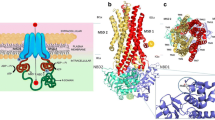
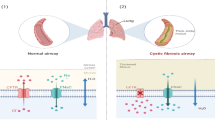
Abstract
Cystic fibrosis is a common genetically inherited, multisystem disorder caused by loss of function of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) protein, an apically situated anion channel. In the lung, lack of CFTR leads to airway surface dehydration, mucociliary clearance failure and an acidic pH in which innate defence molecules are rendered ineffective. Infection occurs early in life, with P. aeruginosa dominating by adolescence. The characteristic features of the CF airway highlighted above encourage persistence of infection, but P. aeruginosa also possess an array of mechanisms with which they attack host defences and render themselves protected from antimicrobials. Early eradication is usually successful, but this is usually transient. Chronic infection is manifest by biofilm formation which is resistant to treatment. Outcomes for people with CF have improved greatly in the last few decades, but particularly so with the recent advent of small molecule CFTR modulators. However, despite impressive efficacy on lung function and exacerbation frequency, most people with chronic infection remain with their pathogens. There is an active pipeline of new treatments including anti-biofilm and anti-quorum sensing molecules and non-drug approaches such as bacteriophage. Studies are reviewed and challenges for future drug development considered.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed B, Bush A, Davies JC (2014) How to use: bacterial cultures in diagnosing lower respiratory tract infections in cystic fibrosis. Arch Dis Child Educ Pract Ed 99:181–187
Alexis NE, Muhlebach MS, Peden DB, Noah TL (2006) Attenuation of host defense function of lung phagocytes in young cystic fibrosis patients. J Cyst Fibros 5:17–25
Armstrong DS, Grimwood K, Carlin JB, Carzino R, Olinsky A, Phelan PD (1996) Bronchoalveolar lavage or oropharyngeal cultures to identify lower respiratory pathogens in infants with cystic fibrosis. Pediatr Pulmonol 21:267–275
Barraud N, Hassett DJ, Hwang SH, Rice SA, Kjelleberg S, Webb JS (2006) Involvement of nitric oxide in biofilm dispersal of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol 188:7344–7353
Behrends V, Ryall B, Wang X, Bundy JG, Williams HD (2010) Metabolic profiling of Pseudomonas aeruginosa demonstrates that the anti-sigma factor MucA modulates osmotic stress tolerance. Mol BioSyst 6:562–569
Bernarde C, Keravec M, Mounier J, Gouriou S, Rault G, Ferec C, Barbier G, Hery-Arnaud G (2015) Impact of the CFTR-potentiator ivacaftor on airway microbiota in cystic fibrosis patients carrying a G551D mutation. PLoS One 10:e0124124
Bjarnsholt T, Jensen PO, Rasmussen TB, Christophersen L, Calum H, Hentzer M, Hougen HP, Rygaard J, Moser C, Eberl L, Hoiby N, Givskov M (2005) Garlic blocks quorum sensing and promotes rapid clearing of pulmonary Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections. Microbiology (Reading) 151:3873–3880
Boucher RC (2007) Evidence for airway surface dehydration as the initiating event in CF airway disease. J Intern Med 261:5–16
Boyle MP, de Boeck K (2013) A new era in the treatment of cystic fibrosis: correction of the underlying CFTR defect. Lancet Respir Med 1:158–163
Briard B, Rasoldier V, Bomme P, Elaouad N, Guerreiro C, Chassagne P, Muszkieta L, Latge JP, Mulard L, Beauvais A (2017) Dirhamnolipids secreted from Pseudomonas aeruginosa modify anjpegungal susceptibility of aspergillus fumigatus by inhibiting beta1,3 glucan synthase activity. ISME J 11:1578–1591
Briard B, Mislin GLA, Latge JP, Beauvais A (2019) Interactions between aspergillus fumigatus and pulmonary bacteria: current state of the field, new data, and future perspective. J Fungi (Basel) 5(2):48
Briottet M, Shum M, Urbach V (2020) The role of specialized pro-resolving mediators in cystic fibrosis airways Disease. Front Pharmacol 11:1290
Brugha R, Edmondson C, Davies JC (2018) Outdoor air pollution and cystic fibrosis. Paediatr Respir Rev 28:80–86
Brussow H (2012) What is needed for phage therapy to become a reality in Western medicine? Virology 434:138–142
Button B, Cai LH, Ehre C, Kesimer M, Hill DB, Sheehan JK, Boucher RC, Rubinstein M (2012) A periciliary brush promotes the lung health by separating the mucus layer from airway epithelia. Science 337:937–941
Camus L, Vandenesch F, Moreau K (2021) From genotype to phenotype: adaptations of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to the cystic fibrosis environment. Microb Genom 7(3):mgen000513
Caskey S, Stirling J, Moore JE, Rendall JC (2018) Occurrence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in waters: implications for patients with cystic fibrosis (CF). Lett Appl Microbiol 66:537–541
Chalmers JD, Fleming GB, Hill AT, Kilpatrick DC (2011) Impact of mannose-binding lectin insufficiency on the course of cystic fibrosis: a review and meta-analysis. Glycobiology 21:271–282
Chan BK, Stanley G, Modak M, Koff JL, Turner PE (2021) Bacteriophage therapy for infections in CF. Pediatr Pulmonol 56(Suppl 1):S4–S9
Chattoraj SS, Ganesan S, Faris A, Comstock A, Lee WM, Sajjan US (2011) Pseudomonas aeruginosa suppresses interferon response to rhinovirus infection in cystic fibrosis but not in normal bronchial epithelial cells. Infect Immun 79:4131–4145
