:40.
Trapnell BC, Nakata K, Bonella F, Campo I, Griese M, Hamilton J, et al. Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2019;5(1):16.
Pattle RE. Properties, function and origin of the alveolar lining layer. Nature. 1955;175:1125–6.
Rosen SG, Castleman B, Liebow AA. Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. N Engl J Med. 1958;258:1123–42.
Golde DW, Territo M, Finley TN, Cline MJ. Defective lung macrophages in pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. Ann Intern Med. 1976;85(3):304–9.
Muller-Quernheim J, Schopf RE, Benes P, Schulz V, Ferlinz R. A macrophage-suppressing 40-kD protein in a case of pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. Klin Wochenschr. 1987;65(19):893–7.
Stratton JA, Sieger L, Wasserman K. The immunoinhibitory activities of the lung lavage materials and sera from patients with pulmonary alveolar proteinosis (PAP). J Clin Lab Immunol. 1981;5(2):81–6.
Bury T, Corhay JL, Saint-Remy P, Radermecker M. Alveolar proteinosis: restoration of the function of the alveolar macrophages after therapeutic lavage. Rev Mal Respir. 1989;6(4):373–5.
Stanley E, Lieschke GJ, Grail D, Metcalf D, Hodgson G, Gall JA, et al. Granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor-deficient mice show no major perturbation of hematopoiesis but develop a characteristic pulmonary pathology. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994;91(12):5592–6.
Dranoff G, Crawford AD, Sadelain M, Ream B, Rashid A, Bronson RT, et al. Involvement of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor in pulmonary homeostasis. Science. 1994;264(5159):713–6.
Tanaka N, Watanabe J, Kitamura T, Yamada Y, Kanegasaki S, Nakata K. Lungs of patients with idiopathic pulmonary alveolar proteinosis express a factor which neutralizes granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor. FEBS Lett. 1999;442(2–3):246–50.
Kitamura T, Tanaka N, Watanabe J, Uchida KS, Yamada Y, et al. Idiopathic pulmonary alveolar proteinosis as an autoimmune disease with neutralizing antibody against granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor. J Exp Med. 1999;190(6):875–80.
Uchida K, Beck DC, Yamamoto T, Berclaz PY, Abe S, Staudt MK, et al. GM-CSF autoantibodies and neutrophil dysfunction in pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. N Engl J Med. 2007;356(6):567–79.
Sakagami T, Uchida K, Suzuki T, Carey BC, Wood RE, Wert SE, et al. Human GM-CSF autoantibodies and reproduction of pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. N Engl J Med. 2009;361(27):2679–81.
Sakagami T, Beck D, Uchida K, Suzuki T, Carey BC, Nakata K, et al. Patient-derived granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor autoantibodies reproduce pulmonary alveolar proteinosis in nonhuman primates. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2010;182(1):49–61.
Bendtzen K, Svenson M, Hansen MB, Busch T, Bercker S, Kaisers U, et al. GM-CSF autoantibodies in pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. N Engl J Med. 2007;356:2001–2.
McCarthy C, Carey B, Trapnell BC. Autoimmune pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2022;205(9):1016–35.
Inoue Y, Trapnell BC, Tazawa R, Arai T, Takada T, Hizawa N, et al. Characteristics of a large cohort of patients with autoimmune pulmonary alveolar proteinosis in Japan. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2008;177(7):752–62.
Dirksen U, Nishinakamura R, Groneck P, Hattenhorst U, Nogee L, Murray R, et al. Human pulmonary alveolar proteinosis associated with a defect in GM- CSF/IL-3/IL-5 receptor common beta chain expression. J Clin Invest. 1997;100(9):2211–7.
Suzuki T, Sakagami T, Rubin BK, Nogee LM, Wood RE, Zimmerman SL, et al. Familial pulmonary alveolar proteinosis caused by mutations in CSF2RA. J Exp Med. 2008;205(12):2703–10.
Asamoto H, Kitaichi M, Nishimura K, Itoh H, Izumi T. Primary pulmonary alveolar proteinosis—clinical observation of 68 patients in Japan. Nihon Kyobu Shikkan Gakkai Zasshi. 1995;33(8):835–45.
McCarthy C, Avetisyan R, Carey BC, Chalk C, Trapnell BC. Prevalence and healthcare burden of pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2018;13(1):129.
