Abstract
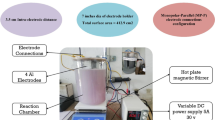
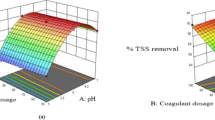
Automobile service stations discharge large quantities of wastewater the contains various organic and inorganic pollutants, causing severe impacts on human health. Hence, experimental work was conducted to treat carwash wastewater (CWW) using the coagulation-flocculation (C/F) process based on a naturally synthesized material, namely Cicer arietinum (CA). A standard jar test method supported by a central composite design (CCD) statistical approach was employed to investigate the effects of experimental factors on the removal efficiencies of turbidity and chemical oxygen demand (COD). The optimal process factors were pH of 4, rapid stirring speed of 180 rpm, and coagulant dosage of 1 g/L, achieving turbidity and COD removal efficiencies of 87.3 and 71.3%, respectively. Quadratic regression models were established to predict the removal efficiencies of turbidity and COD with the coefficient of determination (R2 values) of 0.983 and 0.974, respectively. As supported by the response surface methodology (RSM), the predicted removal efficiencies were 89.7% for turbidity and 68.1% for COD. Based on the experimental data and literature investigation, the application of natural-based coagulants for the treatment of CWW could be eco-friendly and low-cost compared to several inorganic chemical coagulants. The outputs were connected to various social, economic and environmentally-related sustainable development goals (SDGs), suggesting high possibility of scaling up the C/F treatment for real CWW projects.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adesina OA, Abdulkareem F, Yusuff AS, Lala M, Okewale A (2019) Response surface methodology approach to optimization of process parameter for coagulation process of surface water using Moringa oleifera seed. S Afr J Chem Eng 28:46–51
Al-Gheethi AA, Mohamed RMSRSR, Rahman MAAA, Johari MR, Kassim AHMM (2016) Treatment of wastewater from car washes using natural coagulation and filtration system. In: IOP conference series: materials science and engineering (vol 136, p 012046)
Ansari FA, Nasr M, Rawat I, Bux F (2021) Meeting sustainable development goals (SDGs) through progression of pilot-scale algal system to commercial raceway pond (300,000 L). Biomass Convers Biorefinery
Choong Lek BL, Peter AP, Qi Chong KH, Ragu P, Sethu V, Selvarajoo A, Arumugasamy SK (2018) Treatment of palm oil mill effluent (POME) using chickpea (Cicer arietinum) as a natural coagulant and flocculant: evaluation, process optimization and characterization of chickpea powder. J Environ Chem Eng 6:6243–6255
Ezz H, Ibrahim MG, Fujii M, Nasr M (2021) Dual biogas and biochar production from rice straw biomass: a techno-economic and sustainable development approach. Biomass Convers Biorefinery
Gonder B, Vergili I, Kaya Y, Gönder ZB, Balcıoğlu G, Kaya Y, Vergili I (2019) Treatment of carwash wastewater by electrocoagulation using Ti electrode: optimization of the operating parameters. Int J Environ Sci Technol 16:8041–8052
Mohamed R, Kutty N, Mariam AI, Kassim, Amir H, Radin M, Nadira M, Kutty I, Amir H (2014) Efficiency of using commercial and natural coagulants in treating car wash wastewater. Aust J Basic Appl Sci 8:227–234
Monney I, Buamah R, Donkor EA, Etuaful R, Nota HK, Ijzer H (2019) Treating waste with waste: the potential of synthesized alum from bauxite waste for treating car wash wastewater for reuse. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:12755–12764
Monney I, Donkor EA, Buamah R (2020) Clean vehicles, polluted waters: empirical estimates of water consumption and pollution loads of the carwash industry. Heliyon 6:e03952
Nasr M, Tawfik A, Awad HM, Galal A, El-Qelish M, Abdul Qyyum M, Mumtaz Ali Khan M, Rehan M, Nizami AS, Lee M (2021) Dual production of hydrogen and biochar from industrial effluent containing phenolic compounds. Fuel 301:121087
Putra RS, Amri RY, Ayu M (2020) Turbidity removal of synthetic wastewater using biocoagulants based on protein and tannin. In: AIP conference proceedings, p 2242
Rai R, Sharma S, Gurung DB, Sitaula BK, Shah RDT (2020) Assessing the impacts of vehicle wash wastewater on surface water quality through physico-chemical and benthic macroinvertebrates analyses. Water Sci 34:39–49
Subramonian W, Wu TY, Chai SP (2015) An application of response surface methodology for optimizing coagulation process of raw industrial effluent using Cassia obtusifolia seed gum together with alum. Ind Crops Prod 70:107–115
United Nations (2021) Sustainable development goals: 17 goals to transform our world. https://www.un.org/sustainabledevelopment/. Accessed 15 Sept 2021
Veit MT, Novais ÍGV, Juchen PT, Palácio SM, da Gonçalves Gilberto C, Zanette JC (2020) Automotive wash effluent treatment using combined process of coagulation/flocculation/sedimentation–adsorption. Water Air Soil Pollut 231
Zaneti R, Etchepare R, Rubio J (2011) Car wash wastewater reclamation. Full-scale application and upcoming features. Resour Conserv Recycl 55:953–959
Acknowledgements
The first author acknowledges the Seventh Tokyo International Conference on African Development (TICAD7) for the M.Sc. scholarship. Further, thanks to the Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA) for providing equipment used in this research. Also, thanks to Egypt-Japan University of Science and Technology (E-JUST).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Dadebo, D., Nasr, M., Fujii, M., Ibrahim, M.G. (2022). Coagulation/Flocculation Treatment of Carwash Wastewater Using Natural-Based Material: A Sustainable Development Approach. In: Jeon, HY. (eds) Sustainable Development of Water and Environment. Environmental Science and Engineering. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-07500-1_12
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-07500-1_12
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-07499-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-07500-1
eBook Packages: Earth and Environmental ScienceEarth and Environmental Science (R0)