Christiansen SH, Murphy RA, Juul-Madsen K, Fredborg M, Hvam ML, Axelgaard E, Skovdal SM, Meyer RL, Sorensen UBS, Moller A, Nyengaard JR, Norskov-Lauritsen N, Wang M, Gadjeva M, Howard KA, Davies JC, Petersen E, Vorup-Jensen T (2017) The immunomodulatory drug Glatiramer acetate is also an effective antimicrobial agent that kills gram-negative bacteria. Sci Rep 7:15653
Chung JC, Becq J, Fraser L, Schulz-Trieglaff O, Bond NJ, Foweraker J, Bruce KD, Smith GP, Welch M (2012) Genomic variation among contemporary Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates from chronically infected cystic fibrosis patients. J Bacteriol 194:4857–4866
Courtney JM, Bradley J, Mccaughan J, O’Connor TM, Shortt C, Bredin CP, Bradbury I, Elborn JS (2007) Predictors of mortality in adults with cystic fibrosis. Pediatr Pulmonol 42:525–532
Davies J (2020) The coronavirus pandemic has forced rapid changes in care protocols for cystic fibrosis. Nature 583:S15
Martin I, Kenna DTD, Morales S, Alton EWFW, Davies JC (2021) Variability in bacteriophage and antibiotic sensitivity in serial Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates from cystic fibrosis airway cultures over 12 months. Microorganisms 9(3):660. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9030660. PMID: 33810202; PMCID: PMC8004851
Davies J, Dewar A, Bush A, Pitt T, Gruenert D, Geddes DM, Alton EW (1999) Reduction in the adherence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to native cystic fibrosis epithelium with anti-asialoGM1 antibody and neuraminidase inhibition. Eur Respir J 13:565–570
Davies JC, Alton E, Simbo A, Murphy R, Seth I, Williams K, Somerville M, Jolly L, Morant S, Guest C (2019) Training dogs to differentiate Pseudomonas aeruginosa from other cystic fibrosis bacterial pathogens: not to be sniffed at? Eur Respir J 54(5):1900970
Davis TJ, Karanjia AV, Bhebhe CN, West SB, Richardson M, Bean HD (2020) Pseudomonas aeruginosa volatilome characteristics and adaptations in chronic cystic fibrosis lung infections. mSphere 5(5):e00843-20
de Boeck K, Lee T, Amaral M, Drevinek P, Elborn JS, Fajac I, Kerem E, Davies JC (2020) Cystic fibrosis drug trial design in the era of CFTR modulators associated with substantial clinical benefit: stakeholders’ consensus view. J Cyst Fibros 19:688–695
de Koff EM, Groot KM, Bogaert D (2016) Development of the respiratory tract microbiota in cystic fibrosis. Curr Opin Pulm Med 22:623–628
de Vrankrijker AM, Wolfs TF, Ciofu O, Hoiby N, van der Ent CK, Poulsen SS, Johansen HK (2009) Respiratory syncytial virus infection facilitates acute colonization of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in mice. J Med Virol 81:2096–2103
Deretic V, Dikshit R, Konyecsni WM, Chakrabarty AM, Misra TK (1989) The algR gene, which regulates mucoidy in Pseudomonas aeruginosa, belongs to a class of environmentally responsive genes. J Bacteriol 171:1278–1283
Deschaght P, Schelstraete P, van Simaey L, Vanderkercken M, Raman A, Mahieu L, van Daele S, de Baets F, Vaneechoutte M (2013) Is the improvement of CF patients, hospitalized for pulmonary exacerbation, correlated to a decrease in bacterial load? PLoS One 8:e79010
Devereux G, Wrolstad D, Bourke SJ, Daines CL, Doe S, Dougherty R, Franco R, Innes A, Kopp BT, Lascano J, Layish D, Macgregor G, Murray L, Peckham D, Lucidi V, Lovie E, Robertson J, Fraser-Pitt DJ, O’Neil DA (2020) Oral cysteamine as an adjunct treatment in cystic fibrosis pulmonary exacerbations: an exploratory randomized clinical trial. PLoS One 15:e0242945
Dickerhof N, Isles V, Pattemore P, Hampton MB, Kettle AJ (2019) Exposure of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to bactericidal hypochlorous acid during neutrophil phagocytosis is compromised in cystic fibrosis. J Biol Chem 294:13502–13514
Ding F, Oinuma KI, Smalley NE, Schaefer AL, Hamwy O, Greenberg EP, Dandekar AA (2018) The Pseudomonas aeruginosa orphan quorum sensing signal receptor QscR regulates global quorum sensing gene expression by activating a single linked operon. mBio 9(4):e01274-18
Dingemans J, Monsieurs P, Yu SH, Crabbe A, Forstner KU, Malfroot A, Cornelis P, van Houdt R (2016) Effect of shear stress on Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from the cystic fibrosis Lung. mBio 7(4):e00813-16
Dixon E, Dick K, Ollosson S, Jones D, Mattock H, Bentley S, Saunders C, Matthews J, Dobra B, King J, Edmondson C, Davies JC (2021) Telemedicine and cystic fibrosis: do we still need face-to-face clinics? Paediatr Respir Rev. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prrv.2021.05.002
Dorfman R, Taylor C, Lin F, Sun L, Sandford A, Pare P, Berthiaume Y, Corey M, Durie P, Zielenski J, Members of Canadian Consortium for CF Genetic Studies (2011) Modulatory effect of the SLC9A3 gene on susceptibility to infections and pulmonary function in children with cystic fibrosis. Pediatr Pulmonol 46:385–392
Douglas TA, Brennan S, Berry L, Winfield K, Wainwright CE, Grimwood K, Stick SM, Sly PD, Members of AREST CF and ACFBAL Trial (2010) Value of serology in predicting Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection in young children with cystic fibrosis. Thorax 65:985–990
Duesberg U, Wosniok J, Naehrlich L, Eschenhagen P, Schwarz C (2020) Risk factors for respiratory aspergillus fumigatus in German cystic fibrosis patients and impact on lung function. Sci Rep 10:18999