Anderson K, Carey B, Martin A, Roark C, Chalk C, Nowell-Bostic M, et al. Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis: an autoimmune disease lacking an HLA association. PLoS One. 2019;14(3):e0213179.
Sakaue S, Yamaguchi E, Inoue Y, Takahashi M, Hirata J, Suzuki K, et al. Genetic determinants of risk in autoimmune pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1):1032.
Sallese A, Suzuki T, McCarthy C, Bridges J, Filuta A, Arumugam P, et al. Targeting cholesterol homeostasis in lung diseases. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):10211.
McCarthy C, Lee E, Bridges JP, Sallese A, Suzuki T, Woods JC, et al. Statin as a novel pharmacotherapy of pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):3127.
Gschwend J, Sherman SPM, Ridder F, Feng X, Liang HE, Locksley RM, et al. Alveolar macrophages rely on GM-CSF from alveolar epithelial type 2 cells before and after birth. J Exp Med. 2021;218(10):e20210745.
Lieschke GJ, Burgess AW. Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (1). N Engl J Med. 1992;327(1):28–35.
Fleetwood AJ, Cook AD, Hamilton JA. Functions of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. Crit Rev Immunol. 2005;25(5):405–28.
Hamilton JA. Colony-stimulating factors in inflammation and autoimmunity. Nat Rev Immunol. 2008;8(7):533–44.
Nakata K, Akagawa KS, Fukayama M, Hayashi Y, Kadokura M, Tokunaga T. Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor promotes the proliferation of human alveolar macrophages in vitro. J Immunol. 1991;147(4):1266–72.
Shibata Y, Berclaz PY, Chroneos ZC, Yoshida M, Whitsett JA, Trapnell BC. GM-CSF regulates alveolar macrophage differentiation and innate immunity in the lung through PU.1. Immunity. 2001;15(4):557–67.
Berclaz PY, Shibata Y, Whitsett JA, Trapnell BC. GM-CSF, via PU.1, regulates alveolar macrophage Fcgamma R-mediated phagocytosis and the IL-18/IFN-gamma -mediated molecular connection between innate and adaptive immunity in the lung. Blood. 2002;100(12):4193–200.
Berclaz PY, Zsengeller Z, Shibata Y, Otake K, Strasbaugh S, Whitsett JA, et al. Endocytic internalization of adenovirus, nonspecific phagocytosis, and cytoskeletal organization are coordinately regulated in alveolar macrophages by GM-CSF and PU.1. J Immunol. 2002;169(11):6332–42.
Gearing DP, King JA, Gough NM, Nicola NA. Expression cloning of a receptor for human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. EMBO J. 1989;8(12):3667–76.
Hayashida K, Kitamura T, Gorman DM, Arai K, Yokota T, Miyajima A. Molecular cloning of a second subunit of the receptor for human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF): reconstitution of a high-affinity GM-CSF receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990;87(24):9655–9.
D'Andrea RJ, Gonda TJ. A model for assembly and activation of the GM-CSF, IL-3 and IL-5 receptors: insights from activated mutants of the common beta subunit. Exp Hematol. 2000;28(3):231–43.
Matsuguchi T, Zhao Y, Lilly MB, Kraft AS. The cytoplasmic domain of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) receptor alpha subunit is essential for both GM-CSF-mediated growth and differentiation. J Biol Chem. 1997;272(28):17450–9.
Watanabe S, Itoh T, Arai K. Roles of JAK kinases in human GM-CSF receptor signal transduction. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1996;98(6 Pt 2):S183–91.
Lehtonen A, Matikainen S, Miettinen M, Julkunen I. Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF)-induced STAT5 activation and target-gene expression during human monocyte/macrophage differentiation. J Leukoc Biol. 2002;71(3):511–9.
Arumugam P, Suzuki T, Shima K, McCarthy C, Sallese A, Wessendarp M, et al. Long-term safety and efficacy of gene-pulmonary macrophage transplantation therapy of PAP in Csf2ra(−/−) mice. Mol Ther. 2019;27(9):1597–611.
Nishinakamura R, Wiler R, Dirksen U, Morikawa Y, Arai K, Miyajima A, et al. The pulmonary alveolar proteinosis in granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor/interleukins 3/5 beta c receptor-deficient mice is reversed by bone marrow transplantation. J Exp Med. 1996;183(6):2657–62.
