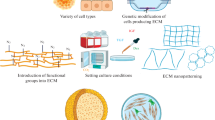
Abstract
Extracellular matrix (ECM), the major component of tissue, plays a critical role in tissue engineering and regeneration. It is well-known that tissue-derived ECM, via serving as a biological scaffold, is actively involved in tissue engineering by guiding stem cells’ specific lineage differentiation. In the last decade, cell-derived ECM (CDM) has become more attractive in promoting stem cells’ rejuvenation in terms of proliferation and differentiation preference through acting as an ex vivo culture substrate. Given the importance of providing a large amount of high-quality stem cells for tissue engineering, this chapter summarizes recent progress in the influence of CDM-donated cells on stem cells’ rejuvenation, the influence of CDM culture microenvironment on stem cells’ differentiation, and the contribution of CDM on stem cells’ rejuvenation and tissue regeneration. The goal of this chapter is to help readers better understand the interaction between stem cells and matrix microenvironment, which facilitates promotion of stem cells’ quantity and quality in developing high-quality tissue-engineered tissues.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antich C, Jiménez G, de Vicente J, et al. Development of a biomimetic hydrogel based on predifferentiated mesenchymal stem-cell-derived ECM for cartilage tissue engineering. Adv Healthc Mater. 2021;10:e2001847.
Aro E, Khatri R, Gerard-O’Riley R, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF-1) but not HIF-2 is essential for hypoxic induction of collagen prolyl 4-hydroxylases in primary newborn mouse epiphyseal growth plate chondrocytes. J Biol Chem. 2012;287:37134–44.
Badylak SF. The extracellular matrix as a scaffold for tissue reconstruction. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2002;13:377–83.
Bateman JF, Cole WG, Pillow JJ, et al. Induction of procollagen processing in fibroblast cultures by neutral polymers. J Biol Chem. 1986;261:4198–203.
Bissell MJ, Hall HG, Parry G. How does the extracellular matrix direct gene expression? J Theor Biol. 1982;99:31–68.
Border WA, Ruoslahti E. Transforming growth factor-beta in disease: the dark side of tissue repair. J Clin Invest. 1992;90:1–7.
Bracaglia LG, Fisher JP. Extracellular matrix-based biohybrid materials for engineering compliant, matrix-dense tissues. Adv Healthc Mater. 2015;4:2475–87.
Carvalho MS, Alves L, Bogalho I, et al. Impact of donor age on the osteogenic supportive capacity of mesenchymal stromal cell-derived extracellular matrix. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:747521.
Cha MH, Do SH, Park GR, et al. Induction of re-differentiation of passaged rat chondrocytes using a naturally obtained extracellular matrix microenvironment. Tissue Eng Part A. 2013;19:978–88.
Chan WW, Yu F, Le QB, et al. Towards biomanufacturing of cell-derived matrices. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22:11929.
Cheng CW, Solorio LD, Alsberg E. Decellularized tissue and cell-derived extracellular matrices as scaffolds for orthopaedic tissue engineering. Biotechnol Adv. 2014;32:462–84.
Cheng HW, Yuan MT, Li CW, et al. Cell-derived matrices (CDM)-methods, challenges and applications. Methods Cell Biol. 2020;156:235–58.
Cigognini D, Gaspar D, Kumar P, et al. Macromolecular crowding meets oxygen tension in human mesenchymal stem cell culture – a step closer to physiologically relevant in vitro organogenesis. Sci Rep. 2016;6:30746.
Crapo PM, Gilbert TW, Badylak SF. An overview of tissue and whole organ decellularization processes. Biomaterials. 2011;32:3233–43.
Cun X, Hosta-Rigau L. Topography: a biophysical approach to direct the fate of mesenchymal stem cells in tissue engineering applications. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2020;10:2070.
Dai X, Shen L. Advances and Trends in Omics Technology Development. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022;9:911861
Datta N, Holtorf HL, Sikavitsas VI, et al. Effect of bone extracellular matrix synthesized in vitro on the osteoblastic differentiation of marrow stromal cells. Biomaterials. 2005;26:971–7.