Emerson J, Rosenfeld M, Mcnamara S, Ramsey B, Gibson RL (2002) Pseudomonas aeruginosa and other predictors of mortality and morbidity in young children with cystic fibrosis. Pediatr Pulmonol 34:91–100
Emond MJ, Louie T, Emerson J, Zhao W, Mathias RA, Knowles MR, Wright FA, Rieder MJ, Tabor HK, Nickerson DA, Barnes KC, National Heart L, Blood Institute (NHLBI) GO Exome Sequencing Project, Lung GO, Gibson RL, Bamshad MJ (2012) Exome sequencing of extreme phenotypes identifies DCTN4 as a modifier of chronic Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection in cystic fibrosis. Nat Genet 44:886–889
Emond MJ, Louie T, Emerson J, Chong JX, Mathias RA, Knowles MR, Rieder MJ, Tabor HK, Nickerson DA, Barnes KC, NHLBI GO Exome Sequencing Project, Go L, Gibson RL, Bamshad MJ (2015) Exome sequencing of phenotypic extremes identifies CAV2 and TMC6 as interacting modifiers of chronic Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection in cystic fibrosis. PLoS Genet 11:e1005273
Epps QJ, Epps KL, Young DC, Zobell JT (2021) State of the art in cystic fibrosis pharmacology optimization of antimicrobials in the treatment of cystic fibrosis pulmonary exacerbations: III. Executive summary. Pediatr Pulmonol 56:1825–1837
Equi AC, Pike SE, Davies J, Bush A (2001) Use of cough swabs in a cystic fibrosis clinic. Arch Dis Child 85:438–439
Feldman M, Bryan R, Rajan S, Scheffler L, Brunnert S, Tang H, Prince A (1998) Role of flagella in pathogenesis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa pulmonary infection. Infect Immun 66:43–51
Ferrari E, Monzani R, Villella VR, Esposito S, Saluzzo F, Rossin F, D’Eletto M, Tosco A, de Gregorio F, Izzo V, Maiuri MC, Kroemer G, Raia V, Maiuri L (2017) Cysteamine re-establishes the clearance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by macrophages bearing the cystic fibrosis-relevant F508del-CFTR mutation. Cell Death Dis 8:e2544
Foundation CF (n.d.) Cystic fibrosis foundation: drug development pipeline [Online]. Available: https://apps.cff.org/trials/pipeline/ [Accessed]
Foweraker JE, Govan JR (2013) Antibiotic susceptibility testing in early and chronic respiratory infections with Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Cyst Fibros 12:302
Fraser-Pitt DJ, Dolan SK, Toledo-Aparicio D, Hunt JG, Smith DW, Lacy-Roberts N, Nupe Hewage PS, Stoyanova TN, Manson E, Mcclean K, Inglis NF, Mercer DK, O’Neil DA (2021) Cysteamine inhibits glycine utilisation and disrupts virulence in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 11:718213
Frayman KB, Armstrong DS, Grimwood K, Ranganathan SC (2017) The airway microbiota in early cystic fibrosis lung disease. Pediatr Pulmonol 52:1384–1404
Garratt LW, Sutanto EN, Ling KM, Looi K, Iosifidis T, Martinovich KM, Shaw NC, Kicic-Starcevich E, Knight DA, Ranganathan S, Stick SM, Kicic A, Australian Respiratory Early Surveillance Team for Cystic Fibrosis (AREST CF) (2015) Matrix metalloproteinase activation by free neutrophil elastase contributes to bronchiectasis progression in early cystic fibrosis. Eur Respir J 46:384–394
Goeminne PC, Nawrot TS, de Boeck K, Nemery B, Dupont LJ (2015) Proximity to blue spaces and risk of infection with Pseudomonas aeruginosa in cystic fibrosis: a case-control analysis. J Cyst Fibros 14:741–747
Goss CH, Kaneko Y, Khuu L, Anderson GD, Ravishankar S, Aitken ML, Lechtzin N, Zhou G, Czyz DM, Mclean K, Olakanmi O, Shuman HA, Teresi M, Wilhelm E, Caldwell E, Salipante SJ, Hornick DB, Siehnel RJ, Becker L, Britigan BE, Singh PK (2018) Gallium disrupts bacterial iron metabolism and has therapeutic effects in mice and humans with lung infections. Sci Transl Med 10:eaat7520
Goss CH, Heltshe SL, West NE, Skalland M, Sanders DB, Jain R, Barto TL, Fogarty B, Marshall BC, Vandevanter DR, Flume PA, Investigators S (2021) A randomized clinical trial of antimicrobial duration for cystic fibrosis pulmonary exacerbation treatment. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 204:1295–1305
Grasemann H, Storm van’s Gravesande K, Buscher R, Knauer N, Silverman ES, Palmer LJ, Drazen JM, Ratjen F (2003) Endothelial nitric oxide synthase variants in cystic fibrosis lung disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 167:390–394
Green DM, Mcdougal KE, Blackman SM, Sosnay PR, Henderson LB, Naughton KM, Collaco JM, Cutting GR (2010) Mutations that permit residual CFTR function delay acquisition of multiple respiratory pathogens in CF patients. Respir Res 11:140
Green DM, Collaco JM, Mcdougal KE, Naughton KM, Blackman SM, Cutting GR (2012) Heritability of respiratory infection with Pseudomonas aeruginosa in cystic fibrosis. J Pediatr 161(290–5):e1
Guimbellot JS, Baines A, Paynter A, Heltshe SL, Vandalfsen J, Jain M, Rowe SM, Sagel SD, Investigators GO-E (2021) Long term clinical effectiveness of ivacaftor in people with the G551D CFTR mutation. J Cyst Fibros 20:213–219
Harrington NE, Littler JL, Harrison F (2022) Transcriptome analysis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm infection in an ex vivo pig model of the cystic fibrosis Lung. Appl Environ Microbiol 88:e0178921
Hassett DJ, Kovall RA, Schurr MJ, Kotagiri N, Kumari H, Satish L (2021) The bactericidal tandem drug, AB569: how to eradicate antibiotic-resistant biofilm Pseudomonas aeruginosa in multiple Disease settings including cystic fibrosis, Burns/wounds and urinary tract infections. Front Microbiol 12:639362
