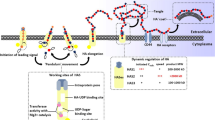
Abstract
Cancer is one of the leading causes of death worldwide. During tumor development and progression, extracellular matrix is being intensively re-organized. One of the most abundant molecules in the extracellular matrix is the polysaccharide hyaluronan. Hyaluronan accumulation and high CD44 expression—the major hyaluronan cellular receptor—correlate with higher malignant states of cancer cells, increased incidence of metastases and poor prognosis of the patients in a wide array of tumor types. Thus, hyaluronan interaction with CD44 emerges as an important target for cancer treatment. In this chapter, recent efforts to exploit hyaluronan/CD44 network for tumor therapy are being discussed. Overall, there is a wide variety of tools available to target this system like anti-CD44 antibodies and peptides, gene therapies against CD44, nanotechnology and modified-hyaluronan. Initial in vivo evidence shows promising results, nominating hyaluronan/CD44 network targeting as a potent candidate to be introduced into clinical settings for tumor therapy.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agren UM, Tammi RH, Tammi MI (1997) Reactive oxygen species contribute to epidermal hyaluronan catabolism in human skin organ culture. Free Radic Biol Med 23:996–1001
Aires A, Ocampo SM, Simoes BM, Josefa Rodriguez M, Cadenas JF, Couleaud P, Spence K, Latorre A, Miranda R, Somoza A, Clarke RB, Carrascosa JL, Cortajarena AL (2016) Multifunctionalized iron oxide nanoparticles for selective drug delivery to CD44- positive cancer cells. Nanotechnology 27:065103
Alshaer W, Hillaireau H, Vergnaud J, Mura S, Delomenie C, Sauvage F, Ismail S, Fattal E (2018) Aptamer-guided siRNA-loaded nanomedicines for systemic gene silencing in CD-44 expressing murine triple-negative breast cancer model. J Control Release 271:98–106
Annabi B, Bouzeghrane M, Currie JC, Hawkins R, Dulude H, Daigneault L, Ruiz M, Wisniewski J, Garde S, Rabbani SA, Panchal C, Wu JJ, Beliveau R (2005) A PSP94-derived peptide PCK3145 inhibits MMP-9 secretion and triggers CD44 cell surface shedding: implication in tumor metastasis. Clin Exp Metastasis 22:429–439
Artus C, Maquarre E, Moubarak RS, Delettre C, Jasmin C, Susin SA, Robert-Lezenes J (2006) CD44 ligation induces caspase-independent cell death via a novel calpain/AIF pathway in human erythroleukemia cells. Oncogene 25:5741–5751
Baba D, Kashiwabara S, Honda A, Yamagata K, Wu Q, Ikawa M, Okabe M, Baba T (2002) Mouse sperm lacking cell surface hyaluronidase PH-20 can pass through the layer of cumulus cells and fertilize the egg. J Biol Chem 277:30310–30314
Bae KH, Tan S, Yamashita A, Ang WX, Gao SJ, Wang S, Chung JE, Kurisawa M (2017) Hyaluronic acid-green tea catechin micellar nanocomplexes: fail-safe cisplatin nanomedicine for the treatment of ovarian cancer without off-target toxicity. Biomaterials 148:41–53
Bai Y, Liu CP, Chen D, Liu CF, Zhuo LH, Li H, Wang C, Bu HT, Tian W (2020) beta-Cyclodextrin-modified hyaluronic acid-based supramolecular self-assemblies for pH- and esterase- dual-responsive drug delivery. Carbohydr Polym 246:116654
Bart G, Vico NO, Hassinen A, Pujol FM, Deen AJ, Ruusala A, Tammi RH, Squire A, Heldin P, Kellokumpu S, Tammi MI (2015) Fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) and proximity ligation assays reveal functionally relevant homo- and heteromeric complexes among hyaluronan synthases HAS1, HAS2, and HAS3. J Biol Chem 290:11479–11490
Bates RC, Elith CA, Thorne RF, Burns GF (1998) Engagement of variant CD44 confers resistance to anti-integrin antibody-mediated apoptosis in a colon carcinoma cell line. Cell Adhes Commun 6:21–38
Bernert B, Porsch H, Heldin P (2011) Hyaluronan synthase 2 (HAS2) promotes breast cancer cell invasion by suppression of tissue metalloproteinase inhibitor 1 (TIMP-1). J Biol Chem 286:42349–42359
Bhattacharya DS, Svechkarev D, Bapat A, Patil P, Hollingsworth MA, Mohs AM (2020) Sulfation modulates the targeting properties of hyaluronic acid to P-selectin and CD44. ACS Biomater Sci Eng 6:3585–3598
Birkenkamp-Demtroder K, Maghnouj A, Mansilla F, Thorsen K, Andersen CL, Oster B, Hahn S, Orntoft TF (2011) Repression of KIAA1199 attenuates Wnt-signalling and decreases the proliferation of colon cancer cells. Br J Cancer 105:552–561
Birzele F, Voss E, Nopora A, Honold K, Heil F, Lohmann S, Verheul H, Le Tourneau C, Delord JP, Van Herpen C, Mahalingam D, Coveler AL, Meresse V, Weigand S, Runza V, Cannarile M (2015) CD44 isoform status predicts response to treatment with anti-CD44 antibody in cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res 21:2753–2762
Borgya A, Woodman A, Sugiyama M, Donie F, Kopetzki E, Matsumura Y, Tarin D (1995) Isolation and characterisation of antibodies which specifically recognise the peptide encoded by exon 7 (v2) of the human CD44 gene. Clin Mol Pathol 48:M241–M250
Bostad M, Kausberg M, Weyergang A, Olsen CE, Berg K, Hogset A, Selbo PK (2014) Light-triggered, efficient cytosolic release of IM7-saporin targeting the putative cancer stem cell marker CD44 by photochemical internalization. Mol Pharm 11:2764–2776
Bourguignon LY, Zhu H, Chu A, Iida N, Zhang L, Hung MC (1997) Interaction between the adhesion receptor, CD44, and the oncogene product, p185HER2, promotes human ovarian tumor cell activation. J Biol Chem 272:27913–27918
Bourguignon LY, Wong G, Earle C, Chen L (2012) Hyaluronan-CD44v3 interaction with Oct4- Sox2-Nanog promotes miR-302 expression leading to self-renewal, clonal formation, and cisplatin resistance in cancer stem cells from head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. J Biol Chem 287:32800–32824
Chanmee T, Ontong P, Kimata K, Itano N (2015) Key roles of hyaluronan and its CD44 receptor in the stemness and survival of cancer stem cells. Front Oncol 5:180
Chen P, Huang H, Wu J, Lu R, Wu Y, Jiang X, Yuan Q, Chen Y (2015) Bone marrow stromal cells protect acute myeloid leukemia cells from anti-CD44 therapy partly through regulating PI3K/Akt-p27(Kip1) axis. Mol Carcinog 54:1678–1685
