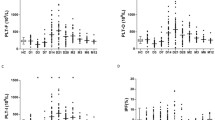
Abstract
The search for biomarkers that help physicians in medical practice has been a topic of great interest in the last decades. Burned patients represent a particular challenge due to the non-infectious systemic inflammatory response that characterizes thermal injury and the high incidence of sepsis in this population. Procalcitonin, a classic biomarker of infection, has demonstrated utility for identification of sepsis in burned patients. In contrast, C-reactive protein does not seem to improve infection diagnostic accuracy in this population. Diverse cytokines have also been studied as potential biomarkers in burned patients. Among these, interleukin-6 and interleukin-8 have shown a predictive value for different outcomes. Considering the importance of availability of biomarkers in everyday clinical practice, parameters derived from complete blood count have raised as interesting tools. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR), and RDW-to-platelet ratio (RPR) have demonstrated usefulness in burned patients. A dynamic profile of these biomarkers can be observed, with significant differences between survivors and non-survivors. The integration of some of these biomarkers with clinical scores could help physicians to better understand and treat burned patients.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AKI:
-
Acute kidney injury
- ARDS:
-
Acute respiratory distress syndrome
- AUC:
-
Area under the curve
- BALF:
-
Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid
- CBC:
-
Complete blood count
- COPD:
-
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- CRP:
-
C-reactive protein
- FEV1:
-
Forced expiratory volume in 1 s
- FVC:
-
Forced vital capacity
- Hb:
-
Hemoglobin
- Htc:
-
Hematocrit
- IL-6:
-
Interleukin-6
- IL-10:
-
Interleukin-10
- IL-1a:
-
Interleukin-1a
- IL-8:
-
Interleukin-8
- LAP:
-
Latency-associated peptide
- MCP-1:
-
Monocyte chemoattractant protein 1
- MLR:
-
Monocyte-to-lymphocyte ratio
- MODS:
-
Multiple organ dysfunction syndrome
- MPV:
-
Mean platelet volume
- NF-κB:
-
Nuclear transcription factor kappa B
- NGAL:
-
Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin
- NLR:
-
Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio
- PC:
-
Platelet count
- PCT:
-
Procalcitonin
- PLR:
-
Platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio
- RBC:
-
Red blood cell count
- RDW:
-
Red blood cell distribution width
- RPR:
-
Ratio between RDW and platelet count
- SIRS:
-
Systemic inflammatory response syndrome
- TBSA:
-
Total body surface area
- TNF-α:
-
Tumor necrosis factor-α
- WBC:
-
White blood cells
References
Afari ME, Bhat T. Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and cardiovascular diseases: an update. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther. 2016;14:573–7.
Albright JM, Davis CS, Bird MD, Ramirez L, Kim H, Burnham EL, Gamelli RL, Kovacs EJ. The acute pulmonary inflammatory response to the graded severity of smoke inhalation injury. Crit Care Med. 2012;40:1113–21.
Angulo M, Moreno L, Aramendi I, Dos Santos G, Cabrera J, Burghi G. Complete blood count and derived indices: evolution pattern and prognostic value in adult burned patients. J Burn Care Res. 2020;41:1260–6.
Barati M, Alinejad F, Bahar MA, Tabrisi MS, Shamshiri AR, Bodouhi NO, Karimi H. Comparison of WBC, ESR, CRP and PCT serum levels in septic and non-septic burn cases. Burns. 2008;34:770–4.
Bergquist M, Hastbacka J, Glaumann C, Freden F, Huss F, Lipcsey M. The time-course of the inflammatory response to major burn injury and its relation to organ failure and outcome. Burns. 2019;45:354–63.
Bermejo-Martin JF, Tamayo E, Ruiz G, Andaluz-Ojeda D, Herran-Monge R, Muriel-Bombin A, Fe Munoz M, Heredia-Rodriguez M, Citores R, Gomez-Herreras J, Blanco J, Express & groups, G. Circulating neutrophil counts and mortality in septic shock. Crit Care. 2014;18:407.
Cabral L, Afreixo V, Almeida L, Paiva JA. The use of Procalcitonin (PCT) for diagnosis of sepsis in burn patients: a meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2016;11:e0168475.
Cabral L, Afreixo V, Meireles R, Vaz M, Marques M, Tourais I, Chaves C, Almeida L, Paiva JA. Procalcitonin kinetics after burn injury and burn surgery in septic and non-septic patients – a retrospective observational study. BMC Anesthesiol. 2018;18:122.
Cato LD, Wearn CM, Bishop JRB, Stone MJ, Harrison P, Moiemen N. Platelet count: a predictor of sepsis and mortality in severe burns. Burns. 2018;44:288–97.