Reed JA, Ikegami M, Cianciolo ER, Lu W, Cho PS, Hull W, et al. Aerosolized GM-CSF ameliorates pulmonary alveolar proteinosis in GM-CSF- deficient mice. Am J Physiol. 1999;276(4 Pt 1):L556–63.
Zsengeller ZK, Reed JA, Bachurski CJ, LeVine AM, Forry-Schaudies S, Hirsch R, et al. Adenovirus-mediated granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor improves lung pathology of pulmonary alveolar proteinosis in granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor-deficient mice. Hum Gene Ther. 1998;9(14):2101–9.
Huffman JA, Hull WM, Dranoff G, Mulligan RC, Whitsett JA. Pulmonary epithelial cell expression of GM-CSF corrects the alveolar proteinosis in GM-CSF-deficient mice. J Clin Invest. 1996;97(3):649–55.
Arumugam P, Suzuki T, Shima K, McCarthy C, Sallese A, Wessendarp M, et al. Long-term safety and efficacy of gene/pulmonary macrophage transplantation therapy of pulmonary alveolar proteinosis in Csf2ra−/− mice. Mol Ther. 2019;27(9):1597–611. In Press
Suzuki T, Arumugam P, Sakagami T, Lachmann N, Chalk C, Sallese A, et al. Pulmonary macrophage transplantation therapy. Nature. 2014;514(7523):450–4.
Suzuki T, McCarthy C, Carey BC, Borchers M, Beck D, Wikenheiser-Brokamp KA, et al. Increased pulmonary GM-CSF causes alveolar macrophage accumulation. Mechanistic implications for Desquamative interstitial pneumonitis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2020;62(1):87–94.
Moore KJ, Rosen ED, Fitzgerald ML, Randow F, Andersson LP, Altshuler D, et al. The role of PPAR-gamma in macrophage differentiation and cholesterol uptake. Nat Med. 2001;7(1):41–7.
Bonfield TL, Raychaudhuri B, Malur A, Abraham S, Trapnell BC, Kavuru MS, et al. PU.1 regulation of human alveolar macrophage differentiation requires granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2003;285(5):L1132–6.
Baker AD, Malur A, Barna BP, Ghosh S, Kavuru MS, Malur AG, et al. Targeted PPAR{gamma} deficiency in alveolar macrophages disrupts surfactant catabolism. J Lipid Res. 2010;51(6):1325–31.
Baker AD, Malur A, Barna BP, Kavuru MS, Malur AG, Thomassen MJ. PPARgamma regulates the expression of cholesterol metabolism genes in alveolar macrophages. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010;393(4):682–7.
Thomassen MJ, Barna BP, Malur AG, Bonfield TL, Farver CF, Malur A, et al. ABCG1 is deficient in alveolar macrophages of GM-CSF knockout mice and patients with pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. J Lipid Res. 2007;48(12):2762–8.
de Aguiar Vallim TQ, Lee E, Merriott DJ, Goulbourne CN, Cheng J, Cheng A, et al. ABCG1 regulates pulmonary surfactant metabolism in mice and men. J Lipid Res. 2017;58(5):941–54.
Baldán A, Tarr P, Vales CS, Frank J, Shimotake TK, Hawgood S, et al. Deletion of the transmembrane transporter ABCG1 results in progressive pulmonary lipidosis. J Biol Chem. 2006;281(39):29401–10.
Bernardino de la Serna J, Perez-Gil J, Simonsen AC, Bagatolli LA. Cholesterol rules: direct observation of the coexistence of two fluid phases in native pulmonary surfactant membranes at physiological temperatures. J Biol Chem. 2004;279(39):40715–22.
Serrano AG, Pérez-Gil J. Protein-lipid interactions and surface activity in the pulmonary surfactant system. Chem Phys Lipids. 2006;141(1–2):105–18.
Orgeig S, Daniels CB. The roles of cholesterol in pulmonary surfactant: insights from comparative and evolutionary studies. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol. 2001;129(1):75–89.
Yancey PG, Jerome WG. Lysosomal sequestration of free and esterified cholesterol from oxidized low density lipoprotein in macrophages of different species. J Lipid Res. 1998;39(7):1349–61.