Chen L, Liu Z, Jin R, Yang X, Bai Y, Liu S, Chen X (2018a) Stepwise co-delivery of an enzyme and prodrug based on a multi-responsive nanoplatform for accurate tumor therapy. J Mater Chem B 6:6262–6268
Chen X, Nagai Y, Zhu Z, Ruan H, Peehl DM, Greene MI, Zhang H (2018b) A spliced form of CD44 expresses the unique glycan that is recognized by the prostate cancer specific antibody F77. Oncotarget 9:3631–3640
Chen Y, Wang H, Zuo Y, Li N, Ding M, Li C (2018c) A novel monoclonal antibody KMP1 has potential antitumor activity of bladder cancer by blocking CD44 in vivo and in vitro. Cancer Med 7:2064–2077
Cheng HW, Chiang CS, Ho HY, Chou SH, Lai YH, Shyu WC, Chen SY (2021) Dextran-modified Quercetin-Cu(II)/hyaluronic acid nanomedicine with natural poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitor and dual targeting for programmed synthetic lethal therapy in triple- negative breast cancer. J Control Release 329:136–147
Cherr GN, Yudin AI, Overstreet JW (2001) The dual functions of GPI-anchored PH-20: hyaluronidase and intracellular signaling. Matrix Biol 20:515–525
Cho JH, Lee SC, Ha NR, Lee SJ, Yoon MY (2015) A novel peptide-based recognition probe for the sensitive detection of CD44 on breast cancer stem cells. Mol Cell Probes 29:492–499
Chong Y, Huang J, Xu X, Yu C, Ning X, Fan S, Zhang Z (2020) Hyaluronic acid-modified au-ag alloy nanoparticles for radiation/nanozyme/ag(+) multimodal synergistically enhanced cancer therapy. Bioconjug Chem 31:1756–1765
Danhier F, Feron O, Preat V (2010) To exploit the tumor microenvironment: passive and active tumor targeting of nanocarriers for anti-cancer drug delivery. J Control Release 148:135–146
D’arena G, Calapai G, Deaglio S (2014) Anti-CD44 mAb for the treatment of B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia and other hematological malignancies: evaluation of WO2013063498. Expert Opin Ther Pat 24:821–828
Debele TA, Wu PC, Wei YF, Chuang JY, Chang KY, Tsai JH, Su WP (2021) Transferrin modified GSH sensitive hyaluronic acid derivative micelle to deliver HSP90 inhibitors to enhance the therapeutic efficacy of brain cancers. Cancers (Basel) 13:2375
Deen AJ, Rilla K, Oikari S, Karna R, Bart G, Hayrinen J, Bathina AR, Ropponen A, Makkonen K, Tammi RH, Tammi MI (2014) Rab10-mediated endocytosis of the hyaluronan synthase HAS3 regulates hyaluronan synthesis and cell adhesion to collagen. J Biol Chem 289:8375–8389
Ding L, Jiang Y, Zhang J, Klok HA, Zhong Z (2018) pH-sensitive coiled-coil peptide-cross-linked hyaluronic acid nanogels: synthesis and targeted intracellular protein delivery to CD44 positive cancer cells. Biomacromolecules 19:555–562
Du YR, Chen Y, Gao Y, Niu XL, Li YJ, Deng WM (2013) Effects and mechanisms of anti-CD44 monoclonal antibody A3D8 on proliferation and apoptosis of sphere-forming cells with stemness from human ovarian cancer. Int J Gynecol Cancer 23:1367–1375
Du T, Jia X, Dong X, Ru X, Li L, Wang Y, Liu J, Feng G, Wen T (2020a) Cosmc disruption-mediated aberrant O-glycosylation suppresses breast cancer cell growth via impairment of CD44. Cancer Manag Res 12:511–522
Du Y, Wang S, Zhang T, He D, Tu J, Shen Y (2020b) Enhanced cytotoxicity of a redox-sensitive hyaluronic acid-based nanomedicine toward different oncocytes via various internalization mechanisms. Drug Deliv 27:128–136
Edelman R, Assaraf YG, Levitzky I, Shahar T, Livney YD (2017) Hyaluronic acid-serum albumin conjugate-based nanoparticles for targeted cancer therapy. Oncotarget 8:24337–24353
Fang J, Nakamura H, Maeda H (2011) The EPR effect: unique features of tumor blood vessels for drug delivery, factors involved, and limitations and augmentation of the effect. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 63:136–151
Fedorchenko O, Stiefelhagen M, Peer-Zada AA, Barthel R, Mayer P, Eckei L, Breuer A, Crispatzu G, Rosen N, Landwehr T, Lilienthal N, Mollmann M, Montesinos-Rongen M, Heukamp L, Durig J, Hallek M, Fingerle-Rowson G, Herling M (2013) CD44 regulates the apoptotic response and promotes disease development in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 121:4126–4136
Fernando J, Malfettone A, Cepeda EB, Vilarrasa-Blasi R, Bertran E, Raimondi G, Fabra A, Alvarez-Barrientos A, Fernandez-Salguero P, Fernandez-Rodriguez CM, Giannelli G, Sancho P, Fabregat I (2015) A mesenchymal-like phenotype and expression of CD44 predict lack of apoptotic response to sorafenib in liver tumor cells. Int J Cancer 136:E161–E172
Finlayson M (2015) Modulation of CD44 activity by A6-peptide. Front Immunol 6:135
Fitzgerald KA, Bowie AG, Skeffington BS, O’neill LA (2000) Ras, protein kinase C zeta, and I kappa B kinases 1 and 2 are downstream effectors of CD44 during the activation of NF-kappa B by hyaluronic acid fragments in T-24 carcinoma cells. J Immunol 164:2053–2063
Flannery CR, Little CB, Hughes CE, Caterson B (1998) Expression and activity of articular cartilage hyaluronidases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 251:824–829
Flores-Diaz M, Alape-Giron A, Persson B, Pollesello P, Moos M, Von Eichel-Streiber C, Thelestam M, Florin I (1997) Cellular UDP-glucose deficiency caused by a single point mutation in the UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase gene. J Biol Chem 272:23784–23791
Fraser JR, Laurent TC, Laurent UB (1997) Hyaluronan: its nature, distribution, functions and turnover. J Intern Med 242:27–33
Fujita Y, Kitagawa M, Nakamura S, Azuma K, Ishii G, Higashi M, Kishi H, Hiwasa T, Koda K, Nakajima N, Harigaya K (2002) CD44 signaling through focal adhesion kinase and its anti- apoptotic effect. FEBS Lett 528:101–108
Gadhoum Z, Delaunay J, Maquarre E, Durand L, Lancereaux V, Qi J, Robert-Lezenes J, Chomienne C, Smadja-Joffe F (2004a) The effect of anti-CD44 monoclonal antibodies on differentiation and proliferation of human acute myeloid leukemia cells. Leuk Lymphoma 45:1501–1510
Gadhoum Z, Leibovitch MP, Qi J, Dumenil D, Durand L, Leibovitch S, Smadja-Joffe F (2004b) CD44: a new means to inhibit acute myeloid leukemia cell proliferation via p27Kip1. Blood 103:1059–1068