Hauser AR (2009) The type III secretion system of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: infection by injection. Nat Rev Microbiol 7:654–665
Hayes DJR, Farrell PM, Li Z, West SE (2010) Pseudomonas aeruginosa serological analysis in young children with cystic fibrosis diagnosed through newborn screening. Pediatr Pulmonol 45:55–61
Hayes E, Murphy MP, Pohl K, Browne N, Mcquillan K, Saw LE, Foley C, Gargoum F, Mcelvaney OJ, Hawkins P, Gunaratnam C, Mcelvaney NG, Reeves EP (2020) Altered degranulation and pH of neutrophil phagosomes impacts antimicrobial efficiency in cystic fibrosis. Front Immunol 11:600033
Heijerman HGM, Mckone EF, Downey DG, van Braeckel E, Rowe SM, Tullis E, Mall MA, Welter JJ, Ramsey BW, Mckee CM, Marigowda G, Moskowitz SM, Waltz D, Sosnay PR, Simard C, Ahluwalia N, Xuan F, Zhang Y, Taylor-Cousar JL, Mccoy KS, VX17-445-103 Trial Group (2019) Efficacy and safety of the elexacaftor plus tezacaftor plus ivacaftor combination regimen in people with cystic fibrosis homozygous for the F508del mutation: a double-blind, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet 394:1940–1948
Hendricks MR, Lashua LP, Fischer DK, Flitter BA, Eichinger KM, Durbin JE, Sarkar SN, Coyne CB, Empey KM, Bomberger JM (2016) Respiratory syncytial virus infection enhances Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm growth through dysregulation of nutritional immunity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 113:1642–1647
Hewer SCL, Smyth AR, Brown M, Jones AP, Hickey H, Kenna D, Ashby D, Thompson A, Williamson PR, TORPEDO-CF Study Group (2020) Intravenous versus oral antibiotics for eradication of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in cystic fibrosis (TORPEDO-CF): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet Respir Med 8:975–986
Hey J, Paulsen M, Toth R, Weichenhan D, Butz S, Schatterny J, Liebers R, Lutsik P, Plass C, Mall MA (2021) Epigenetic reprogramming of airway macrophages promotes polarization and inflammation in muco-obstructive lung disease. Nat Commun 12:6520
Hill D, Rose B, Pajkos A, Robinson M, Bye P, Bell S, Elkins M, Thompson B, Macleod C, Aaron SD, Harbour C (2005) Antibiotic susceptabilities of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates derived from patients with cystic fibrosis under aerobic, anaerobic, and biofilm conditions. J Clin Microbiol 43:5085–5090
Hill DB, Button B, Rubinstein M, Boucher RC (2022) Physiology and pathophysiology of human airway mucus. Physiol Rev. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00004.2021
Hisert KB, Heltshe SL, Pope C, Jorth P, Wu X, Edwards RM, Radey M, Accurso FJ, Wolter DJ, Cooke G, Adam RJ, Carter S, Grogan B, Launspach JL, Donnelly SC, Gallagher CG, Bruce JE, Stoltz DA, Welsh MJ, Hoffman LR, Mckone EF, Singh PK (2017) Restoring cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator function reduces airway bacteria and inflammation in people with cystic fibrosis and chronic Lung infections. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 195:1617–1628
Hogardt M, Heesemann J (2010) Adaptation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa during persistence in the cystic fibrosis lung. Int J Med Microbiol 300:557–562
Hogardt M, Hoboth C, Schmoldt S, Henke C, Bader L, Heesemann J (2007) Stage-specific adaptation of hypermutable Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates during chronic pulmonary infection in patients with cystic fibrosis. J Infect Dis 195:70–80
Høiby N, Ciofu O, Bjarnsholt T (2010) Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms in cystic fibrosis. Future Microbiol 5:1663–1674
Howlin RP, Cathie K, Hall-Stoodley L, Cornelius V, Duignan C, Allan RN, Fernandez BO, Barraud N, Bruce KD, Jefferies J, Kelso M, Kjelleberg S, Rice SA, Rogers GB, Pink S, Smith C, Sukhtankar PS, Salib R, Legg J, Carroll M, Daniels T, Feelisch M, Stoodley P, Clarke SC, Connett G, Faust SN, Webb JS (2017) Low-dose nitric oxide as targeted anti-biofilm adjunctive therapy to treat chronic Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection in cystic fibrosis. Mol Ther 25:2104–2116
Hughes, D. A., Archangelidi, O., Coates, M., Armstrong-James, D., Elborn, S. J., Carr, S. B. & Davies, J. C. 2021a. Clinical characteristics of pseudomonas and aspergillus co-infected cystic fibrosis patients: a UK registry study. J Cyst Fibros, (In press)
Hughes DA, Price H, Rosenthal M, Davies JC (2021b) Pseudomonas aeruginosa in the cystic fibrosis airway: does it deserve its reputation as a predatory “bully”? Am J Respir Crit Care Med 203:1027–1030
Hughes DA, Cuthbertson L, Price H, Felton I, Coates M, Simmonds NJ, Loebinger MR, Armstrong-James D, Elborn JS, Cookson WO, Moffatt MF, Davies JC (2021c) P130 Pseudomonas aeruginosa impairs growth of aspergillus from CF airway samples British Thoracic Society winter meeting. Thorax, London
Johansen HK, Hoiby N (1992) Seasonal onset of initial colonisation and chronic infection with Pseudomonas aeruginosa in patients with cystic fibrosis in Denmark. Thorax 47:109–111
Kaneko Y, Thoendel M, Olakanmi O, Britigan BE, Singh PK (2007) The transition metal gallium disrupts Pseudomonas aeruginosa iron metabolism and has antimicrobial and antibiofilm activity. J Clin Invest 117:877–888