Seymour JF, Doyle IR, Nakata K, Presneill JJ, Schoch OD, Hamano E, et al. Relationship of anti-GM-CSF antibody concentration, surfactant protein a and B levels, and serum LDH to pulmonary parameters and response to GM-CSF therapy in patients with idiopathic alveolar proteinosis. Thorax. 2003;58(3):252–7.
Samson CM, Jurickova I, Molden E, Schreiner W, Colliver J, Bonkowski E, et al. Granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor blockade promotes ccr9(+) lymphocyte expansion in Nod2 deficient mice. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2011;17(12):2443–55.
Ikegami M, Jobe AH, Huffman Reed JA, Whitsett JA. Surfactant metabolic consequences of overexpression of GM-CSF in the epithelium of GM-CSF-deficient mice. Am J Physiol. 1997;273(4 Pt 1):L709–14.
McGeachy MJ. GM-CSF: the secret weapon in the T(H)17 arsenal. Nat Immunol. 2011;12(6):521–2.
Milleron BJ, Costabel U, Teschler H, Ziesche R, Cadranel JL, Matthys H, et al. Bronchoalveolar lavage cell data in alveolar proteinosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1991;144(6):1330–2.
Caparros D, Steenhouwer F, Marquette CH, Carpentier F, Foulet A. Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. A sequential analysis of the alveolar cell population after complete pulmonary lavage. Apropos of a case. Rev Mal Respir. 1994;11(1):63–6.
Schoch OD, Schanz U, Koller M, Nakata K, Seymour JF, Russi EW, et al. BAL findings in a patient with pulmonary alveolar proteinosis successfully treated with GM-CSF. Thorax. 2002;57(3):277–80.
Punatar AD, Kusne S, Blair JE, Seville MT, Vikram HR. Opportunistic infections in patients with pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. J Infect. 2012;65(2):173–9.
Uchida K, Nakata K, Suzuki T, Luisetti M, Watanabe M, Koch DE, et al. Granulocyte/macrophage-colony-stimulating factor autoantibodies and myeloid cell immune functions in healthy subjects. Blood. 2009;113(11):2547–56.
Presneill JJ, Nakata K, Inoue Y, Seymour JF. Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. Clin Chest Med. 2004;25(3):593–613. viii
Seymour JF, Lieschke GJ, Grail D, Quilici C, Hodgson G, Dunn AR. Mice lacking both granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (CSF) and granulocyte-macrophage CSF have impaired reproductive capacity, perturbed neonatal granulopoiesis, lung disease, amyloidosis, and reduced long-term survival. Blood. 1997;90(8):3037–49.
Agarwal PP, Seely JM, Perkins DG, Matzinger FR, Alikhan Q. Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis and end-stage pulmonary fibrosis: a rare association. J Thorac Imaging. 2005;20(3):242–4.
King TE Jr, Bradford WZ, Castro-Bernardini S, Fagan EA, Glaspole I, Glassberg MK, et al. A phase 3 trial of pirfenidone in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. N Engl J Med. 2014;370(22):2083–92.
Richeldi L, du Bois RM, Raghu G, Azuma A, Brown KK, Costabel U, et al. Efficacy and safety of Nintedanib in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. N Engl J Med. 2014;370(22):2071–82.
Wells AU, Flaherty KR, Brown KK, Inoue Y, Devaraj A, Richeldi L, et al. Nintedanib in patients with progressive fibrosing interstitial lung diseases-subgroup analyses by interstitial lung disease diagnosis in the INBUILD trial: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group trial. Lancet Respir Med. 2020;8(5):453–60.
Goldstein LS, Kavuru MS, Curtis-McCarthy P, Christie HA, Farver C, Stoller JK. Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis: clinical features and outcomes. Chest. 1998;114(5):1357–62.
Lee KN, Levin DL, Webb WR, Chen D, Storto ML, Golden JA. Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis: high-resolution CT, chest radiographic, and functional correlations. Chest. 1997;111(4):989–95.
Johkoh T, Itoh H, Muller NL, Ichikado K, Nakamura H, Ikezoe J, et al. Crazy-paving appearance at thin-section CT: spectrum of disease and pathologic findings. Radiology. 1999;211(1):155–60.
Ishii H, Trapnell BC, Tazawa R, Inoue Y, Akira M, Kogure Y, et al. Comparative study of high-resolution CT findings between autoimmune and secondary pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. Chest. 2009;136(5):1348–55.