Galandrini R, De Maria R, Piccoli M, Frati L, Santoni A (1994) CD44 triggering enhances human NK cell cytotoxic functions. J Immunol 153:4399–4407
Gao Y, Foster R, Yang X, Feng Y, Shen JK, Mankin HJ, Hornicek FJ, Amiji MM, Duan Z (2015) Up-regulation of CD44 in the development of metastasis, recurrence and drug resistance of ovarian cancer. Oncotarget 6:9313–9326
Gao S, Wang J, Tian R, Wang G, Zhang L, Li Y, Li L, Ma Q, Zhu L (2017) Construction and evaluation of a targeted hyaluronic acid nanoparticle/photosensitizer complex for cancer photodynamic therapy. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:32509–32519
Gao S, Islam R, Fang J (2021) Tumor environment-responsive hyaluronan conjugated zinc protoporphyrin for targeted anticancer photodynamic therapy. J Pers Med 11:136
Gatti V, Fierro C, Compagnone M, Giangrazi F, Markert EK, Bongiorno-Borbone L, Melino G, Peschiaroli A (2018) DeltaNp63 regulates the expression of hyaluronic acid- related genes in breast cancer cells. Oncogenesis 7:65
Ghatak S, Misra S, Toole BP (2005) Hyaluronan constitutively regulates ErbB2 phosphorylation and signaling complex formation in carcinoma cells. J Biol Chem 280:8875–8883
Golan M, Feinshtein V, Polyak D, Scomparin A, Satchi-Fainaro R, David A (2016) Inhibition of gene expression and cancer cell migration by CD44v3/6-targeted Polyion complexes. Bioconjug Chem 27:947–960
Gong H, Chao Y, Xiang J, Han X, Song G, Feng L, Liu J, Yang G, Chen Q, Liu Z (2016) Hyaluronidase to enhance nanoparticle-based photodynamic tumor therapy. Nano Lett 16:2512–2521
Gu W, An J, Meng H, Yu N, Zhong Y, Meng F, Xu Y, Cornelissen J, Zhong Z (2019) CD44-specific A6 short peptide boosts targetability and anticancer efficacy of polymersomal epirubicin to orthotopic human multiple myeloma. Adv Mater 31:e1904742
Gu W, Liu T, Fan D, Zhang J, Xia Y, Meng F, Xu Y, Cornelissen J, Liu Z, Zhong Z (2021) A6 peptide-tagged, ultra-small and reduction-sensitive polymersomal vincristine sulfate as a smart and specific treatment for CD44+ acute myeloid leukemia. J Control Release 329:706–716
Guo J, Cheng H, Zhao S, Yu L (2006) GG: a domain involved in phage LTF apparatus and implicated in human MEB and non-syndromic hearing loss diseases. FEBS Lett 580:581–584
Haist C, Schulte E, Bartels N, Bister A, Poschinski Z, Ibach TC, Geipel K, Wiek C, Wagenmann M, Monzel C, Scheckenbach K, Hanenberg H (2021) CD44v6-targeted CAR T-cells specifically eliminate CD44 isoform 6 expressing head/neck squamous cell carcinoma cells. Oral Oncol 116:105259
Han S, Guo J, Liu Y, Zhang Z, He Q, Li P, Zhang M, Sun H, Li R, Li Y, Zeng W, Liu J, Lian L, Gao Y, Shen L (2015) Knock out CD44 in reprogrammed liver cancer cell C3A increases CSCs stemness and promotes differentiation. Oncotarget 6:44452–44465
Han HS, Choi KY, Lee H, Lee M, An JY, Shin S, Kwon S, Lee DS, Park JH (2016) Gold-nanoclustered hyaluronan nano-assemblies for photothermally maneuvered photodynamic tumor ablation. ACS Nano 10:10858–10868
Hascall VC, Wang A, Tammi M, Oikari S, Tammi R, Passi A, Vigetti D, Hanson RW, Hart GW (2014) The dynamic metabolism of hyaluronan regulates the cytosolic concentration of UDP-GlcNAc. Matrix Biol 35:14–17
Hayward SL, Wilson CL, Kidambi S (2016) Hyaluronic acid-conjugated liposome nanoparticles for targeted delivery to CD44 overexpressing glioblastoma cells. Oncotarget 7:34158–34171
He QY, Liu XH, Li Q, Studholme DJ, Li XW, Liang SP (2006) G8: a novel domain associated with polycystic kidney disease and non-syndromic hearing loss. Bioinformatics 22:2189–2191
Heldin P, Delatorre M, Ytterberg D, Bergh J (1996) Differential synthesis and binding of hyaluronan by human breast cancer cell lines. Oncol Rep 3:1011–1016
Heldin P, Basu K, Kozlova I, Porsch H (2014) HAS2 and CD44 in breast tumorigenesis. Adv Cancer Res 123:211–229
Heldin P, Lin CY, Kolliopoulos C, Chen YH, Skandalis SS (2019) Regulation of hyaluronan biosynthesis and clinical impact of excessive hyaluronan production. Matrix Biol 78-79:100–117
Hibino S, Shibuya M, Hoffman MP, Engbring JA, Hossain R, Mochizuki M, Kudoh S, Nomizu M, Kleinman HK (2005) Laminin alpha5 chain metastasis- and angiogenesis- inhibiting peptide blocks fibroblast growth factor 2 activity by binding to the heparan sulfate chains of CD44. Cancer Res 65:10494–10501
Ishii S, Ford R, Thomas P, Nachman A, Steele G Jr, Jessup JM (1993) CD44 participates in the adhesion of human colorectal carcinoma cells to laminin and type IV collagen. Surg Oncol 2:255–264
Ishizuka Y, Yokota A, Nishimura M, Saito Y, Nakaseko C (2008) Ligation of CD44 leads to killing activity in human peripheral mononuclear cells via MAP kinase and tyrosine kinases. Hematology 13:230–235
Itano N, Kimata K (2002) Mammalian hyaluronan synthases. IUBMB Life 54:195–199
Itano N, Sawai T, Yoshida M, Lenas P, Yamada Y, Imagawa M, Shinomura T, Hamaguchi M, Yoshida Y, Ohnuki Y, Miyauchi S, Spicer AP, McDonald JA, Kimata K (1999) Three isoforms of mammalian hyaluronan synthases have distinct enzymatic properties. J Biol Chem 274:25085–25092
Jafari Malek S, Khoshchehreh R, Goodarzi N, Khoshayand MR, Amini M, Atyabi F, Esfandyari-Manesh M, Tehrani S, Mohammad Jafari R, Maghazei MS, Alvandifar F, Ebrahimi M, Dinarvand R (2014) cis-Dichlorodiamminoplatinum (II) glyconanoparticles by drug-induced ionic gelation technique targeted to prostate cancer: preparation, optimization and in vitro characterization. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 122:350–358
Jauw YWS, Huisman MC, Nayak TK, Vugts DJ, Christen R, Naegelen VM, Ruettinger D, Heil F, Lammertsma AA, Verheul HMW, Hoekstra OS, Van Dongen G, Menke-Van Der Houven Van Oordt CW (2018) Assessment of target-mediated uptake with immuno-PET: analysis of a phase I clinical trial with an anti-CD44 antibody. EJNMMI Res 8:6
Kajita M, Itoh Y, Chiba T, Mori H, Okada A, Kinoh H, Seiki M (2001) Membrane-type 1 matrix metalloproteinase cleaves CD44 and promotes cell migration. J Cell Biol 153:893–904
Karousou E, Kamiryo M, Skandalis SS, Ruusala A, Asteriou T, Passi A, Yamashita H, Hellman U, Heldin CH, Heldin P (2010) The activity of hyaluronan synthase 2 is regulated by dimerization and ubiquitination. J Biol Chem 285:23647–23654