Decaris ML, Mojadedi A, Bhat A, et al. Transferable cell-secreted extracellular matrices enhance osteogenic differentiation. Acta Biomater. 2012;8:744–52.
Dimri GP, Lee X, Basile G, et al. A biomarker that identifies senescent human cells in culture and in aging skin in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995;92:9363–7.
Du HC, Jiang L, Geng WX, et al. Growth factor-reinforced ECM fabricated from chemically hypoxic MSC sheet with improved in vivo wound repair activity. Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017:2578017.
Engler AJ, Sen S, Sweeney HL, et al. Matrix elasticity directs stem cell lineage specification. Cell. 2006;126:677–89.
Feng G, Li L, Liu H, et al. Hypoxia differentially regulates human nucleus pulposus and annulus fibrosus cell extracellular matrix production in 3D scaffolds. Osteoarthr Cartil. 2013;21:582–8.
Fitzpatrick LE, McDevitt TC. Cell-derived matrices for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine applications. Biomater Sci. 2015;3:12–24.
Funamoto S, Nam K, Kimura T, et al. The use of high-hydrostatic pressure treatment to decellularize blood vessels. Biomaterials. 2010;31:3590–5.
Gao G, Chen S, Pei YA, et al. Impact of perlecan, a core component of basement membrane, on regeneration of cartilaginous tissues. Acta Biomater. 2021;135:13–26.
Gilbert PM, Havenstrite KL, Magnusson KE, et al. Substrate elasticity regulates skeletal muscle stem cell self-renewal in culture. Science. 2010;329:1078–81.
Gilpin A, Yang Y. Decellularization strategies for regenerative medicine: from processing techniques to applications. Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017:9831534.
Grinnell F, Fukamizu H, Pawelek P, et al. Collagen processing, crosslinking, and fibril bundle assembly in matrix produced by fibroblasts in long-term cultures supplemented with ascorbic acid. Exp Cell Res. 1989;181:483–1491.
Han S, Li YY, Chan BP. Protease inhibitors enhance extracellular collagen fibril deposition in human mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015;6:197.
He F, Pei M. Rejuvenation of nucleus pulposus cells using extracellular matrix deposited by synovium-derived stem cells. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2012;37:459–69.
He F, Pei M. Extracellular matrix enhances differentiation of adipose stem cells from infrapatellar fat pad toward chondrogenesis. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2013;7:73–84.
He F, Chen X, Pei M. Reconstruction of an in vitro tissue-specific microenvironment to rejuvenate synovium-derived stem cells for cartilage tissue engineering. Tissue Eng Part A. 2009;15:3809–21.
He F, Liu X, Xiong K, et al. Extracellular matrix modulates the biological effects of melatonin in mesenchymal stem cells. J Endocrinol. 2014;223:167–80.
Hong Y, Huber A, Takanari K, et al. Mechanical properties and in vivo behavior of a biodegradable synthetic polymer microfiber-extracellular matrix hydrogel biohybrid scaffold. Biomaterials. 2011;32:3387–94.
Ignotz RA, Massagué J. Transforming growth factor-beta stimulates the expression of fibronectin and collagen and their incorporation into the extracellular matrix. J Biol Chem. 1986;261:4337–45.
Jin CZ, Park SR, Choi BH, et al. In vivo cartilage tissue engineering using a cell-derived extracellular matrix scaffold. Artif Organs. 2007;31:183–92.
Jones BA, Pei M. Synovium-derived stem cells: a tissue-specific stem cell for cartilage engineering and regeneration. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2012;18:301–11.
Kang Y, Kim S, Khademhosseini A, et al. Creation of bony microenvironment with CaP and cell-derived ECM to enhance human bone-marrow MSC behavior and delivery of BMP-2. Biomaterials. 2011;32:6119–30.