Costabel U, Guzman J, Bonella F, Oshimo S. Bronchoalveolar lavage in other interstitial lung diseases. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2007;28(5):514–24.
Bonella F, Ohshimo S, Bauer P, Guzman J, Costabel U. Bronchoalveolar lavage. In: Strausz J, Bolliger CT, editors. Interventional pneumology. European Respiratory Society monograph, vol. 48. Lausanne: European Respiratory Society; 2010. p. 59–72.
Doyle IR, Davidson KG, Barr HA, Nicholas TE, Payne K, Pfitzner J. Quantity and structure of surfactant proteins vary among patients with alveolar proteinosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1998;157(2):658–64.
Martin RJ, Rogers RM, Myers NM. Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis: shunt fraction and lactic acid dehydrogenase concentration as aids to diagnosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1978;117(6):1059–62.
Fujishima T, Honda Y, Shijubo N, Takahashi H, Abe S. Increased carcinoembryonic antigen concentrations in sera and bronchoalveolar lavage fluids of patients with pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. Respiration. 1995;62(6):317–21.
Arai T, Hamano E, Inoue Y, Ryushi T, Nukiwa T, Sakatani M, et al. Serum neutralizing capacity of GM-CSF reflects disease severity in a patient with pulmonary alveolar proteinosis successfully treated with inhaled GM-CSF. Respir Med. 2004;98(12):1227–30.
Fang SC, Lu KH, Wang CY, Zhang HT, Zhang YM. Elevated tumor markers in patients with pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2013;51(7):1493–8.
Takahashi T, Munakata M, Suzuki I, Kawakami Y. Serum and bronchoalveolar fluid KL-6 levels in patients with pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1998;158(4):1294–8.
Kuroki Y, Tsutahara S, Shijubo N, Takahashi H, Shiratori M, Hattori A, et al. Elevated levels of lung surfactant protein a in sera from patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1993;147(3):723–9.
Seymour JF, Presneill JJ, Schoch OD, Downie GH, Moore PE, Doyle IR, et al. Therapeutic efficacy of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor in patients with idiopathic acquired alveolar proteinosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001;163(2):524–31.
Iyonaga K, Suga M, Yamamoto T, Ichiyasu H, Miyakawa H, Ando M. Elevated bronchoalveolar concentrations of MCP-1 in patients with pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. Eur Respir J. 1999;14(2):383–9.
Uchida K, Nakata K, Trapnell BC, Terakawa T, Hamano E, Mikami A, et al. High-affinity autoantibodies specifically eliminate granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor activity in the lungs of patients with idiopathic pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. Blood. 2004;103(3):1089–98.
Kitamura T, Uchida K, Tanaka N, Tsuchiya T, Watanabe J, Yamada Y, et al. Serological diagnosis of idiopathic pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000;162(2 Pt 1):658–62.
McCarthy C, Carey B, Trapnell BC. Blood testing for differential diagnosis of pulmonary alveolar proteinosis syndrome. Chest. 2019;155(2):450–2.
Carey B, Uchida K, Nakata K, Tazawa R, Inoue Y, Hirose M, et al. A multicenter, international evaluation of blood testing for the diagnosis of autoimmune pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2012:A1624.
Kusakabe Y, Uchida K, Hiruma T, Suzuki Y, Totsu T, Suzuki T, et al. A standardized blood test for the routine clinical diagnosis of impaired GM-CSF signaling using flow cytometry. J Immunol Methods. 2014;413:1–11.
Carey B, Heald C, Chalk C, Suzuki T, Uchida K, Trapnell BC. Use of serum GM-CSF for diagnosis of patients with hereditary pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2013;187:A850.
Ito M, Nakagome K, Ohta H, Akasaka K, Uchida Y, Hashimoto A, et al. Elderly-onset hereditary pulmonary alveolar proteinosis and its cytokine profile. BMC Pulm Med. 2017;17(1):40.
Suzuki T, Maranda B, Sakagami T, Catellier P, Couture CY, Carey BC, et al. Hereditary pulmonary alveolar proteinosis caused by recessive CSF2RB mutations. Eur Respir J. 2011;37(1):201–4.
Suzuki T, Sakagami T, Young LR, Carey BC, Wood RE, Luisetti M, et al. Hereditary pulmonary alveolar proteinosis: pathogenesis, presentation, diagnosis, and therapy. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2010;182(10):1292–304.