Karousou E, Misra S, Ghatak S, Dobra K, Gotte M, Vigetti D, Passi A, Karamanos NK, Skandalis SS (2017) Roles and targeting of the HAS/hyaluronan/CD44 molecular system in cancer. Matrix Biol 59:3–22
Khan F, Gurung S, Gunassekaran GR, Vadevoo SMP, Chi L, Permpoon U, Haque ME, Lee YK, Lee SW, Kim S, Lee B (2021) Identification of novel CD44v6-binding peptides that block CD44v6 and deliver a pro-apoptotic peptide to tumors to inhibit tumor growth and metastasis in mice. Theranostics 11:1326–1344
Koyama H, Hibi T, Isogai Z, Yoneda M, Fujimori M, Amano J, Kawakubo M, Kannagi R, Kimata K, Taniguchi S, Itano N (2007) Hyperproduction of hyaluronan in neu-induced mammary tumor accelerates angiogenesis through stromal cell recruitment: possible involvement of versican/PG-M. Am J Pathol 170:1086–1099
Kubens BS, Zanker KS (1998) Differences in the migration capacity of primary human colon carcinoma cells (SW480) and their lymph node metastatic derivatives (SW620). Cancer Lett 131:55–64
Lakshman M, Subramaniam V, Rubenthiran U, Jothy S (2004) CD44 promotes resistance to apoptosis in human colon cancer cells. Exp Mol Pathol 77:18–25
Larsen M, Artym VV, Green JA, Yamada KM (2006) The matrix reorganized: extracellular matrix remodeling and integrin signaling. Curr Opin Cell Biol 18:463–471
Lee SY, Kim KA, Kim CH, Kim YJ, Lee JH, Kim HR (2017) CD44-shRNA recombinant adenovirus inhibits cell proliferation, invasion, and migration, and promotes apoptosis in HCT116 colon cancer cells. Int J Oncol 50:329–336
Lee IC, Wu YC, Hung WS (2018) Hyaluronic acid-based multilayer films regulate hypoxic multicellular aggregation of pancreatic cancer cells with distinct cancer stem-cell-like properties. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 10:38769–38779
Li L, Heldin CH, Heldin P (2006) Inhibition of platelet-derived growth factor-BB-induced receptor activation and fibroblast migration by hyaluronan activation of CD44. J Biol Chem 281:26512–26519
Li J, Yang J, Yuan J, Li Y, Wang RC, Wang SY, Hao HL (2016) Effect of anti-CD44 monoclonal antibody A3D8 on expression of AP-1 in HL-60 cells. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi 24:1360–1364
Li W, Jia H, Wang J, Guan H, Li Y, Zhang D, Tang Y, Wang TD, Lu S (2017a) A CD44-specific peptide, RP-1, exhibits capacities of assisting diagnosis and predicting prognosis of gastric cancer. Oncotarget 8:30063–30076
Li W, Ma H, Zhang J, Zhu L, Wang C, Yang Y (2017b) Unraveling the roles of CD44/CD24 and ALDH1 as cancer stem cell markers in tumorigenesis and metastasis. Sci Rep 7:13856
Liang Y, Peng J, Li N, Yu-Wai-Man C, Wang Q, Xu Y, Wang H, Tagalakis AD, Du Z (2019) Smart nanoparticles assembled by endogenous molecules for siRNA delivery and cancer therapy via CD44 and EGFR dual-targeting. Nanomedicine 15:208–217
Liang Y, Wang Y, Wang L, Liang Z, Li D, Xu X, Chen Y, Yang X, Zhang H, Niu H (2021) Self-crosslinkable chitosan-hyaluronic acid dialdehyde nanoparticles for CD44-targeted siRNA delivery to treat bladder cancer. Bioact Mater 6:433–446
Lin C, Yang X, Li H, Zou Y, Mohammad IS, Rong H, Rao Y, Song J, Leung SSY, Hu H (2021) Self-assembled nanomedicine combining a berberine derivative and doxorubicin for enhanced antitumor and antimetastatic efficacy via mitochondrial pathways. Nanoscale 13:6605–6623
Liu T, Yan Z, Liu Y, Choy E, Hornicek FJ, Mankin H, Duan Z (2018) CRISPR-Cas9-mediated silencing of CD44 in human highly metastatic osteosarcoma cells. Cell Physiol Biochem 46:1218–1230
Liu J, Sun Y, Liu X, Yang Y, Widjaya AS, Long Z, Jiang Y (2020) Efficiency of different treatment regimens combining anti-tumor and anti-inflammatory liposomes for metastatic breast cancer. AAPS PharmSciTech 21:259
Lobo S, Pereira C, Oliveira C, Almeida GM (2020) Skipping exon-v6 from CD44v6-containing isoforms influences chemotherapy response and self-renewal capacity of gastric cancer cells. Cancers (Basel) 12:2378
Lusche DF, Wessels DJ, Reis RJ, Forrest CC, Thumann AR, Soll DR (2021) New monoclonal antibodies that recognize an unglycosylated, conserved, extracellular region of CD44 in vitro and in vivo, and can block tumorigenesis. PLoS One 16:e0250175
Mahira S, Kommineni N, Husain GM, Khan W (2019) Cabazitaxel and silibinin co-encapsulated cationic liposomes for CD44 targeted delivery: A new insight into nanomedicine based combinational chemotherapy for prostate cancer. Biomed Pharmacother 110:803–817
Maiolino S, Russo A, Pagliara V, Conte C, Ungaro F, Russo G, Quaglia F (2015) Biodegradable nanoparticles sequentially decorated with polyethyleneimine and hyaluronan for the targeted delivery of docetaxel to airway cancer cells. J Nanobiotechnology 13:29
Maisel D, Birzele F, Voss E, Nopora A, Bader S, Friess T, Goller B, Laifenfeld D, Weigand S, Runza V (2016) Targeting tumor cells with anti-CD44 antibody triggers macrophage-mediated immune modulatory effects in a cancer xenograft model. PLoS One 11:e0159716
Marengo A, Forciniti S, Dando I, Dalla Pozza E, Stella B, Tsapis N, Yagoubi N, Fanelli G, Fattal E, Heeschen C, Palmieri M, Arpicco S (2019) Pancreatic cancer stem cell proliferation is strongly inhibited by diethyldithiocarbamate-copper complex loaded into hyaluronic acid decorated liposomes. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj 1863:61–72
Matzke-Ogi A, Jannasch K, Shatirishvili M, Fuchs B, Chiblak S, Morton J, Tawk B, Lindner T, Sansom O, Alves F, Warth A, Schwager C, Mier W, Kleeff J, Ponta H, Abdollahi A, Orian-Rousseau V (2016) Inhibition of tumor growth and metastasis in pancreatic cancer models by interference with CD44v6 signaling. Gastroenterology 150:513–525 e10
McClements L, Yakkundi A, Papaspyropoulos A, Harrison H, Ablett MP, Jithesh PV, McKeen HD, Bennett R, Donley C, Kissenpfennig A, Mcintosh S, McCarthy HO, O’neill E, Clarke RB, Robson T (2013) Targeting treatment-resistant breast cancer stem cells with FKBPL and its peptide derivative, AD-01, via the CD44 pathway. Clin Cancer Res 19:3881–3893