Kim IG, Hwang MP, Du P, et al. Bioactive cell-derived matrices combined with polymer mesh scaffold for osteogenesis and bone healing. Biomaterials. 2015;50:75–86.
Kimura T, Yasui N, Ohsawa S, et al. Chondrocytes embedded in collagen gels maintain cartilage phenotype during long-term cultures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1984;186:231–9.
Kretlow JD, Jin YQ, Liu W, et al. Donor age and cell passage affects differentiation potential of murine bone marrow-derived stem cells. BMC Cell Biol. 2008;9:60.
Kumar P, Satyam A, Fan X, et al. Macromolecularly crowded in vitro microenvironments accelerate the production of extracellular matrix-rich supramolecular assemblies. Sci Rep. 2015a;5:8729.
Kumar P, Satyam A, Fan X, et al. Accelerated development of supramolecular corneal stromal-like assemblies from corneal fibroblasts in the presence of macromolecular crowders. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2015b;21:660–70.
Kumar P, Satyam A, Cigognini D, et al. Low oxygen tension and macromolecular crowding accelerate extracellular matrix deposition in human corneal fibroblast culture. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2018;12:6–18.
Lee HJ, Kim YB, Ahn SH, et al. A new approach for fabricating collagen/ECM-based bioinks using preosteoblasts and human adipose stem cells. Adv Healthc Mater. 2015;4:1359–68.
Li J, Pei M. Optimization of an in vitro three-dimensional microenvironment to reprogram synovium-derived stem cells for cartilage tissue engineering. Tissue Eng Part A. 2011;17:703–12.
Li JT, Pei M. Cell senescence: a challenge in cartilage engineering and regeneration. Tissue Eng Part B. 2012;18:270–87.
Li J, Pei M. A protocol to prepare decellularized stem cell matrix for rejuvenation of cell expansion and cartilage regeneration. Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1577:147–54.
Li WJ, Laurencin CT, Caterson EJ, et al. Electrospun nanofibrous structure: a novel scaffold for tissue engineering. J Biomed Mater Res. 2002;60:613–21.
Li J, Hansen KC, Zhang Y, et al. Rejuvenation of chondrogenic potential in a young stem cell microenvironment. Biomaterials. 2014;35:642–53.
Li M, Chen X, Yan J, et al. Inhibition of osteoclastogenesis by stem cell-derived extracellular matrix through modulation of intracellular reactive oxygen species. Acta Biomater. 2018;71:118–31.
Li J, Narayanan K, Zhang Y, et al. Role of lineage-specific matrix in stem cell chondrogenesis. Biomaterials. 2020a;231:119681.
Li L, Wei X, Wang D, et al. Positive effects of a young systemic environment and high growth differentiation factor 11 levels on chondrocyte proliferation and cartilage matrix synthesis in old mice. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020b;72:1123–33.
Liu X, Zhou L, Chen X, et al. Culturing on decellularized extracellular matrix enhances antioxidant properties of human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2016;61:437–48.
Liu C, Pei M, Li Q, et al. Decellularized extracellular matrix mediates tissue construction and regeneration. Front Med. 2022;16:56–82.
Lu H, Hoshiba T, Kawazoe N, et al. Cultured cell-derived extracellular matrix scaffolds for tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2011;32:9658–66.
Lu H, Hoshiba T, Kawazoe N, et al. Comparison of decellularization techniques for preparation of extracellular matrix scaffolds derived from three-dimensional cell culture. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2012;100:2507–16.
Lynch K, Pei M. Age associated communication between cells and matrix: a potential impact on stem cell-based tissue regeneration strategies. Organogenesis. 2014;10:289–98.
Mandal A, Clegg JR, Anselmo AC, et al. Hydrogels in the clinic. Bioeng Transl Med. 2020;5:e10158.
Mantha S, Pillai S, Khayambashi P, et al. Smart hydrogels in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. Materials (Basel). 2019;12:3323.