Martinez-Moczygemba M, Doan ML, Elidemir O, Fan LL, Cheung SW, Lei JT, et al. Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis caused by deletion of the GM-CSFRalpha gene in the X chromosome pseudoautosomal region 1. J Exp Med. 2008;205(12):2711–6.
Tredano M, van Elburg RM, Kaspers AG, Zimmermann LJ, Houdayer C, Aymard P, et al. Compound SFTPB 1549C-->GAA (121ins2) and 457delC heterozygosity in severe congenital lung disease and surfactant protein B (SP-B) deficiency. Hum Mutat. 1999;14(6):502–9.
Nogee LM, Garnier G, Dietz HC, Singer L, Murphy AM, deMello DE, et al. A mutation in the surfactant protein B gene responsible for fatal neonatal respiratory disease in multiple kindreds. J Clin Invest. 1994;93(4):1860–3.
Griese M, Schumacher S, Tredano M, Steinecker M, Braun A, Guttentag S, et al. Expression profiles of hydrophobic surfactant proteins in children with diffuse chronic lung disease. Respir Res. 2005;6:80.
Tredano M, Griese M, Brasch F, Schumacher S, de Blic J, Marque S, et al. Mutation of SFTPC in infantile pulmonary alveolar proteinosis with or without fibrosing lung disease. Am J Med Genet A. 2004;126A(1):18–26.
Stevens PA, Pettenazzo A, Brasch F, Mulugeta S, Baritussio A, Ochs M, et al. Nonspecific interstitial pneumonia, alveolar proteinosis, and abnormal proprotein trafficking resulting from a spontaneous mutation in the surfactant protein C gene. Pediatr Res. 2005;57(1):89–98.
Saugstad OD, Hansen TW, Ronnestad A, Nakstad B, Tollofsrud PA, Reinholt F, et al. Novel mutations in the gene encoding ATP binding cassette protein member A3 (ABCA3) resulting in fatal neonatal lung disease. Acta Paediatr. 2007;96(2):185–90.
Leonidas DD, Maiti TK, Samanta A, Dasgupta S, Pathak T, Zographos SE, et al. The binding of 3'-N-piperidine-4-carboxyl-3′-deoxy-ara-uridine to ribonuclease a in the crystal. Bioorg Med Chem. 2006;14(17):6055–64.
Hamvas A, Deterding RR, Wert SE, White FV, Dishop MK, Alfano DN, et al. Heterogeneous pulmonary phenotypes associated with mutations in the thyroid transcription factor gene NKX2-1. Chest. 2013;144(3):794–804.
Sebastio G, Nunes V. Lysinuric protein intolerance. In: Adam MP, Ardinger HH, Pagon RA, Wallace SE, LJH B, Stephens K, et al., editors. Gene reviews (R). Seattle, WA: University of Washington; 1993.
Ceruti M, Rodi G, Stella GM, Adami A, Bolongaro A, Baritussio A, et al. Successful whole lung lavage in pulmonary alveolar proteinosis secondary to lysinuric protein intolerance: a case report. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2007;2:14.
Enaud L, Hadchouel A, Coulomb A, Berteloot L, Lacaille F, Boccon-Gibod L, et al. Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis in children on La Reunion Island: a new inherited disorder? Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2014;9:85.
Hadchouel A, Wieland T, Griese M, Baruffini E, Lorenz-Depiereux B, Enaud L, et al. Biallelic mutations of Methionyl-tRNA Synthetase cause a specific type of pulmonary alveolar proteinosis prevalent on Reunion Island. Am J Hum Genet. 2015;96(5):826–31.
McCarthy C, Carey B, Trapnell BC. Blood testing in the diagnosis of pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. Lancet Respir Med. 2018;6(11):e54.
Ishii H, Tazawa R, Kaneko C, Saraya T, Inoue Y, Hamano E, et al. Clinical features of secondary pulmonary alveolar proteinosis: pre-mortem cases in Japan. Eur Respir J. 2011;37(2):465–8.
Ramirez J, Schultz RB, Dutton RE. Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis: a new technique and rationale for treatment. Arch Intern Med. 1963;112:419–31.