Mehic M, De Sa VK, Hebestreit S, Heldin CH, Heldin P (2017) The deubiquitinating enzymes USP4 and USP17 target hyaluronan synthase 2 and differentially affect its function. Oncogenesis 6:e348
Menke-Van Der Houven Van Oordt CW, Gomez-Roca C, Van Herpen C, Coveler AL, Mahalingam D, Verheul HM, Van Der Graaf WT, Christen R, Ruttinger D, Weigand S, Cannarile MA, Heil F, Brewster M, Walz AC, Nayak TK, Guarin E, Meresse V, Le Tourneau C (2016) First-in-human phase I clinical trial of RG7356, an anti- CD44 humanized antibody, in patients with advanced, CD44-expressing solid tumors. Oncotarget 7:80046–80058
Miletti-Gonzalez KE, Chen S, Muthukumaran N, Saglimbeni GN, Wu X, Yang J, Apolito K, Shih WJ, Hait WN, Rodriguez-Rodriguez L (2005) The CD44 receptor interacts with P-glycoprotein to promote cell migration and invasion in cancer. Cancer Res 65:6660–6667
Miletti-Gonzalez KE, Murphy K, Kumaran MN, Ravindranath AK, Wernyj RP, Kaur S, Miles GD, Lim E, Chan R, Chekmareva M, Heller DS, Foran D, Chen W, Reiss M, Bandera EV, Scotto K, Rodriguez-Rodriguez L (2012) Identification of function for CD44 intracytoplasmic domain (CD44-ICD): modulation of matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP-9) transcription via novel promoter response element. J Biol Chem 287:18995–19007
Misra S, Ghatak S, Toole BP (2005) Regulation of MDR1 expression and drug resistance by a positive feedback loop involving hyaluronan, phosphoinositide 3-kinase, and ErbB2. J Biol Chem 280:20310–20315
Misra S, Hascall VC, De Giovanni C, Markwald RR, Ghatak S (2009) Delivery of CD44 shRNA/nanoparticles within cancer cells: perturbation of hyaluronan/CD44v6 interactions and reduction in adenoma growth in Apc Min/+ MICE. J Biol Chem 284:12432–12446
Misra S, Heldin P, Hascall VC, Karamanos NK, Skandalis SS, Markwald RR, Ghatak S (2011) Hyaluronan-CD44 interactions as potential targets for cancer therapy. FEBS J 278:1429–1443
Mizrahy S, Raz SR, Hasgaard M, Liu H, Soffer-Tsur N, Cohen K, Dvash R, Landsman-Milo D, Bremer MG, Moghimi SM, Peer D (2011) Hyaluronan-coated nanoparticles: the influence of the molecular weight on CD44-hyaluronan interactions and on the immune response. J Control Release 156:231–238
Mizrahy S, Goldsmith M, Leviatan-Ben-Arye S, Kisin-Finfer E, Redy O, Srinivasan S, Shabat D, Godin B, Peer D (2014) Tumor targeting profiling of hyaluronan-coated lipid based-nanoparticles. Nanoscale 6:3742–3752
Montanari E, Di Meo C, Oates A, Coviello T, Matricardi P (2018) Pursuing intracellular pathogens with hyaluronan. From a ‘Pro-Infection’ polymer to a biomaterial for ‘Trojan Horse’ Systems. Molecules 23:939
Morath I, Hartmann TN, Orian-Rousseau V (2016) CD44: more than a mere stem cell marker. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 81:166–173
Mori H, Tomari T, Koshikawa N, Kajita M, Itoh Y, Sato H, Tojo H, Yana I, Seiki M (2002) CD44 directs membrane-type 1 matrix metalloproteinase to lamellipodia by associating with its hemopexin-like domain. EMBO J 21:3949–3959
Navarro-Marchal SA, Grinan-Lison C, Entrena JM, Ruiz-Alcala G, Tristan-Manzano M, Martin F, Perez-Victoria I, Peula-Garcia JM, Marchal JA (2021) Anti-CD44-conjugated olive oil liquid nanocapsules for targeting pancreatic cancer stem cells. Biomacromolecules 22:1374–1388
Ndinguri MW, Zheleznyak A, Lauer JL, Anderson CJ, Fields GB (2012) Application of collagen-model triple-helical peptide-amphiphiles for CD44-targeted drug delivery systems. J Drug Deliv 2012:592602
Ni J, Cozzi PJ, Hao JL, Beretov J, Chang L, Duan W, Shigdar S, Delprado WJ, Graham PH, Bucci J, Kearsley JH, Li Y (2014) CD44 variant 6 is associated with prostate cancer metastasis and chemo-/radioresistance. Prostate 74:602–617
Nurwidya F, Takahashi F, Kato M, Baskoro H, Hidayat M, Wirawan A, Takahashi K (2017) CD44 silencing decreases the expression of stem cell-related factors induced by transforming growth factor beta1 and tumor necrosis factor alpha in lung cancer: preliminary findings. Bosn J Basic Med Sci 17:228–234
Ogoshi T, Ishii S, Mizoi T, Harada N, Sato W, Saito K, Ogawa H, Inabe K, Shiiba K, Matsuno S (1998) CD44H participates in the intrahepatic growth of murine colon 26 adenocarcinoma cells. Jpn J Cancer Res 89:1160–1168
Ota T, Matsui T, Kohno H, Maeda M, Tanino M, Odashima S (1995) CD44 participates in tumor cell adhesion to endothelial cells in the experimental metastatic process in B16BL6 melanoma cells. Anticancer Res 15:1215–1219
Pandey MS, Harris EN, Weigel JA, Weigel PH (2008) The cytoplasmic domain of the hyaluronan receptor for endocytosis (HARE) contains multiple endocytic motifs targeting coated pit-mediated internalization. J Biol Chem 283:21453–21461
Park HY, Lee KJ, Lee SJ, Yoon MY (2012a) Screening of peptides bound to breast cancer stem cell specific surface marker CD44 by phage display. Mol Biotechnol 51:212–220
Park YS, Huh JW, Lee JH, Kim HR (2012b) shRNA against CD44 inhibits cell proliferation, invasion and migration, and promotes apoptosis of colon carcinoma cells. Oncol Rep 27:339–346
Patel S, Shah K, Mirza S, Shah K, Rawal R (2016) Circulating tumor stem like cells in oral squamous cell carcinoma: An unresolved paradox. Oral Oncol 62:139–146
Peck D, Isacke CM (1998) Hyaluronan-dependent cell migration can be blocked by a CD44 cytoplasmic domain peptide containing a phosphoserine at position 325. J Cell Sci 111(Pt 11):1595–1601
Peng Y, Prater AR, Deutscher SL (2017) Targeting aggressive prostate cancer-associated CD44v6 using phage display selected peptides. Oncotarget 8:86747–86768
Piotrowicz RS, Damaj BB, Hachicha M, Incardona F, Howell SB, Finlayson M (2011) A6 peptide activates CD44 adhesive activity, induces FAK and MEK phosphorylation, and inhibits the migration and metastasis of CD44-expressing cells. Mol Cancer Ther 10:2072–2082
Porsch H, Bernert B, Mehic M, Theocharis AD, Heldin CH, Heldin P (2013) Efficient TGFbeta-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition depends on hyaluronan synthase HAS2. Oncogene 32:4355–4365
Qian H, Xia L, Ling P, Waxman S, Jing Y (2012) CD44 ligation with A3D8 antibody induces apoptosis in acute myeloid leukemia cells through binding to CD44s and clustering lipid rafts. Cancer Biol Ther 13:1276–1283