Marinkovic M, Sridharan R, Santarella F, et al. Optimization of extracellular matrix production from human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived fibroblasts for scaffold fabrication for application in wound healing. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2021;109:1803–11.
Matsiko A, Gleeson JP, O’Brien FJ. Scaffold mean pore size influences mesenchymal stem cell chondrogenic differentiation and matrix deposition. Tissue Eng Part A. 2015;21:486–97.
Murad S, Grove D, Lindberg KA, et al. Regulation of collagen synthesis by ascorbic acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981a;78:2879–82.
Murad S, Sivarajah A, Pinnell SR. Regulation of prolyl and lysyl hydroxylase activates in cultured human skin fibroblasts by ascorbic acid. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981b;101:868–75.
Murphy C, Mobasheri A, Táncos Z, et al. The potency of induced pluripotent stem cells in cartilage regeneration and osteoarthritis treatment. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018;1079:55–68.
Nellinger S, Mrsic I, Keller S, et al. Cell-derived and enzyme-based decellularized extracellular matrix exhibit compositional and structural differences that are relevant for its use as a biomaterial. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2022;119:1142–56.
Noh YK, Du P, Kim IG, et al. Polymer mesh scaffold combined with cell-derived ECM for osteogenesis of human mesenchymal stem cells. Biomater Res. 2016;20:6.
Ozguldez HO, Cha J, Hong Y, et al. Nanoengineered, cell-derived extracellular matrix influences ECM-related gene expression of mesenchymal stem cells. Biomater Res. 2018;22:32.
Pang K, Du L, Wu X. A rabbit anterior cornea replacement derived from acellular porcine cornea matrix, epithelial cells and keratocytes. Biomaterials. 2010;31:7257–65.
Pati F, Song TH, Rijal G, et al. Ornamenting 3D printed scaffolds with cell-laid extracellular matrix for bone tissue regeneration. Biomaterials. 2015;37:230–41.
Pei M. Environmental preconditioning rejuvenates adult stem cells’ proliferation and chondrogenic potential. Biomaterials. 2017;117:10–23.
Pei M, He F. Extracellular matrix deposited by synovium-derived stem cells delays replicative senescent chondrocyte dedifferentiation and enhances redifferentiation. J Cell Physiol. 2012;227:2163–74.
Pei M, Li JT, Shoukry M, et al. A review of decellularized stem cell matrix: a novel cell expansion system for cartilage tissue engineering. Eur Cell Mater. 2011a;22:333–43.
Pei M, He F, Kish VL. Expansion on extracellular matrix deposited by human bone marrow stromal cells facilitates stem cell proliferation and tissue-specific lineage potential. Tissue Eng Part A. 2011b;17:3067–76.
Pei M, He F, Wei L. Three-dimensional cell expansion substrate for cartilage tissue engineering and regeneration: a comparison in decellularized matrix deposited by synovium-derived stem cells and chondrocytes. J Tissue Sci Eng. 2011c;2:2.
Pei M, Shoukry M, Li J, et al. Modulation of in vitro microenvironment facilitates synovium-derived stem cell-based nucleus pulposus tissue regeneration. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2012;37:1538–47.
Pei M, Zhang Y, Li J, et al. Antioxidation of decellularized stem cell matrix promotes human synovium-derived stem cell-based chondrogenesis. Stem Cells Dev. 2013a;22:889–900.
Pei M, He F, Li J, et al. Repair of large animal partial-thickness cartilage defects through intraarticular injection of matrix-rejuvenated synovium-derived stem cells. Tissue Eng Part A. 2013b;19:1144–54.
Pei M, Li J, Zhang Y, et al. Expansion on a matrix deposited by nonchondrogenic urine stem cells strengthens the chondrogenic capacity of repeated-passage bone marrow stromal cells. Cell Tissue Res. 2014;356:391–403.
Pellegata AF, Asnaghi MA, Stefani I, et al. Detergent-enzymatic decellularization of swine blood vessels: insight on mechanical properties for vascular tissue engineering. Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:918753.