Ben-Abraham R, Greenfeld A, Rozenman J, Ben-Dov I. Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis: step-by-step perioperative care of whole lung lavage procedure. Heart Lung. 2002;31(1):43–9.
Wasserman K, Blank N, Fletcher G. Lung lavage (alveolar washing) in alveolar proteinosis. Am J Med. 1968;44(4):611–7.
Beccaria M, Luisetti M, Rodi G, Corsico A, Zoia MC, Colato S, et al. Long-term durable benefit after whole lung lavage in pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. Eur Respir J. 2004;23(4):526–31.
Wood RE. Pediatric bronchoscopy. Chest Surg Clin N Am. 1996;6(2):237–51.
Awab A, Khan MS, Youness HA. Whole lung lavage-technical details, challenges and management of complications. J Thorac Dis. 2017;9(6):1697–706.
Campo I, Luisetti M, Griese M, Trapnell BC, Bonella F, Grutters J, et al. Whole lung lavage therapy for pulmonary alveolar proteinosis: a global survey of current practices and procedures. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2016;11(1):115.
Campo I, Luisetti M, Griese M, Trapnell BC, Bonella F, Grutters JC, et al. A global survey on whole lung lavage in pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. Chest. 2016;150(1):251–3.
Cohen ES, Elpern E, Silver MR. Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis causing severe hypoxemic respiratory failure treated with sequential whole-lung lavage utilizing venovenous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation: a case report and review. Chest. 2001;120(3):1024–6.
Jansen HM, Zuurmond WW, Roos CM, Schreuder JJ, Bakker DJ. Whole-lung lavage under hyperbaric oxygen conditions for alveolar proteinosis with respiratory failure. Chest. 1987;91(6):829–32.
Cheng SL, Chang HT, Lau HP, Lee LN, Yang PC. Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis: treatment by bronchofiberscopic lobar lavage. Chest. 2002;122(4):1480–5.
Selecky PA, Wasserman K, Benfield JR, Lippmann M. The clinical and physiological effect of whole-lung lavage in pulmonary alveolar proteinosis: a ten-year experience. Ann Thorac Surg. 1977;24(5):451–61.
Rogers RM, Levin DC, Gray BA, Moseley LW Jr. Physiologic effects of bronchopulmonary lavage in alveolar proteinosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1978;118(2):255–64.
Seymour JF, Dunn AR, Vincent JM, Presneill JJ, Pain MC. Efficacy of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor in acquired alveolar proteinosis. N Engl J Med. 1996;335(25):1924–5.
Venkateshiah SB, Yan TD, Bonfield TL, Thomassen MJ, Meziane M, Czich C, et al. An open-label trial of granulocyte macrophage colony stimulating factor therapy for moderate symptomatic pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. Chest. 2006;130(1):227–37.
Tazawa R, Hamano E, Arai T, Ohta H, Ishimoto O, Uchida K, et al. Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor and lung immunity in pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2005;171(10):1142–9.
Tazawa R, Nakata K, Inoue Y, Nukiwa T. Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor inhalation therapy for patients with idiopathic pulmonary alveolar proteinosis: a pilot study; and long-term treatment with aerosolized granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor: a case report. Respirology. 2006;11(Suppl):S61–4.
Moore BB, Coffey MJ, Christensen P, Sitterding S, Ngan R, Wilke CA, et al. GM-CSF regulates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis via a prostaglandin-dependent mechanism. J Immunol. 2000;165(7):4032–9.
Wylam ME, Ten R, Prakash UB, Nadrous HF, Clawson ML, Anderson PM. Aerosol granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor for pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. Eur Respir J. 2006;27(3):585–93.
Tazawa R, Trapnell BC, Inoue Y, Arai T, Takada T, Nasuhara Y, et al. Inhaled granulocyte/macrophage-colony stimulating factor as therapy for pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2010;181(12):1345–54.
Tazawa R, Inoue Y, Arai T, Takada T, Kasahara Y, Hojo M, et al. Duration of benefit in patients with autoimmune pulmonary alveolar proteinosis after inhaled granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor therapy. Chest. 2014;145(4):729–37.
Tian X, Yang Y, Chen L, Sui X, Xu W, Li X, et al. Inhaled granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor for mild-to-moderate autoimmune pulmonary alveolar proteinosis—a six month phase II randomized study with 24 months of follow-up. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2020;15(1):174.