Reinke LM, Xu Y, Cheng C (2012) Snail represses the splicing regulator epithelial splicing regulatory protein 1 to promote epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Biol Chem 287:36435–36442
Rilla K, Oikari S, Jokela TA, Hyttinen JM, Karna R, Tammi RH, Tammi MI (2013) Hyaluronan synthase 1 (HAS1) requires higher cellular UDP-GlcNAc concentration than HAS2 and HAS3. J Biol Chem 288:5973–5983
Rodriguez MM, Fiore E, Bayo J, Atorrasagasti C, Garcia M, Onorato A, Dominguez L, Malvicini M, Mazzolini G (2018) 4Mu decreases CD47 expression on hepatic cancer stem cells and primes a potent antitumor T cell response induced by interleukin-12. Mol Ther 26:2738–2750
Sadvakassova G, Dobocan MC, Congote LF (2009) Osteopontin and the C-terminal peptide of thrombospondin-4 compete for CD44 binding and have opposite effects on CD133+ cell colony formation. BMC Res Notes 2:215
Seki K, Yamaguchi A, Goi T, Nakagawara G, Matsukawa S, Urano T, Furukawa K (1997) Inhibition of liver metastasis formation by anti-CD44 variant exon 9 monoclonal antibody. Int J Oncol 11:1257–1261
Shabani Ravari N, Goodarzi N, Alvandifar F, Amini M, Souri E, Khoshayand MR, Hadavand Mirzaie Z, Atyabi F, Dinarvand R (2016) Fabrication and biological evaluation of chitosan coated hyaluronic acid-docetaxel conjugate nanoparticles in CD44(+) cancer cells. Daru 24:21
Shah KN, Ditto AJ, Crowder DC, Overmeyer JH, Tavana H, Maltese WA, Yun YH (2017) Receptor-mediated attachment and uptake of hyaluronan conjugates by breast cancer cells. Mol Pharm 14:3968–3977
Shao J, Fan W, Ma B, Wu Y (2016) Breast cancer stem cells expressing different stem cell markers exhibit distinct biological characteristics. Mol Med Rep 14:4991–4998
Shuttleworth TL, Wilson MD, Wicklow BA, Wilkins JA, Triggs-Raine BL (2002) Characterization of the murine hyaluronidase gene region reveals complex organization and cotranscription of Hyal1 with downstream genes, Fus2 and Hyal3. J Biol Chem 277:23008–23018
Skandalis SS, Kozlova I, Engstrom U, Hellman U, Heldin P (2010) Proteomic identification of CD44 interacting proteins. IUBMB Life 62:833–840
Skandalis SS, Karalis TT, Chatzopoulos A, Karamanos NK (2019) Hyaluronan-CD44 axis orchestrates cancer stem cell functions. Cell Signal 63:109377
Skandalis SS, Karalis T, Heldin P (2020) Intracellular hyaluronan: importance for cellular functions. Semin Cancer Biol 62:20–30
Solis MA, Chen YH, Wong TY, Bittencourt VZ, Lin YC, Huang LL (2012) Hyaluronan regulates cell behavior: a potential niche matrix for stem cells. Biochem Res Int 2012:346972
Soltes L, Mendichi R, Kogan G, Schiller J, Stankovska M, Arnhold J (2006) Degradative action of reactive oxygen species on hyaluronan. Biomacromolecules 7:659–668
Song G, Liao X, Zhou L, Wu L, Feng Y, Han ZC (2004) HI44a, an anti-CD44 monoclonal antibody, induces differentiation and apoptosis of human acute myeloid leukemia cells. Leuk Res 28:1089–1096
Stamenkovic I, Yu Q (2009) Shedding light on proteolytic cleavage of CD44: the responsible sheddase and functional significance of shedding. J Invest Dermatol 129:1321–1324
Su J, Wu S, Wu H, Li L, Guo T (2016) CD44 is functionally crucial for driving lung cancer stem cells metastasis through Wnt/beta-catenin-FoxM1-twist signaling. Mol Carcinog 55:1962–1973
Surace C, Arpicco S, Dufay-Wojcicki A, Marsaud V, Bouclier C, Clay D, Cattel L, Renoir JM, Fattal E (2009) Lipoplexes targeting the CD44 hyaluronic acid receptor for efficient transfection of breast cancer cells. Mol Pharm 6:1062–1073
Takahashi Y, Li L, Kamiryo M, Asteriou T, Moustakas A, Yamashita H, Heldin P (2005) Hyaluronan fragments induce endothelial cell differentiation in a CD44- and CXCL1/GRO1- dependent manner. J Biol Chem 280:24195–24204
Takei J, Kaneko MK, Ohishi T, Hosono H, Nakamura T, Yanaka M, Sano M, Asano T, Sayama Y, Kawada M, Harada H, Kato Y (2020) A defucosylated antiCD44 monoclonal antibody 5mG2af exerts antitumor effects in mouse xenograft models of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol Rep 44:1949–1960
Tan PH, Santos EB, Rossbach HC, Sandmaier BM (1993) Enhancement of natural killer activity by an antibody to CD44. J Immunol 150:812–820
Thankamony SP, Knudson W (2006) Acylation of CD44 and its association with lipid rafts are required for receptor and hyaluronan endocytosis. J Biol Chem 281:34601–34609
Theocharis AD, Skandalis SS, Gialeli C, Karamanos NK (2016) Extracellular matrix structure. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 97:4–27
Tirella A, Kloc-Muniak K, Good L, Ridden J, Ashford M, PURI, S. & Tirelli, N. (2019) CD44 targeted delivery of siRNA by using HA-decorated nanotechnologies for KRAS silencing in cancer treatment. Int J Pharm 561:114–123
Torronen K, Nikunen K, Karna R, Tammi M, Tammi R, Rilla K (2014) Tissue distribution and subcellular localization of hyaluronan synthase isoenzymes. Histochem Cell Biol 141:17–31
Tremmel M, Matzke A, Albrecht I, Laib AM, Olaku V, Ballmer-Hofer K, Christofori G, Heroult M, Augustin HG, Ponta H, Orian-Rousseau V (2009) A CD44v6 peptide reveals a role of CD44 in VEGFR-2 signaling and angiogenesis. Blood 114:5236–5244
Ugarte-Berzal E, Bailon E, Amigo-Jimenez I, Albar JP, Garcia-Marco JA, Garcia-Pardo A (2014) A novel CD44-binding peptide from the pro-matrix metalloproteinase-9 hemopexin domain impairs adhesion and migration of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) cells. J Biol Chem 289:15340–15349
Vahidian F, Safarzadeh E, Mohammadi A, Najjary S, Mansoori B, Majidi J, Babaloo Z, Aghanejad A, Shadbad MA, Mokhtarzadeh A, Baradaran B (2020) siRNA-mediated silencing of CD44 delivered by jet Pei enhanced doxorubicin chemo sensitivity and altered miRNA expression in human breast cancer cell line (MDA-MB468). Mol Biol Rep 47:9541–9551
Valentine A, O’rourke M, Yakkundi A, Worthington J, Hookham M, Bicknell R, McCarthy HO, McClelland K, McCallum L, Dyer H, McKeen H, Waugh DJ, Roberts J, McGregor J, Cotton G, James I, Harrison T, Hirst DG, Robson T (2011) FKBPL and peptide derivatives: novel biological agents that inhibit angiogenesis by a CD44- dependent mechanism. Clin Cancer Res 17:1044–1056