Pizzute T, Lynch K, Pei M. Impact of tissue-specific stem cells on lineage specific differentiation: a focus on musculoskeletal system. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2015;11:119–32.
Pizzute T, Zhang Y, He F, et al. Ascorbate-dependent impact on cell-derived matrix in modulation of stiffness and rejuvenation of infrapatellar fat derived stem cells toward chondrogenesis. Biomed Mater. 2016;11:045009.
Prewitz MC, Seib FP, von Bonin M, et al. Tightly anchored tissue-mimetic matrices as instructive stem cell microenvironments. Nat Methods. 2013;10:788–94.
Prewitz MC, Stißel A, Friedrichs J, et al. Extracellular matrix deposition of bone marrow stroma enhanced by macromolecular crowding. Biomaterials. 2015;73:60–9.
Rabbani M, Zakian N, Alimoradi N. Contribution of physical methods in decellularization of animal tissues. J Med Signals Sens. 2021;11:1–11.
Rashid R, Lim NS, Chee SM, et al. Novel use for polyvinylpyrrolidone as a macromolecular crowder for enhanced extracellular matrix deposition and cell proliferation. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2014;20:994–1002.
Reing JE, Brown BN, Daly KA, et al. The effects of processing methods upon mechanical and biologic properties of porcine dermal extracellular matrix scaffolds. Biomaterials. 2010;31:8626–33.
Risbud MV, Schipani E, Shapiro IM. Hypoxic regulation of nucleus pulposus cell survival: from niche to notch. Am J Pathol. 2010;176:1577–83.
Rothrauff BB, Yang G, Tuan RS. Tissue-specific bioactivity of soluble tendon-derived and cartilage-derived extracellular matrices on adult mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8:133.
Sart S, Jeske R, Chen X, et al. Engineering stem cell-derived extracellular matrices: decellularization, characterization, and biological function. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2020;26:402–22.
Satyam A, Kumar P, Fan X, et al. Macromolecular crowding meets tissue engineering by self-assembly: a paradigm shift in regenerative medicine. Adv Mater. 2014;26:3024–34.
Shamis Y, Hewitt KJ, Bear SE, et al. iPSC-derived fibroblasts demonstrate augmented production and assembly of extracellular matrix proteins. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2012;48:112–22.
Shanmugasundaram S, Chaudhry H, Arinzeh TL. Microscale versus nanoscale scaffold architecture for mesenchymal stem cell chondrogenesis. Tissue Eng Part A. 2011;17:831–40.
Sheridan WS, Duffy GP, Murphy BP. Optimum parameters for freeze-drying decellularized arterial scaffolds. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2013;19:981–90.
Shih YR, Tseng KF, Lai HY, et al. Matrix stiffness regulation of integrin-mediated mechanotransduction during osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. J Bone Miner Res. 2011;26:730–8.
Sun Y, Li W, Lu Z, et al. Rescuing replication and osteogenesis of aged mesenchymal stem cells by exposure to a young extracellular matrix. FASEB J. 2011;25:1474–85.
Sun Y, Wang TL, Toh WS, et al. The role of laminins in cartilaginous tissues: from development to regeneration. Eur Cell Mater. 2017;34:40–54.
Sun Y, Yan L, Chen S, et al. Functionality of decellularized matrix in cartilage regeneration: a comparison of tissue versus cell sources. Acta Biomater. 2018;74:56–73.
Thibault RA, Scott Baggett L, Mikos AG, et al. Osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells on pregenerated extracellular matrix scaffolds in the absence of osteogenic cell culture supplements. Tissue Eng Part A. 2010;16:431–40.
Throm AM, Liu WC, Lock CH, et al. Development of a cell-derived matrix: effects of epidermal growth factor in chemically defined culture. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2010;92:533–41.
Tour G, Wendel M, Tcacencu I. Cell-derived matrix enhances osteogenic properties of hydroxyapatite. Tissue Eng Part A. 2011;17:127–37.