Chen Z, Turxun N, Ning F. Meta-analysis of the diagnostic value of procalcitonin in adult burn sepsis. Adv Clin Exp Med. 2021;30:455–63.
Davis CS, Janus SE, Mosier MJ, Carter SR, Gibbs JT, Ramirez L, Gamelli RL, Kovacs EJ. Inhalation injury severity and systemic immune perturbations in burned adults. Ann Surg. 2013;257:1137–46.
de Bandt JP, Chollet-Martin S, Hernvann A, Lioret N, du Roure LD, Lim SK, Vaubourdolle M, Guechot J, Saizy R, Giboudeau J, et al. Cytokine response to burn injury: relationship with protein metabolism. J Trauma. 1994;36:624–8.
Djordjevic D, Rondovic G, Surbatovic M, Stanojevic I, Udovicic I, Andjelic T, Zeba S, Milosavljevic S, Stankovic N, Abazovic D, Jevdjic J, Vojvodic D. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, monocyte-to-lymphocyte ratio, platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio, and mean platelet volume-to-platelet count ratio as biomarkers in critically ill and injured patients: which ratio to choose to predict outcome and nature of bacteremia? Mediat Inflamm. 2018;2018:3758068.
Egea-Guerrero JJ, Martinez-Fernandez C, Rodriguez-Rodriguez A, Bohorquez-Lopez A, Vilches-Arenas A, Pacheco-Sanchez M, Guerrero JM, Murillo-Cabezas F. The utility of C-reactive protein and procalcitonin for sepsis diagnosis in critically burned patients: a preliminary study. Plast Surg (Oakv). 2015;23:239–43.
Ethier JL, Desautels D, Templeton A, Shah PS, Amir E. Prognostic role of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Breast Cancer Res. 2017;19:2.
Finnerty CC, Herndon DN, Chinkes DL, Jeschke MG. Serum cytokine differences in severely burned children with and without sepsis. Shock. 2007;27:4–9.
Fox ED, Heffernan DS, Cioffi WG, Reichner JS. Neutrophils from critically ill septic patients mediate profound loss of endothelial barrier integrity. Crit Care. 2013;17:R226.
Fuchs PC, Demir E, Reuber K, Stromps P, Wolter T, Pallua N. Intra-alveolar IL-6 levels following burn and inhalation injury. Burns. 2009;35:840–4.
Gao X, Coull B, Lin X, Vokonas P, Sparrow D, Hou L, DeMeo DL, Litonjua AA, Schwartz J, Baccarelli AA. Association of Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio with pulmonary function in a 30-year longitudinal study of US veterans. JAMA Netw Open. 2020;3:e2010350.
Guell E, Martin-Fernandez M, De la Torre MC, Palomera E, Serra M, Martinez R, Solsona M, Miro G, Valles J, Fernandez S, Cortes E, Ferrer V, Morales M, Yebenes JC, Almirall J, Bermejo-Martin JF. Impact of lymphocyte and neutrophil counts on mortality risk in severe community-acquired pneumonia with or without septic shock. J Clin Med. 2019;8(5):754. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8050754. PMID: 31137863; PMCID: PMC6572378.
Guo F, Wang X, Huan J, Liang X, Chen B, Tang J, Gao C. Association of platelet counts decline and mortality in severely burnt patients. J Crit Care. 2012;27(529):e1–7.
Guo J, Qin Q, Hu H, Zhou D, Sun Y, Deng A. Red cell distribution width (RDW) as a prognostic tool in burn patients. Clin Lab. 2016;62:1973–8.
Hager S, Foldenauer AC, Rennekampff HO, Deisz R, Kopp R, Tenenhaus M, Gernot M, Pallua N. Interleukin-6 serum levels correlate with severity of burn injury but not with gender. J Burn Care Res. 2018;39:379–86.
Hirahara T, Arigami T, Yanagita S, Matsushita D, Uchikado Y, Kita Y, Mori S, Sasaki K, Omoto I, Kurahara H, Maemura K, Okubo K, Uenosono Y, Ishigami S, Natsugoe S. Combined neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio and platelet-lymphocyte ratio predicts chemotherapy response and prognosis in patients with advanced gastric cancer. BMC Cancer. 2019;19:672.
Hu L, Wang B, Hong Y, Xu L, Jiang Y, Wang C, Zhu B, Yu Q, Hou W, Chen Z, Zhu F, Wu G, Sun Y. Admission neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) predicts survival in patients with extensive burns. Burns. 2021;47:594–600.
Huang X, Guo F, Zhou Z, Chang M, Wang F, Dou Y, Wang Z, Huan J. Relation between dynamic changes of platelet counts and 30-day mortality in severely burned patients. Platelets. 2019;30:158–63.
Jeschke MG, Finnerty CC, Kulp GA, Kraft R, Herndon DN. Can we use C-reactive protein levels to predict severe infection or sepsis in severely burned patients? Int J Burns Trauma. 2013;3:137–43.