Van Hal NL, Van Dongen GA, Rood-Knippels EM, Van Der Valk P, Snow GB, Brakenhoff RH (1996) Monoclonal antibody U36, a suitable candidate for clinical immunotherapy of squamous-cell carcinoma, recognizes a CD44 isoform. Int J Cancer 68:520–527
Varghese OP, Sun W, Hilborn J, Ossipov DA (2009) In situ cross-linkable high molecular weight hyaluronan-bisphosphonate conjugate for localized delivery and cell-specific targeting: a hydrogel linked prodrug approach. J Am Chem Soc 131:8781–8783
Vey N, Delaunay J, Martinelli G, Fiedler W, Raffoux E, Prebet T, Gomez-Roca C, Papayannidis C, Kebenko M, Paschka P, Christen R, Guarin E, Broske AM, Baehner M, Brewster M, Walz AC, Michielin F, Runza V, Meresse V, Recher C (2016) Phase I clinical study of RG7356, an anti-CD44 humanized antibody, in patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Oncotarget 7:32532–32542
Vigetti D, Clerici M, Deleonibus S, Karousou E, Viola M, Moretto P, Heldin P, Hascall VC, De Luca G, Passi A (2011) Hyaluronan synthesis is inhibited by adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase through the regulation of HAS2 activity in human aortic smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem 286:7917–7924
Vigetti D, Deleonibus S, Moretto P, Karousou E, Viola M, Bartolini B, Hascall VC, Tammi M, De Luca G, Passi A (2012) Role of UDP-N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) and O-GlcNAcylation of hyaluronan synthase 2 in the control of chondroitin sulfate and hyaluronan synthesis. J Biol Chem 287:35544–35555
Vugts DJ, Heuveling DA, Stigter-Van Walsum M, Weigand S, Bergstrom M, Van Dongen GA, Nayak TK (2014) Preclinical evaluation of 89Zr-labeled anti-CD44 monoclonal antibody RG7356 in mice and cynomolgus monkeys: prelude to phase 1 clinical studies. MAbs 6:567–575
Vyas D, Lopez-Hisijos N, Gandhi S, El-Dakdouki M, Basson MD, Walsh MF, Huang X, Vyas AK, Chaturvedi LS (2015) Doxorubicin-hyaluronan conjugated super-paramagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (DOX-HA-SPION) enhanced cytoplasmic uptake of doxorubicin and modulated apoptosis, IL-6 release and NF-kappaB activity in human MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 15:6413–6422
Wang SJ, Wreesmann VB, Bourguignon LY (2007) Association of CD44 V3-containing isoforms with tumor cell growth, migration, matrix metalloproteinase expression, and lymph node metastasis in head and neck cancer. Head Neck 29:550–558
Wang A, Midura RJ, Vasanji A, Wang AJ, Hascall VC (2014) Hyperglycemia diverts dividing osteoblastic precursor cells to an adipogenic pathway and induces synthesis of a hyaluronan matrix that is adhesive for monocytes. J Biol Chem 289:11410–11420
Wang H, Zhu Z, Zhang G, Lin F, Liu Y, Zhang Y, Feng J, Chen W, Meng Q, Chen L (2019) AS1411 aptamer/hyaluronic acid-bifunctionalized microemulsion co-loading shikonin and docetaxel for enhanced antiglioma therapy. J Pharm Sci 108:3684–3694
Wang Z, Li Y, Wang Y, Wu D, Lau AHY, Zhao P, Zou C, Dai Y, Chan FL (2020) Targeting prostate cancer stem-like cells by an immunotherapeutic platform based on immunogenic peptide-sensitized dendritic cells-cytokine-induced killer cells. Stem Cell Res Ther 11:123
Wang Y, Gao D, Liu Y, Guo X, Chen S, Zeng L, Ma J, Zhang X, Tian Z, Yang Z (2021) Immunogenic-cell-killing and immunosuppression-inhibiting nanomedicine. Bioact Mater 6:1513–1527
Wei W, Hu H, Tan H, Chow LW, Yip AY, Loo WT (2012) Relationship of CD44+CD24−/low breast cancer stem cells and axillary lymph node metastasis. J Transl Med 10(Suppl 1):S6
Weigand S, Herting F, Maisel D, Nopora A, Voss E, Schaab C, Klammer M, Tebbe A (2012) Global quantitative phosphoproteome analysis of human tumor xenografts treated with a CD44 antagonist. Cancer Res 72:4329–4339
Weigel PH (2015) Hyaluronan synthase: the mechanism of initiation at the reducing end and a pendulum model for polysaccharide translocation to the cell exterior. Int J Cell Biol 2015:367579
Wiranowska M, Ladd S, Moscinski LC, Hill B, Haller E, Mikecz K, Plaas A (2010) Modulation of hyaluronan production by CD44 positive glioma cells. Int J Cancer 127:532–542
Wu J, Deng C, Meng F, Zhang J, Sun H, Zhong Z (2017) Hyaluronic acid coated PLGA nanoparticulate docetaxel effectively targets and suppresses orthotopic human lung cancer. J Control Release 259:76–82
Xiao Z, Wan J, Nur AA, Dou P, Mankin H, Liu T, Ouyang Z (2018) Targeting CD44 by CRISPR-Cas9 in multi-drug resistant osteosarcoma cells. Cell Physiol Biochem 51:1879–1893
Xu H, Tian Y, Yuan X, Wu H, Liu Q, Pestell RG, Wu K (2015) The role of CD44 in epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer development. Onco Targets Ther 8:3783–3792
Xu J, Zhang Y, Xu J, Wang M, Liu G, Wang J, Zhao X, Qi Y, Shi J, Cheng K, Li Y, Qi S, Nie G (2019) Reversing tumor stemness via orally targeted nanoparticles achieves efficient colon cancer treatment. Biomaterials 216:119247
Xu K, Yao H, Fan D, Zhou L, Wei S (2021) Hyaluronic acid thiol modified injectable hydrogel: synthesis, characterization, drug release, cellular drug uptake and anticancer activity. Carbohydr Polym 254:117286
Yaghobi Z, Movassaghpour A, Talebi M, Abdoli Shadbad M, Hajiasgharzadeh K, Pourvahdani S, Baradaran B (2021) The role of CD44 in cancer chemoresistance: A concise review. Eur J Pharmacol 903:174147
Yakkundi A, McCallum L, O’kane A, Dyer H, Worthington J, McKeen HD, McClements L, Elliott C, McCarthy HO, Hirst DG, Robson T (2013) The anti-migratory effects of FKBPL and its peptide derivative, AD-01: regulation of CD44 and the cytoskeletal pathway. PLoS One 8:e55075
Yamaguchi Y, Yamamoto H, Tobisawa Y, Irie F (2019) TMEM2: A missing link in hyaluronan catabolism identified? Matrix Biol 78-79:139–146
Yamamoto H, Tobisawa Y, Inubushi T, Irie F, Ohyama C, Yamaguchi Y (2017) A mammalian homolog of the zebrafish transmembrane protein 2 (TMEM2) is the long-sought-after cell-surface hyaluronidase. J Biol Chem 292:7304–7313