Wakitani S, Imoto K, Yamamoto T, et al. Human autologous culture expanded bone marrow mesenchymal cell transplantation for repair of cartilage defects in osteoarthritic knees. Osteoarthr Cartil. 2002;10:199–206.
Wang X, Chen Z, Zhou B, et al. Cell-sheet-derived ECM coatings and their effects on BMSCs responses. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018;10:11508–18.
Wang Y, Chen S, Yan Z, et al. A prospect of cell immortalization combined with matrix microenvironmental optimization strategy for tissue engineering and regeneration. Cell Biosci. 2019a;9:7.
Wang Y, Fu Y, Yan Z, et al. Impact of fibronectin knockout on proliferation and differentiation of human infrapatellar fat pad-derived stem cells. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2019b;7:321.
Wang TL, Hill RC, Dzieciatkowska M, et al. Site dependent lineage preference of adipose stem cells. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8:237.
Wang Y, Hu G, Hill RC, et al. Matrix reverses immortalization-mediated stem cell fate determination. Biomaterials. 2021a;265:120387.
Wang Y, Pei YA, Sun Y, et al. Stem cells immortalized by hTERT perform differently from those immortalized by SV40LT in proliferation, differentiation, and reconstruction of matrix microenvironment. Acta Biomater. 2021b;136:184–98.
Wolchok JC, Tresco PA. Using growth factor conditioning to modify the properties of human cell derived extracellular matrix. Biotechnol Prog. 2012;28:1581–7.
Xing Q, Yates K, Tahtinen M, et al. Decellularization of fibroblast cell sheets for natural extracellular matrix scaffold preparation. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2015;21:77–87.
Yan J, Chen X, Pu C, et al. Synovium stem cell-derived matrix enhances anti-inflammatory properties of rabbit articular chondrocytes via the SIRT1 pathway. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020;106:110286.
Yang Q, Peng J, Guo Q, et al. A cartilage ECM-derived 3-D porous acellular matrix scaffold for in vivo cartilage tissue engineering with PKH26-labeled chondrogenic bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Biomaterials. 2008;29:2378–87.
Yang J, Chen X, Yuan T, et al. Regulation of the secretion of immunoregulatory factors of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) by collagen-based scaffolds during chondrogenesis. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017;70(Pt 2):983–91.
Zhang Y, Li J, Davis ME, et al. Delineation of in vitro chondrogenesis of human synovial stem cells following preconditioning using decellularized matrix. Acta Biomater. 2015a;20:39–50.
Zhang Y, Pizzute T, Li J, et al. sb203580 preconditioning recharges matrix-expanded human adult stem cells for chondrogenesis in an inflammatory environment – a feasible approach for autologous stem cell based osteoarthritic cartilage repair. Biomaterials. 2015b;64:88–97.
Zhou L, Chen X, Liu T, et al. SIRT1-dependent anti-senescence effects of cell-deposited matrix on human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2018;12:e1008–21.
Zhou S, Chen S, Pei YA, et al. Nidogen: a matrix protein with potential roles in musculoskeletal tissue regeneration. Genes Diseases. 2021;9:598–609.
Acknowledgments
We thank the MD/PhD Program within the Office of Research and Graduate Education at West Virginia University to fund S.F.N on this project as an internship. This work was supported by research grants from the National Institutes of Health (1R01AR067747) to M.P.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this entry
Cite this entry
Zhang, Y., Ndifon, SF., Pei, M. (2023). Cell-Derived Matrix, Stem Cell Rejuvenation, and Tissue Regeneration. In: Maia, F.R.A., Oliveira, J.M., Reis, R.L. (eds) Handbook of the Extracellular Matrix. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-92090-6_37-1
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-92090-6_37-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-92090-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-92090-6
eBook Packages: Springer Reference Biomedicine and Life SciencesReference Module Biomedical and Life Sciences