Khan S, Tondervik A, Sletta H, Klinkenberg G, Emanuel C, Onsoyen E, Myrvold R, Howe RA, Walsh TR, Hill KE, Thomas DW (2012) Overcoming drug resistance with alginate oligosaccharides able to potentiate the action of selected antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 56:5134–5141
Kiedrowski MR, Bomberger JM (2018) Viral-bacterial co-infections in the cystic fibrosis respiratory tract. Front Immunol 9:3067
Kopp BT, Ortega-Garcia JA, Sadreameli SC, Wellmerling J, Cormet-Boyaka E, Thompson R, Mcgrath-Morrow S, Groner JA (2016) The impact of secondhand smoke exposure on children with cystic fibrosis: a review. Int J Environ Res Public Health 13(10):1003
Kos R, Brinkman P, Neerincx AH, Paff T, Gerritsen MG, Lammers A, Kraneveld AD, Heijerman HGM, Janssens HM, Davies JC, Majoor CJ, Weersink EJ, Sterk PJ, Haarman EG, Bos LD, Maitland-van der Zee AH, Amsterdam Mucociliary Clearance Disease (AMCD) Research Group and the Amsterdam UMC Breath Research Group (2021) Targeted exhaled breath analysis for detection of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in cystic fibrosis patients. J Cyst Fibros 21(1):e28–e34
Kosorok MR, Zeng L, West SE, Rock MJ, Splaingard ML, Laxova A, Green CG, Collins J, Farrell PM (2001) Acceleration of lung disease in children with cystic fibrosis after Pseudomonas aeruginosa acquisition. Pediatr Pulmonol 32:277–287
Kutty SK, Barraud N, Ho KK, Iskander GM, Griffith R, Rice SA, Bhadbhade M, Willcox MD, Black DS, Kumar N (2015) Hybrids of acylated homoserine lactone and nitric oxide donors as inhibitors of quorum sensing and virulence factors in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Org Biomol Chem 13:9850–9861
Kyle H, Ward JP, Widdicombe JG (1990) Control of pH of airway surface liquid of the ferret trachea in vitro. J Appl Physiol 1985(68):135–140
Lam JC, Somayaji R, Surette MG, Rabin HR, Parkins MD (2015) Reduction in Pseudomonas aeruginosa sputum density during a cystic fibrosis pulmonary exacerbation does not predict clinical response. BMC Infect Dis 15:145
Langton Hewer SC, Smyth AR (2017) Antibiotic strategies for eradicating Pseudomonas aeruginosa in people with cystic fibrosis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 4:CD004197
Larsen GY, Stull TL, Burns JL (1993) Marked phenotypic variability in pseudomonas cepacia isolated from a patient with cystic fibrosis. J Clin Microbiol 31:788–792
Law N, Logan C, Yung G, Furr CL, Lehman SM, Morales S, Rosas F, Gaidamaka A, Bilinsky I, Grint P, Schooley RT, Aslam S (2019) Successful adjunctive use of bacteriophage therapy for treatment of multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection in a cystic fibrosis patient. Infection 47:665–668
Lee AJ, Einarsson GG, Gilpin DF, Tunney MM (2020) Multi-omics approaches: the key to improving respiratory health in people with cystic fibrosis? Front Pharmacol 11:569821
Ling KM, Garratt LW, Gill EE, Lee AHY, Agudelo-Romero P, Sutanto EN, Iosifidis T, Rosenow T, Turvey SE, Lassmann T, Hancock REW, Kicic A, Stick SM (2020) Rhinovirus infection drives complex host airway molecular responses in children with cystic fibrosis. Front Immunol 11:1327
Magalhaes AP, Lopes SP, Pereira MO (2016) Insights into cystic fibrosis Polymicrobial consortia: the role of species interactions in biofilm development, phenotype, and response to in-use antibiotics. Front Microbiol 7:2146
Mahenthiralingam E, Campbell ME, Speert DP (1994) Nonmotility and phagocytic resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates from chronically colonized patients with cystic fibrosis. Infect Immun 62:596–605
Manfredi P, Jenal U (2015) Bacteria in the CF Lung: isolation drives diversity. Cell Host Microbe 18:268–269
Manwar AV, Khandelwal SR, Chaudhari BL, Meyer JM, Chincholkar SB (2004) Siderophore production by a marine Pseudomonas aeruginosa and its antagonistic action against phytopathogenic fungi. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 118:243–251
Martin AC, Laing IA, Zhang G, Brennan S, Winfield K, Sly PD, Stick SM, Goldblatt J, Lesouef PN (2005) CD14 C-159T and early infection with Pseudomonas aeruginosa in children with cystic fibrosis. Respir Res 6:63
Martin I, Davies JC, Morales S et al (2017) WS07.4 combined killing effects of lytic bacteriophages and antibiotics in biofilm-grown Pseudomonas aeruginosa from CF airway cultures. J Cystic Fibrosis 16(1):S12–S13
Mcelvaney OJ, Wade P, Murphy M, Reeves EP, Mcelvaney NG (2019) Targeting airway inflammation in cystic fibrosis. Expert Rev Respir Med 13:1041–1055
Middleton PG, Mall MA, Drevinek P, Lands LC, Mckone EF, Polineni D, Ramsey BW, Taylor-Cousar JL, Tullis E, Vermeulen F, Marigowda G, Mckee CM, Moskowitz SM, Nair N, Savage J, Simard C, Tian S, Waltz D, Xuan F, Rowe SM, Jain R, VX17-445-102 Study Group (2019) Elexacaftor-Tezacaftor-Ivacaftor for cystic fibrosis with a single Phe508del allele. N Engl J Med 381:1809–1819
Moore MP, Lamont IL, Williams D, Paterson S, Kukavica-Ibrulj I, Tucker NP, Kenna DTD, Turton JF, Jeukens J, Freschi L, Wee BA, Loman NJ, Holden S, Manzoor S, Hawkey P, Southern KW, Walshaw MJ, Levesque RC, Fothergill JL, Winstanley C (2021) Transmission, adaptation and geographical spread of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa Liverpool epidemic strain. Microb Genom 7(3):000511. https://doi.org/10.1099/mgen.0.000511