Yan Y, Li Z, Kong X, Jia Z, Zuo X, Gagea M, Huang S, Wei D, Xie K (2016) KLF4-mediated suppression of CD44 Signaling negatively impacts pancreatic cancer stemness and metastasis. Cancer Res 76:2419–2431
Yang X, Sarvestani SK, Moeinzadeh S, He X, Jabbari E (2013) Effect of CD44 binding peptide conjugated to an engineered inert matrix on maintenance of breast cancer stem cells and tumorsphere formation. PLoS One 8:e59147
Yang Y, Zhao X, Li X, Yan Z, Liu Z, Li Y (2017) Effects of anti-CD44 monoclonal antibody IM7 carried with chitosan polylactic acid-coated nano-particles on the treatment of ovarian cancer. Oncol Lett 13:99–104
Yao H, Sun L, Li J, Zhou X, Li R, Shao R, Zhang Y, Li L (2020) A novel therapeutic siRNA nanoparticle designed for dual-targeting CD44 and Gli1 of gastric cancer stem cells. Int J Nanomedicine 15:7013–7034
Yasothamani V, Karthikeyan L, Shyamsivappan S, Haldorai Y, Seetha D, Vivek R (2021) Synergistic effect of photothermally targeted NIR-responsive nanomedicine-induced immunogenic cell death for effective triple negative breast cancer therapy. Biomacromolecules 22:2472–2490
Yasuda M, Tanaka Y, Fujii K, Yasumoto K (2001) CD44 stimulation down-regulates Fas expression and Fas-mediated apoptosis of lung cancer cells. Int Immunol 13:1309–1319
Yoo J, Rejinold NS, Lee D, Noh I, Koh WG, Jon S, Kim YC (2020) CD44-mediated methotrexate delivery by hyaluronan-coated nanoparticles composed of a branched cell-penetrating peptide. ACS Biomater Sci Eng 6:494–504
Yoshida H, Okada Y (2019) Role of HYBID (hyaluronan binding protein involved in hyaluronan depolymerization), alias KIAA1199/CEMIP, in hyaluronan degradation in normal and photoaged skin. Int J Mol Sci 20:5804
Yoshida H, Nagaoka A, Kusaka-Kikushima A, Tobiishi M, Kawabata K, Sayo T, Sakai S, Sugiyama Y, Enomoto H, Okada Y, Inoue S (2013a) KIAA1199, a deafness gene of unknown function, is a new hyaluronan binding protein involved in hyaluronan depolymerization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110:5612–5617
Yoshida H, Nagaoka A, Nakamura S, Sugiyama Y, Okada Y, Inoue S (2013b) Murine homologue of the human KIAA1199 is implicated in hyaluronan binding and depolymerization. FEBS Open Bio 3:352–356
Yu Q, Stamenkovic I (1999) Localization of matrix metalloproteinase 9 to the cell surface provides a mechanism for CD44-mediated tumor invasion. Genes Dev 13:35–48
Zada AA, Singh SM, Reddy VA, Elsasser A, Meisel A, Haferlach T, Tenen DG, Hiddemann W, Behre G (2003) Downregulation of c-Jun expression and cell cycle regulatory molecules in acute myeloid leukemia cells upon CD44 ligation. Oncogene 22:2296–2308
Zhang S, Wu CC, Fecteau JF, Cui B, Chen L, Zhang L, Wu R, Rassenti L, Lao F, Weigand S, Kipps TJ (2013) Targeting chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells with a humanized monoclonal antibody specific for CD44. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110:6127–6132
Zhang D, Jia H, Wang Y, Li WM, Hou YC, Yin SW, Wang TD, He SX, Lu SY (2015) A CD44 specific peptide developed by phage display for targeting gastric cancer. Biotechnol Lett 37:2311–2320
Zhang D, Jia H, Li W, Hou Y, Lu S, He S (2016) Screening and identification of a phage display derived peptide that specifically binds to the CD44 protein region encoded by variable exons. J Biomol Screen 21:44–53
Zhao C, Thompson BJ, Chen K, Gao F, Blouw B, Marella M, Zimmerman S, Kimbler T, Garrovillo S, Bahn J, Huang L, Huang Z, Shepard HM, Rosengren S, Thanos CD, Maneval DC (2019) The growth of a xenograft breast cancer tumor model with engineered hyaluronan-accumulating stroma is dependent on hyaluronan and independent of CD44. Oncotarget 10:6561–6576
Zhao Y, Wang K, Zheng Y, Zeng X, Lim YC, Liu T (2020) Co-delivery of salinomycin and curcumin for cancer stem cell treatment by inhibition of cell proliferation, cell cycle arrest, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Front Chem 8:601649
Zhong Y, Meng F, Deng C, Mao X, Zhong Z (2017) Targeted inhibition of human hematological cancers in vivo by doxorubicin encapsulated in smart lipoic acid-crosslinked hyaluronic acid nanoparticles. Drug Deliv 24:1482–1490
Zhong W, Pang L, Feng H, Dong H, Wang S, Cong H, Shen Y, Bing Y (2020) Recent advantage of hyaluronic acid for anti-cancer application: a review of “3S” transition approach. Carbohydr Polym 238:116204
Zhou L, Sheng D, Deng Q, Wang D, Liu S (2018) Development of a novel method for rapid cloning of shRNA vectors, which successfully knocked down CD44 in mesenchymal triple-negative breast cancer cells. Cancer Commun (Lond) 38:57
Zhu C, Zhang H, Li W, Luo L, Guo X, Wang Z, Kong F, Li Q, Yang J, Du Y, You J (2018) Suppress orthotopic colon cancer and its metastasis through exact targeting and highly selective drug release by a smart nanomicelle. Biomaterials 161:144–153
Zoller M (2011) CD44: can a cancer-initiating cell profit from an abundantly expressed molecule? Nat Rev Cancer 11:254–267
Zoller M (2015) CD44, hyaluronan, the hematopoietic stem cell, and leukemia-initiating cells. Front Immunol 6:235
Zoltan-Jones A, Huang L, Ghatak S, Toole BP (2003) Elevated hyaluronan production induces mesenchymal and transformed properties in epithelial cells. J Biol Chem 278:45801–45810
Zou L, Song X, Yi T, Li S, Deng H, Chen X, Li Z, Bai Y, Zhong Q, Wei Y, Zhao X (2013) Administration of PLGA nanoparticles carrying shRNA against focal adhesion kinase and CD44 results in enhanced antitumor effects against ovarian cancer. Cancer Gene Ther 20:242–250
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Karalis, T.T., Skandalis, S.S. (2022). Exploiting Hyaluronan-CD44 Network in Tumor Therapy. In: Kovalszky, I., Franchi, M., Alaniz, L.D. (eds) The Extracellular Matrix and the Tumor Microenvironment. Biology of Extracellular Matrix, vol 11. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-99708-3_18
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-99708-3_18
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-99707-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-99708-3
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)