Abstract
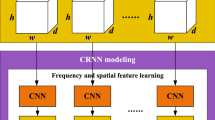
Automatic emotion recognition based on EEG is an important issue in Brain-Computer Interface (BCI) applications. In this paper, baseline signals were taken into account to improve recognition accuracy. Multi-Layer Perceptron (MLP), Decision Tree (DT) and our proposed approach were adopted to verify the effectiveness of baseline signals on classification results. Besides, a 3D representation of EEG segment was proposed to combine features of signals from different frequency bands while preserving spatial information among channels. The continuous convolutional neural network takes the constructed 3D EEG cube as input and makes prediction. Extensive experiments on public DEAP dataset indicate that the proposed method is well suited for emotion recognition tasks after considering the baseline signals. Our comparative experiments also confirmed that higher frequency bands of EEG signals can better characterize emotional states, and that the combination of features of multiple bands can complement each other and further improve the recognition accuracy.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alarcao, S.M., Fonseca, M.J.: Emotions recognition using EEG signals: a survey. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. (2017)
Anderson, K., McOwan, P.W.: A real-time automated system for the recognition of human facial expressions. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part B Cybern. 36(1), 96–105 (2006)
Petrushin, V.A.: Emotion in speech: recognition and application to call centers. In: Proceedings of Artificial Neural Networks in Engineering, vol. 710 (1999)
Soleymani, M., Pantic, M., Pun, T.: Multimodal emotion recognition in response to videos. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 3(2), 211–223 (2012)
Zheng, W.L., Lu, B.L.: Investigating critical frequency bands and channels for EEG-based emotion recognition with deep neural networks. IEEE Trans. Auton. Mental Dev. 7(3), 162–175 (2015)
Li, J., Zhang, Z., He, H.: Hierarchical convolutional neural networks for EEG-based emotion recognition. Cogn. Comput. 1–13 (2017)
Tang, H., Liu, W., Zheng, W.L., Lu, B.L.: Multimodal Emotion Recognition Using Deep Neural Networks. In: Liu, D., Xie, S., Li, Y., Zhao, D., El-Alfy, E.S. (eds.) Neural Information Processing. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 10637, pp. 811–819. Springer, Cham (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-70093-9_86
Li, X., Song, D., Zhang, P., Yu, G., Hou, Y., Hu, B.: Emotion recognition from multi-channel EEG data through convolutional recurrent neural network. In: BIBM, pp. 352–359 (2016)
Li, Y., Huang, J., Zhou, H., Zhong, N.: Human emotion recognition with electroencephalographic multidimensional features by hybrid deep neural networks. Appl. Sci. 7(10), 1060 (2017)
Koelstra, S., Muhl, C., Soleymani, M., Lee, J.S., Yazdani, A., Ebrahimi, T., Pun, T., Nijholt, A., Patras, I.: Deap: a database for emotion analysis; using physiological signals. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 3(1), 18–31 (2012)
Li, X.: Signal Processing in Neuroscience. Springer, Singapore (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-1822-0
Başar, E., Dumermuth, G.: EEG-Brain dynamics: relation between EEG and brain evoked potentials. Comput. Programs Biomed. 14(2), 227–228 (1980)
Steriade, M.: Alertness, Quiet Sleep, Dreaming. Normal and Altered States of Function. Springer, US (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-6622-9_8
Zhang, X., Yao, L., Kanhere, S.S., Liu, Y., Gu, T., Chen, K.: MindID: Person identification from brain waves through attention-based recurrent neural network (2017). arXiv preprint arXiv:1711.06149
Shi, L.C., Jiao, Y.Y., Lu, B.L.: Differential entropy feature for EEG-based vigilance estimation. In: 35th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, pp. 6627–6630 (2013)
Duan, R.N., Zhu, J.Y., Lu, B.L.: Differential entropy feature for EEG-based emotion classification. In: 2013 6th International IEEE/EMBS Conference on Neural Engineering, pp. 81–84. (2013)
Wang, X.W., Nie, D., Lu, B.L.: Emotional state classification from EEG data using machine learning approach. Neurocomputing 129, 94–106 (2014)
Yin, Z., Zhao, M., Wang, Y., Yang, J., Zhang, J.: Recognition of emotions using multimodal physiological signals and an ensemble deep learning model. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 140(C), 93–110 (2017)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2017YFC1703303); the Fundamental Research Funds for Central Universities of China (No. 20720180070).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Yang, Y., Wu, Q., Fu, Y., Chen, X. (2018). Continuous Convolutional Neural Network with 3D Input for EEG-Based Emotion Recognition. In: Cheng, L., Leung, A., Ozawa, S. (eds) Neural Information Processing. ICONIP 2018. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 11307. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-04239-4_39
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-04239-4_39
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-04238-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-04239-4
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)