Moradali MF, Ghods S, Rehm BH (2017) Pseudomonas aeruginosa lifestyle: a paradigm for adaptation, survival, and persistence. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 7:39
Moreau-Marquis S, Coutermarsh B, Stanton BA (2015) Combination of hypothiocyanite and lactoferrin (ALX-109) enhances the ability of tobramycin and aztreonam to eliminate Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms growing on cystic fibrosis airway epithelial cells. J Antimicrob Chemother 70:160–166
Moskowitz SM, Foster JM, Emerson JC, Gibson RL, Burns JL (2005) Use of pseudomonas biofilm susceptibilities to assign simulated antibiotic regimens for cystic fibrosis airway infection. J Antimicrob Chemother 56:879–886
Mowat E, Rajendran R, Williams C, Mcculloch E, Jones B, Lang S, Ramage G (2010) Pseudomonas aeruginosa and their small diffusible extracellular molecules inhibit aspergillus fumigatus biofilm formation. FEMS Microbiol Lett 313:96–102
Muhlebach MS, Stewart PW, Leigh MW, Noah TL (1999) Quantitation of inflammatory responses to bacteria in young cystic fibrosis and control patients. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 160:186–191
Muirhead CA, Lanocha N, Markwardt S, Macdonald KD (2021) Evaluation of rescue oral glucocorticoid therapy during inpatient cystic fibrosis exacerbations. Pediatr Pulmonol 56:891–900
Murphy RA, Thrane S, Harrison J, Schelenz S, Vorup-Jensen T, Davies JC (2020) Synergy with Glatirmaer acetate reduces Tobramycin minimum inhibitory concentrations against Pseudomonas aeruginosa from cystic fibrosis airways. The 34th North American Cystic Fibrosis Conference. Pediatric Pulmonology
Nardoni S, Mancianti F, Sgorbini M, Taccini F, Corazza M (2005) Identification and seasonal distribution of airborne fungi in three horse stables in Italy. Mycopathologia 160:29–34
Neerincx AH, Whiteson K, Phan JL, Brinkman P, Abdel-Aziz MI, Weersink EJM, Altenburg J, Majoor CJ, Maitland-van der Zee AH, Bos LDJ (2021) Lumacaftor/ivacaftor changes the lung microbiome and metabolome in cystic fibrosis patients. ERJ Open Res 7(2):00731–02020
Nixon GM, Armstrong DS, Carzino R, Carlin JB, Olinsky A, Robertson CF, Grimwood K (2001) Clinical outcome after early Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection in cystic fibrosis. J Pediatr 138:699–704
O’Toole GA, Crabbe A, Kummerli R, Lipuma JJ, Bomberger JM, Davies JC, Limoli D, Phelan VV, Bliska JB, Depas WH, Dietrich LE, Hampton TH, Hunter R, Khursigara CM, Price-Whelan A, Ashare A, Cramer RA, Goldberg JB, Harrison F, Hogan DA, Henson MA, Madden DR, Mayers JR, Nadell C, Newman D, Prince A, Rivett DW, Schwartzman JD, Schultz D, Sheppard DC, Smyth AR, Spero MA, Stanton BA, Turner PE, van der Gast C, Whelan FJ, Whitaker R, Whiteson K (2021) Model systems to study the chronic, Polymicrobial infections in cystic fibrosis: current approaches and exploring future directions. mBio 12:e0176321
Pabary R, Singh C, Morales S, Bush A, Alshafi K, Bilton D, Alton EW, Smithyman A, Davies JC (2016) Antipseudomonal bacteriophage reduces infective burden and inflammatory response in murine Lung. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 60:744–751
Penner JC, Ferreira JAG, Secor PR, Sweere JM, Birukova MK, Joubert LM, Haagensen JAJ, Garcia O, Malkovskiy AV, Kaber G, Nazik H, Manasherob R, Spormann AM, Clemons KV, Stevens DA, Bollyky PL (2016) Pf4 bacteriophage produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa inhibits aspergillus fumigatus metabolism via iron sequestration. Microbiology (Reading) 162:1583–1594
Pernet E, Guillemot L, Burgel PR, Martin C, Lambeau G, Sermet-Gaudelus I, Sands D, Leduc D, Morand PC, Jeammet L, Chignard M, wu, Y. & Touqui, L. (2014) Pseudomonas aeruginosa eradicates Staphylococcus aureus by manipulating the host immunity. Nat Commun 5:5105
Persson T, Hansen TH, Rasmussen TB, Skinderso ME, Givskov M, Nielsen J (2005) Rational design and synthesis of new quorum-sensing inhibitors derived from acylated homoserine lactones and natural products from garlic. Org Biomol Chem 3:253–262
Pezzulo AA, Tang XX, Hoegger MJ, Abou Alaiwa MH, Ramachandran S, Moninger TO, Karp PH, Wohlford-Lenane CL, Haagsman HP, van Eijk M, Banfi B, Horswill AR, Stoltz DA, Mccray PBJR, Welsh MJ, Zabner J (2012) Reduced airway surface pH impairs bacterial killing in the porcine cystic fibrosis lung. Nature 487:109–113
Principi N, Blasi F, Esposito S (2015) Azithromycin use in patients with cystic fibrosis. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 34:1071–1079
Pritchard MF, Powell LC, Menzies GE, Lewis PD, Hawkins K, Wright C, Doull I, Walsh TR, Onsoyen E, Dessen A, Myrvold R, Rye PD, Myrset AH, Stevens HN, Hodges LA, Macgregor G, Neilly JB, Hill KE, Thomas DW (2016) A new class of safe oligosaccharide polymer therapy to modify the mucus barrier of chronic respiratory Disease. Mol Pharm 13:863–872
Pritt B, O’Brien L, Winn W (2007) Mucoid pseudomonas in cystic fibrosis. Am J Clin Pathol 128:32–34
Psoter KJ, de Roos AJ, Mayer JD, Kaufman JD, Wakefield J, Rosenfeld M (2015) Fine particulate matter exposure and initial Pseudomonas aeruginosa acquisition in cystic fibrosis. Ann Am Thorac Soc 12:385–391
Psoter KJ, de Roos AJ, Wakefield J, Mayer JD, Bryan M, Rosenfeld M (2016) Association of meteorological and geographical factors and risk of initial Pseudomonas aeruginosa acquisition in young children with cystic fibrosis. Epidemiol Infect 144:1075–1083
