Abstract
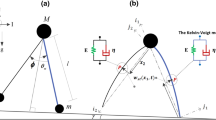
This paper investigates modeling and stable motion generation of a planar passive-dynamic walker with a tensegrity structure formed by four rigid limbs and eight viscoelastic elements. The robot model looks a lot like the traditional one, but has a fundamentally different mechanism for connecting limbs. First, we derive the equations of motion, constraint conditions and collision. Second, we conduct numerical simulations to investigate the fundamental properties of the generated passive-dynamic gaits. The simulation results show that the addition of a small amount of viscosity significantly improves the gait stability.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
McGeer, T.: Passive dynamic walking. Int. J. Robot. Res. 9(2), 62–82 (1990)
Goswami, A., Thuilot, B., Espiau, B.: A study of the passive gait of a compass-like biped robot: symmetry and chaos. Int. J. Robot. Res. 17(12), 1282–1301 (1998)
Paul, C., Valero-Cuevas, F.J., Lipson, H.: Design and control of tensegrity robots for locomotion. IEEE Trans. Robot. 22(5), 944–957 (2006)
Rovira, A.G., Mirats-Tur, J.M.: Control and simulation of a tensegrity-based mobile robot. Robot. Auton. Syst. 57(5), 526–535 (2009)
Du, W., Ma, S., Li, B., Wang, M., Hirai, S.: Force analytic method for rolling gaits of tensegrity robots. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 21(5), 2249–2259 (2016)
Asano, F., Kawamoto, J.: Modeling and analysis of passive viscoelastic-legged rimless wheel that generates measurable period of double-limb support. Multibody Syst. Dyn. 31(2), 111–126 (2014)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Asano, F., Zheng, Y., Li, L. (2022). Modeling and Motion Analysis of Planar Passive-Dynamic Walker with Tensegrity Structure Formed by Four Limbs andEight Viscoelastic Elements. In: Chugo, D., Tokhi, M.O., Silva, M.F., Nakamura, T., Goher, K. (eds) Robotics for Sustainable Future. CLAWAR 2021. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, vol 324. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-86294-7_21
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-86294-7_21
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-86293-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-86294-7
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)