Jeschke MG, Gauglitz GG, Finnerty CC, Kraft R, Mlcak RP, Herndon DN. Survivors versus nonsurvivors postburn: differences in inflammatory and hypermetabolic trajectories. Ann Surg. 2014;259:814–23.
Jones SW, Zhou H, Ortiz-Pujols SM, Maile R, Herbst M, Joyner BL Jr, Zhang H, Kesic M, Jaspers I, Short KA, Meyer AA, Peden DB, Cairns BA, Noah TL. Bronchoscopy-derived correlates of lung injury following inhalational injuries: a prospective observational study. PLoS One. 2013;8:e64250.
Karakaya E, Akdur A, Aydogan C, Turk E, Sayin CB, Ayvazoglu Soy E, Yucebas SC, Alshalabi O, Haberal M. A model for acute kidney injury in severe burn patients. Burns. 2022;48:69–77.
Kim HS, Yang HT, Hur J, Chun W, Ju YS, Shin SH, Kang HJ, Lee KM. Procalcitonin levels within 48 hours after burn injury as a prognostic factor. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 2012;42:57–64.
Kim HY, Kong YG, Park JH, Kim YK. Acute kidney injury after burn surgery: preoperative neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio as a predictive factor. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2019;63:240–7.
Kraft R, Herndon DN, Finnerty CC, Cox RA, Song J, Jeschke MG. Predictive value of IL-8 for sepsis and severe infections after burn injury: a clinical study. Shock. 2015;43:222–7.
Lavrentieva A, Papadopoulou S, Kioumis J, Kaimakamis E, Bitzani M. PCT as a diagnostic and prognostic tool in burn patients. Whether time course has a role in monitoring sepsis treatment. Burns. 2012;38:356–63.
Li Q, Xie J, Huang Y, Liu S, Guo F, Liu L, Yang Y. Leukocyte kinetics during the early stage acts as a prognostic marker in patients with septic shock in intensive care unit. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021;100:e26288.
Li W, Ai X, Ni Y, Ye Z, Liang Z. The association between the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and mortality in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome: a retrospective cohort study. Shock. 2019;51:161–7.
Liu Y, Du X, Chen J, Jin Y, Peng L, Wang HHX, Luo M, Chen L, Zhao Y. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as an independent risk factor for mortality in hospitalized patients with COVID-19. J Infect. 2020;81:e6–e12.
Ma A, Cheng J, Yang J, Dong M, Liao X, Kang Y. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as a predictive biomarker for moderate-severe ARDS in severe COVID-19 patients. Crit Care. 2020;24:288.
Maile R, Jones S, Pan Y, Zhou H, Jaspers I, Peden DB, Cairns BA, Noah TL. Association between early airway damage-associated molecular patterns and subsequent bacterial infection in patients with inhalational and burn injury. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2015;308:L855–60.
Mann EA, Wood GL, Wade CE. Use of procalcitonin for the detection of sepsis in the critically ill burn patient: a systematic review of the literature. Burns. 2011;37:549–58.
Marck RE, Montagne HL, Tuinebreijer WE, Breederveld RS. Time course of thrombocytes in burn patients and its predictive value for outcome. Burns. 2013;39:714–22.
Osuka A, Ishihara T, Shimizu K, Shintani A, Ogura H, Ueyama M. Natural kinetics of blood cells following major burn: impact of early decreases in white blood cells and platelets as prognostic markers of mortality. Burns. 2019;45:1901–7.
Paliogiannis P, Fois AG, Sotgia S, Mangoni AA, Zinellu E, Pirina P, Negri S, Carru C, Zinellu A. Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio and clinical outcomes in COPD: recent evidence and future perspectives. Eur Respir Rev. 2018;27(147):170113. https://doi.org/10.1183/16000617.0113-2017. PMID: 29436405.
Pepys MB, Hirschfield GM. C-reactive protein: a critical update. J Clin Invest. 2003;111:1805–12.
Petzelbauer P, Watson CA, Pfau SE, Pober JS. IL-8 and angiogenesis: evidence that human endothelial cells lack receptors and do not respond to IL-8 in vitro. Cytokine. 1995;7:267–72.
Prescott HC, Osterholzer JJ, Langa KM, Angus DC, Iwashyna TJ. Late mortality after sepsis: propensity matched cohort study. BMJ. 2016;353:i2375.
Qiu L, Chen C, Li SJ, Wang C, Guo F, Peszel A, Liu S, Wang F, Sun YX, Wang YJ, Chen XL. Prognostic values of red blood cell distribution width, platelet count, and red cell distribution width-to-platelet ratio for severe burn injury. Sci Rep. 2017;7:13720.