Quinton PM (2008) Cystic fibrosis: impaired bicarbonate secretion and mucoviscidosis. Lancet 372:415–417
Quinton PM (2010) Role of epithelial HCO3(−) transport in mucin secretion: lessons from cystic fibrosis. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 299:C1222–C1233
Ralhan A, Laval J, Lelis F, Ballbach M, Grund C, Hector A, Hartl D (2016) Current concepts and controversies in innate immunity of cystic fibrosis Lung Disease. J Innate Immun 8:531–540
Ramsey BW, Wentz KR, Smith AL, Richardson M, Williams-Warren J, Hedges DL, Gibson R, Redding GJ, Lent K, Harris K (1991) Predictive value of oropharyngeal cultures for identifying lower airway bacteria in cystic fibrosis patients. Am Rev Respir Dis 144:331–337
Ramsey BW, Davies J, Mcelvaney NG, Tullis E, Bell SC, Drevinek P, Griese M, Mckone EF, Wainwright CE, Konstan MW, Moss R, Ratjen F, Sermet-Gaudelus I, Rowe SM, Dong Q, Rodriguez S, Yen K, Ordonez C, Elborn JS, VX08-770-102 Study Group (2011) A CFTR potentiator in patients with cystic fibrosis and the G551D mutation. N Engl J Med 365:1663–1672
Ratjen F, Walter H, Haug M, Meisner C, Grasemann H, Doring G (2007) Diagnostic value of serum antibodies in early Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection in cystic fibrosis patients. Pediatr Pulmonol 42:249–255
Reece E, Segurado R, Jackson A, Mcclean S, Renwick J, Greally P (2017) Co-colonisation with aspergillus fumigatus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa is associated with poorer health in cystic fibrosis patients: an Irish registry analysis. BMC Pulm Med 17:70
Reece E, Bettio PHA, Renwick J (2021) Polymicrobial interactions in the cystic fibrosis airway microbiome impact the antimicrobial susceptibility of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antibiotics (Basel) 10(7):827
Registry CFT (2020) CF Trust Registry Annual Report Data 2020
Reid DW, Latham R, Lamont IL, Camara M, Roddam LF (2013) Molecular analysis of changes in Pseudomonas aeruginosa load during treatment of a pulmonary exacerbation in cystic fibrosis. J Cyst Fibros 12:688–699
Riquelme SA, Prince A (2021) Pseudomonas aeruginosa consumption of airway metabolites promotes Lung infection. Pathogens 10(8):957
Riquelme SA, Lozano C, Moustafa AM, Liimatta K, Tomlinson KL, Britto C, Khanal S, Gill SK, Narechania A, Azcona-Gutierrez JM, Dimango E, Saenz Y, Planet P, Prince A (2019) CFTR-PTEN-dependent mitochondrial metabolic dysfunction promotes Pseudomonas aeruginosa airway infection. Sci Transl Med 11(499):eaav4634
Rosenfeld M, Emerson J, Accurso F, Armstrong D, Castile R, Grimwood K, Hiatt P, Mccoy K, Mcnamara S, Ramsey B, Wagener J (1999) Diagnostic accuracy of oropharyngeal cultures in infants and young children with cystic fibrosis. Pediatr Pulmonol 28:321–328
Rosenfeld M, Emerson J, Mcnamara S, Thompson V, Ramsey BW, Morgan W, Gibson RL, EPIC Study Group (2012) Risk factors for age at initial pseudomonas acquisition in the cystic fibrosis epic observational cohort. J Cyst Fibros 11:446–453
Ross-Gillespie A, Weigert M, Brown SP, Kummerli R (2014) Gallium-mediated siderophore quenching as an evolutionarily robust antibacterial treatment. Evol Med Public Health 2014:18–29
Rossi E, la Rosa R, Bartell JA, Marvig RL, Haagensen JAJ, Sommer LM, Molin S, Johansen HK (2021) Pseudomonas aeruginosa adaptation and evolution in patients with cystic fibrosis. Nat Rev Microbiol 19:331–342
Rowe SM, Heltshe SL, Gonska T, Donaldson SH, Borowitz D, Gelfond D, Sagel SD, Khan U, Mayer-Hamblett N, van Dalfsen JM, Joseloff E, Ramsey BW, GOAL Investigators of the Cystic Fibrosis Foundation Therapeutics Development Network (2014) Clinical mechanism of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator potentiator ivacaftor in G551D-mediated cystic fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 190:175–184
Sabnis A, Hagart KL, Klockner A, Becce M, Evans LE, Furniss RCD, Mavridou DA, Murphy R, Stevens MM, Davies JC, Larrouy-Maumus GJ, Clarke TB, Edwards AM (2021) Colistin kills bacteria by targeting lipopolysaccharide in the cytoplasmic membrane. elife 10:e65836
Saiman L, Prince A (1993) Pseudomonas aeruginosa pili bind to asialoGM1 which is increased on the surface of cystic fibrosis epithelial cells. J Clin Invest 92:1875–1880
Sarkar S (2020) Release mechanisms and molecular interactions of Pseudomonas aeruginosa extracellular DNA. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 104:6549–6564
Schroeder TH, Lee MM, Yacono PW, Cannon CL, Gerceker AA, Golan DE, Pier GB (2002) CFTR is a pattern recognition molecule that extracts Pseudomonas aeruginosa LPS from the outer membrane into epithelial cells and activates NF-kappa B translocation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99:6907–6912
Scott JE, O’Toole GA (2019) The yin and Yang of streptococcus Lung infections in cystic fibrosis: a model for studying Polymicrobial interactions. J Bacteriol 201(11):e00115-19
Sepahzad A, Morris-Rosendahl DJ, Davies JC (2021) Cystic fibrosis Lung Disease modifiers and their relevance in the new era of precision medicine. Genes (Basel) 12(4):562
Smith S, Waters V, Jahnke N, Ratjen F (2020) Standard versus biofilm antimicrobial susceptibility testing to guide antibiotic therapy in cystic fibrosis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 6:CD009528
