Abstract
Several deep learning based medical image segmentation methods use U-Net architecture and its variants as a baseline model. This is because U-Net has been successfully applied to many other tasks. It was noticed that the U-Net-based models are unable to extract features for segmenting small masks or fine edges.
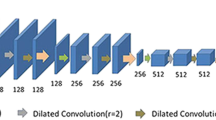
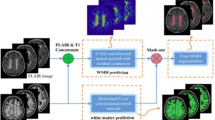
To overcome this issue, we propose a new 3D U-Net-based model, baptized Y- Net. In this model, we make use of dilated convolution which has shown its effectiveness in grasping different features at different scales. This allows us to capture more information from small anatomical parts.
Our model is assessed on MRbrains13 dataset for brain tissue segmentation task. Compared to the traditional UNet 3D, the obtained results show that the proposed model performs better in segmenting cerebrospinal fluid, white matter and gray matter tissues.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chang, J., Zhang, X., Ye, M., Huang, D., Wang, P., Yao, C.: Brain tumor segmentation based on 3D UNET with multi-class focal loss. In: 2018 11th International Congress on Image and Signal Processing, BioMedical Engineering and Informatics (CISP-BMEI), pp. 1–5. IEEE (2018)
Chen, W., Liu, B., Peng, S., Sun, J., Qiao, X.: S3D-UNet: separable 3D U-Net for brain tumor segmentation. In: Crimi, A., Bakas, S., Kuijf, H., Keyvan, F., Reyes, M., van Walsum, T. (eds.) BrainLes 2018. LNCS, vol. 11384, pp. 358–368. Springer, Cham (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-11726-9_32
Chim, S., Lee, J.G., Park, H.H.: Dilated skip convolution for facial landmark detection. Sensors 19(24), 5350 (2019)
Çiçek, Ö., Abdulkadir, A., Lienkamp, S.S., Brox, T., Ronneberger, O.: 3D U-Net: learning dense volumetric segmentation from sparse annotation. In: Ourselin, S., Joskowicz, L., Sabuncu, M.R., Unal, G., Wells, W. (eds.) MICCAI 2016. LNCS, vol. 9901, pp. 424–432. Springer, Cham (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46723-8_49
Feng, X., Meyer, C.: Patch-based 3D U-NET for brain tumor segmentation. In: International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (MICCAI), pp. 67–72 (2017)
Hamaguchi, R., Fujita, A., Nemoto, K., Imaizumi, T., Hikosaka, S.: Effective use of dilated convolutions for segmenting small object instances in remote sensing imagery. In: 2018 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), pp. 1442–1450. IEEE (2018)
Lei, Z., Qi, L., Wei, Y., Zhou, Y.: Infant brain MRI segmentation with dilated convolution pyramid down sampling and self-attention. arXiv preprint arXiv:1912.12570 (2019)
Li, J., Yu, Z.L., Gu, Z., Liu, H., Li, Y.: MMAN: multi-modality aggregation network for brain segmentation from MR images. Neurocomputing 358, 10–19 (2019)
Long, J., Shelhamer, E., Darrell, T.: Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 3431–3440 (2015)
Mendrik, A.M., et al.: MRBrainS challenge: online evaluation framework for brain image segmentation in 3T MRI scans. In: Computational Intelligence and Neuroscience 2015 (2015)
Peng, S., Chen, W., Sun, J., Liu, B.: Multi-scale 3D U-Nets: an approach to automatic segmentation of brain tumor. Int. J. Imaging Syst. Technol. 30(1), 5–17 (2020)
Perone, C.S., Calabrese, E., Cohen-Adad, J.: Spinal cord gray matter segmentation using deep dilated convolutions. Sci. Rep. 8(1), 1–13 (2018)
Rehman, M.U., Cho, S., Kim, J.H., Chong, K.T.: BU-Net: brain tumor segmentation using modified U-Net architecture. Electronics 9(12), 2203 (2020)
Ronneberger, O., Fischer, P., Brox, T.: U-Net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: Navab, N., Hornegger, J., Wells, W.M., Frangi, A.F. (eds.) MICCAI 2015. LNCS, vol. 9351, pp. 234–241. Springer, Cham (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-24574-4_28
Tiu, E.: Metrics to evaluate your semantic segmentation model. Towards datascience, recuperado de (2019). https://towardsdatascience.com/metrics-to-evaluateyour-semantic-segmentation-model-6bcb99639aa2#:\(^{\sim }\): text= Simply% 20put% 2C% 20the% 20Dice% 20Coefficient, of% 2 0pixels% 20in% 20both% 20images 8
Valanarasu, J.M.J., Sindagi, V.A., Hacihaliloglu, I., Patel, V.M.: KiU-Net: overcomplete convolutional architectures for biomedical image and volumetric segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2010.01663 (2020)
Yang, B., Zhang, W.: FD-FCN: 3D fully dense and fully convolutional network for semantic segmentation of brain anatomy. arXiv preprint arXiv:1907.09194 (2019)
Zeng, G., Zheng, G.: Multi-stream 3D FCN with multi-scale deep supervision for multi-modality isointense infant brain MR image segmentation. In: 2018 IEEE 15th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI 2018), pp. 136–140. IEEE (2018)
Zhang, Q., Cui, Z., Niu, X., Geng, S., Qiao, Y.: Image segmentation with pyramid dilated convolution based on ResNet and U-Net. In: Liu, D., Xie, S., Li, Y., Zhao, D., El-Alfy, E.S. (eds.) ICONIP 2017. LNCS, vol. 10635, pp. 364–372. Springer, Heidelberg (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-70096-0_38
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Kemassi, O., Maamri, O., Bouanane, K., Kriker, O. (2022). Dilated Convolutions Based 3D U-Net for Multi-modal Brain Image Segmentation. In: Lejdel, B., Clementini, E., Alarabi, L. (eds) Artificial Intelligence and Its Applications. AIAP 2021. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, vol 413. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-96311-8_39
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-96311-8_39
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-96310-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-96311-8
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)