Qiu L, Jin X, Wang JJ, Tang XD, Fang X, Li SJ, Wang F, Chen XL. Plasma neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio on the third day Postburn is associated with 90-day mortality among patients with burns over 30% of Total body surface area in two Chinese burns centers. J Inflamm Res. 2021;14:519–26.
Rehman FU, Khan A, Aziz A, Iqbal M, Mahmood SBZ, Ali N. Neutrophils to lymphocyte ratio: earliest and efficacious markers of sepsis. Cureus. 2020;12:e10851.
Ren H, Li Y, Han C, Hu H. Serum procalcitonin as a diagnostic biomarker for sepsis in burned patients: a meta-analysis. Burns. 2015;41:502–9.
Sachse C, Machens HG, Felmerer G, Berger A, Henkel E. Procalcitonin as a marker for the early diagnosis of severe infection after thermal injury. J Burn Care Rehabil. 1999;20:354–60.
Scheller J, Chalaris A, Schmidt-Arras D, Rose-John S. The pro- and anti-inflammatory properties of the cytokine interleukin-6. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011;1813:878–88.
Sen S, Hsei L, Tran N, Romanowski K, Palmieri T, Greenhalgh D, Cho K. Early clinical complete blood count changes in severe burn injuries. Burns. 2019;45:97–102.
Seymour CW, Gesten F, Prescott HC, Friedrich ME, Iwashyna TJ, Phillips GS, Lemeshow S, Osborn T, Terry KM, Levy MM. Time to treatment and mortality during mandated emergency Care for Sepsis. N Engl J Med. 2017;376:2235–44.
Singer M, Deutschman CS, Seymour CW, Shankar-Hari M, Annane D, Bauer M, Bellomo R, Bernard GR, Chiche JD, Coopersmith CM, Hotchkiss RS, Levy MM, Marshall JC, Martin GS, Opal SM, Rubenfeld GD, van der Poll T, Vincent JL, Angus DC. The third international consensus definitions for sepsis and septic shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA. 2016;315:801–10.
Sproston NR, Ashworth JJ. Role of C-reactive protein at sites of inflammation and infection. Front Immunol. 2018;9:754.
Steinvall I, Elmasry M, Abdelrahman I, El-Serafi A, Sjoberg F. Addition of admission lactate levels to Baux score improves mortality prediction in severe burns. Sci Rep. 2021;11:18038.
Temiz A, Albayrak A, Peksoz R, Disci E, Korkut E, Tanrikulu Y, Albayrak Y. Factors affecting the mortality at patients with burns: single Centre results. Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg. 2020;26:777–83.
Templeton AJ, McNamara MG, Seruga B, Vera-Badillo FE, Aneja P, Ocana A, Leibowitz-Amit R, Sonpavde G, Knox JJ, Tran B, Tannock IF, Amir E. Prognostic role of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in solid tumors: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2014;106:dju124.
Thakkar RK, Diltz Z, Drews JD, Wheeler KK, Shi J, Devine R, Fabia R, Hall M. Abnormal lymphocyte response after pediatric thermal injury is associated with adverse outcomes. J Surg Res. 2018;228:221–7.
Wang Y, Ju M, Chen C, Yang D, Hou D, Tang X, Zhu X, Zhang D, Wang L, Ji S, Jiang J, Song Y. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as a prognostic marker in acute respiratory distress syndrome patients: a retrospective study. J Thorac Dis. 2018;10:273–82.
Xiao CH, Wan J, Liu H, Qiu L, Wang F, Liu S, Lu XW, Chen XL. Red blood cell distribution width is an independent risk factor in the prediction of acute respiratory distress syndrome after severe burns. Burns. 2019;45:1158–63.
Yang HT, Yim H, Cho YS, Kym D, Hur J, Kim JH, Chun W, Kim HS. Assessment of biochemical markers in the early post-burn period for predicting acute kidney injury and mortality in patients with major burn injury: comparison of serum creatinine, serum cystatin-C, plasma and urine neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin. Crit Care. 2014;18:R151.
Zhou Y, Wei Q, Fan J, Cheng S, Ding W, Hua Z. Prognostic role of the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in pancreatic cancer: a meta-analysis containing 8252 patients. Clin Chim Acta. 2018;479:181–9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this entry
Cite this entry
Aramendi, I., Angulo, M., Burghi, G. (2023). Blood Count Profiles as Biomarkers in Burns: Red Cells, Platelets, and Beyond. In: Rajendram, R., Preedy, V.R., Patel, V.B. (eds) Biomarkers in Trauma, Injury and Critical Care. Biomarkers in Disease: Methods, Discoveries and Applications. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-07395-3_19
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-07395-3_19
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-07394-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-07395-3
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesReference Module Biomedical and Life Sciences