Soren O, Rineh A, Silva DG, Cai Y, Howlin RP, Allan RN, Feelisch M, Davies JC, Connett GJ, Faust SN, Kelso MJ, Webb JS (2020) Cephalosporin nitric oxide-donor prodrug DEA-C3D disperses biofilms formed by clinical cystic fibrosis isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Antimicrob Chemother 75:117–125
Southern KW, Clancy JP, Ranganathan S (2019) Aerosolized agents for airway clearance in cystic fibrosis. Pediatr Pulmonol 54:858–864
Stoltz DA, Meyerholz DK, Welsh MJ (2015) Origins of cystic fibrosis lung disease. N Engl J Med 372:351–362
Taccetti G, Francalanci M, Pizzamiglio G, Messore B, Carnovale V, Cimino G, Cipolli M (2021) Cystic fibrosis: recent insights into inhaled antibiotic treatment and future perspectives, Antibiotics (Basel), p 10
Tarran R, Button B, Picher M, Paradiso AM, Ribeiro CM, Lazarowski ER, Zhang L, Collins PL, Pickles RJ, Fredberg JJ, Boucher RC (2005) Normal and cystic fibrosis airway surface liquid homeostasis. The effects of phasic shear stress and viral infections. J Biol Chem 280:35751–35759
Tognon M, Kohler T, Gdaniec BG, Hao Y, Lam JS, Beaume M, Luscher A, Buckling A, van Delden C (2017) Co-evolution with Staphylococcus aureus leads to lipopolysaccharide alterations in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. ISME J 11:2233–2243
Valentini M, Filloux A (2016) Biofilms and cyclic di-GMP (c-di-GMP) signaling: lessons from Pseudomonas aeruginosa and other bacteria. J Biol Chem 291:12547–12555
van den Bossche S, de Broe E, Coenye T, van Braeckel E, Crabbe A (2021) The cystic fibrosis lung microenvironment alters antibiotic activity: causes and effects. Eur Respir Rev 30(161):210055
van der Kooi AJ, de Visser M, van Meegen M, Ginjaar HB, van Essen AJ, Jennekens FG, Jongen PJ, Leschot NJ, Bolhuis PA (1998) A novel gamma-sarcoglycan mutation causing childhood onset, slowly progressive limb girdle muscular dystrophy. Neuromuscul Disord 8:305–308
van Ewijk BE, Wolfs TF, Aerts PC, van Kessel KP, Fleer A, Kimpen JL, van der Ent CK (2007) RSV mediates Pseudomonas aeruginosa binding to cystic fibrosis and normal epithelial cells. Pediatr Res 61:398–403
van Koningsbruggen-Rietschel S, Davies JC, Pressler T, Fischer R, Macgregor G, Donaldson SH, Smerud K, Meland N, Mortensen J, Fosbol MO, Downey DG, Myrset AH, Flaten H, Rye PD (2020) Inhaled dry powder alginate oligosaccharide in cystic fibrosis: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover phase 2b study. ERJ Open Res 6(4):00132-2020
Vandevanter DR, van Dalfsen JM (2005) How much do pseudomonas biofilms contribute to symptoms of pulmonary exacerbation in cystic fibrosis? Pediatr Pulmonol 39:504–506
Veit G, Avramescu RG, Chiang AN, Houck SA, Cai Z, Peters KW, Hong JS, Pollard HB, Guggino WB, Balch WE, Skach WR, Cutting GR, Frizzell RA, Sheppard DN, Cyr DM, Sorscher EJ, Brodsky JL, Lukacs GL (2016) From CFTR biology toward combinatorial pharmacotherapy: expanded classification of cystic fibrosis mutations. Mol Biol Cell 27:424–433
Viel M, Hubert D, Burgel PR, Genin E, Honore I, Martinez B, Gaitch N, Chapron J, Kanaan R, Dusser D, Girodon E, Bienvenu T (2016) DCTN4 as a modifier of chronic Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection in cystic fibrosis. Clin Respir J 10:777–783
Wainwright CE, Vidmar S, Armstrong DS, Byrnes CA, Carlin JB, Cheney J, Cooper PJ, Grimwood K, Moodie M, Robertson CF, Tiddens HA, Investigators AS (2011) Effect of bronchoalveolar lavage-directed therapy on Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection and structural lung injury in children with cystic fibrosis: a randomized trial. JAMA 306:163–171
Wilton M, Charron-Mazenod L, Moore R, Lewenza S (2016) Extracellular DNA acidifies biofilms and induces aminoglycoside resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 60:544–553
Winstanley C, O’Brien S, Brockhurst MA (2016) Pseudomonas aeruginosa evolutionary adaptation and diversification in cystic fibrosis chronic Lung infections. Trends Microbiol 24:327–337
Worlitzsch D, Tarran R, Ulrich M, Schwab U, Cekici A, Meyer KC, Birrer P, Bellon G, Berger J, Weiss T, Botzenhart K, Yankaskas JR, Randell S, Boucher RC, Doring G (2002) Effects of reduced mucus oxygen concentration in airway pseudomonas infections of cystic fibrosis patients. J Clin Invest 109:317–325
Yau YC, Ratjen F, Tullis E, Wilcox P, Freitag A, Chilvers M, Grasemann H, Zlosnik J, Speert D, Corey M, Stanojevic S, Matukas L, Leahy TR, Shih S, Waters V (2015) Randomized controlled trial of biofilm antimicrobial susceptibility testing in cystic fibrosis patients. J Cyst Fibros 14:262–266
Yepuri NR, Barraud N, Mohammadi NS, Kardak BG, Kjelleberg S, Rice SA, Kelso MJ (2013) Synthesis of cephalosporin-3′-diazeniumdiolates: biofilm dispersing NO-donor prodrugs activated by beta-lactamase. Chem Commun (Camb) 49:4791–4793
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
King, J., Murphy, R., Davies, J.C. (2022). Pseudomonas aeruginosa in the Cystic Fibrosis Lung. In: Filloux, A., Ramos, JL. (eds) Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, vol 1386. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-08491-1_13
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-08491-1_13
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-08490-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-08491-1
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)