Tazawa R, Ueda T, Abe M, Tatsumi K, Eda R, Kondoh S, et al. Inhaled GM-CSF for pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. N Engl J Med. 2019;381(10):923–32.
Trapnell BC, Inoue Y, Bonella F, Morgan C, Jouneau S, Bendstrup E, et al. Inhaled molgramostim therapy in autoimmune pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. N Engl J Med. 2020;383(17):1635–44.
Campo I, Mariani F, Paracchini E, Kadija Z, Zoretto M, Tinelli C, et al. Inhaled sargramostim and whole lung lavage (WLL) as therapy of autoimmune pulmonary alveolar proteinosis (aPAP). Eur Respir J. 2016;48:PA3870.
Ohkouchi S, Akasaka K, Ichiwata T, Hisata S, Iijima H, Takada T, et al. Sequential granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor inhalation after whole-lung lavage for pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. A report of five intractable cases. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2017;14(8):1298–304.
Yamamoto H, Yamaguchi E, Agata H, Kandatsu N, Komatsu T, Kawai S, et al. A combination therapy of whole lung lavage and GM-CSF inhalation in pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2008;43(8):828–30.
Dupin C, Hurtado M, Cazes A, Taille C, Debray MP, Guenée C, et al. Pioglitazone in pulmonary alveolar proteinosis: promising first clinical experience. Respir Med Res. 2020;78:100756.
Kavuru MS, Bonfield TL, Thomassen MJ. Plasmapheresis, GM-CSF, and alveolar proteinosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2003;167(7):1036; author reply -7.
Kavuru MS, Malur A, Marshall I, Barna BP, Meziane M, Huizar I, et al. An open-label trial of rituximab therapy in pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. Eur Respir J. 2011;38(6):1361–7.
Soyez B, Borie R, Menard C, Cadranel J, Chavez L, Cottin V, et al. Rituximab for auto-immune alveolar proteinosis, a real life cohort study. Respir Res. 2018;19(1):74.
Borie R, Debray MP, Laine C, Aubier M, Crestani B. Rituximab therapy in autoimmune pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. Eur Respir J. 2009;33(6):1503–6.
Akasaka K, Tanaka T, Kitamura N, Ohkouchi S, Tazawa R, Takada T, et al. Outcome of corticosteroid administration in autoimmune pulmonary alveolar proteinosis: a retrospective cohort study. BMC Pulm Med. 2015;15:88.
Parker LA, Novotny DB. Recurrent alveolar proteinosis following double lung transplantation. Chest. 1997;111(5):1457–8.
Sui X, Du Q, Xu KF, Tian X, Song L, Wang X, et al. Quantitative assessment of pulmonary alveolar proteinosis (PAP) with ultra-dose CT and correlation with pulmonary function tests (PFTs). PLoS One. 2017;12(3):e0172958.
Tokura S, Akira M, Okuma T, Tazawa R, Arai T, Sugimoto C, et al. A semiquantitative computed tomographic grading system for evaluating therapeutic response in pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2017;14(9):1403–11.
Jacob J, Bartholmai BJ, Rajagopalan S, van Moorsel CHM, van Es HW, van Beek FT, et al. Predicting outcomes in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis using automated computed tomographic analysis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2018;198(6):767–76.
Zavaletta VA, Bartholmai BJ, Robb RA. High resolution multidetector CT-aided tissue analysis and quantification of lung fibrosis. Acad Radiol. 2007;14(7):772–87.
Kelly A, McCarthy C. Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis syndrome. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2020;41(2):288–98.
McCarthy C, Bartholmai BJ, Woods JC, McCormack FX, Trapnell BC. Automated parenchymal pattern analysis of treatment responses in pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2019;199(9):1151–2.
Griese M, Bonella F, Costabel U, de Blic J, Tran NB, Liebisch G. Quantitative lipidomics in pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2019;200(7):881–7.
Trapnell BC, McCarthy C. The alveolar Lipidome in pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. A new target for therapeutic development? Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2019;200(7):800–2.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
O’Callaghan, M., McCarthy, C., Trapnell, B.C. (2023). Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis Syndrome. In: Cottin, V., Richeldi, L., Brown, K., McCormack, F.X. (eds) Orphan Lung Diseases. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-12950-6_22
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-12950-6_22
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-12949-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-12950-6
eBook Packages: MedicineMedicine (R0)