Abstract
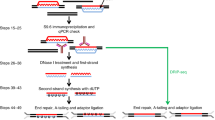
R-loop is a three-stranded chromatin structure, comprising one single-stranded DNA and another DNA:RNA hybrid strand, plays various and essential biological functions in many organisms. Developing a precise, efficient, faithful, and unbiased genome-wide R-loop detection method with extensive adaptability in all organisms is at the top priority for R-loop biology. Here, we provide a straightforward and highly efficient protocol for genome-wide strand-specific R-loop profiling in various organisms. In brief, genomic DNA is extracted and fragmented by the cocktail of restriction enzymes, and then the DNA:RNA hybrids are immunoprecipitated, following by the single-stranded DNA adaptor ligation and next-generation sequencing (named as ssDRIP-seq). Coupling with a straightforward and step-by-step bioinformatic pipeline, this method can provide high resolution and comprehensive strand-specific information for R-loop formation. ssDRIP-seq has been successfully applied for detecting R-loops from prokaryotes such as E. coli, to eukaryotes such as S. cerevisiae, mammalian cell culture and tissues, as well as plants Arabidopsis and rice, with high reproducibility and sensitivity.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Santos-Pereira JM, Aguilera A (2015) R loops: new modulators of genome dynamics and function. Nat Rev Gen 16(10):583–597. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg3961
Richard P, Manley JL (2017) R loops and links to human disease. J Mol Biol 429(21):3168–3180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2016.08.031
Costantino L, Koshland D (2015) The Yin and Yang of R-loop biology. Curr Opin Cell Biol 34:39–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceb.2015.04.008
Xu W, Xu H, Li K, Fan Y, Liu Y, Yang X et al (2017) The R-loop is a common chromatin feature of the Arabidopsis genome. Nat Plants 3(9):704–714. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41477-017-0004-x
Yuan W, Zhou J, Tong J, Zhuo W, Wang L, Li Y et al (2019) ALBA protein complex reads genic R-loops to maintain genome stability in Arabidopsis. Sci Adv 5(5):eaav9040. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aav9040
Li Y, Song Y, Xu W, Li Q, Wang X, Li K et al (2020) R-loops coordinate with SOX2 in regulating reprogramming to pluripotency. Sci Adv 6(24):eaba0777. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aba0777
Yan P, Liu Z, Song M, Wu Z, Xu W, Li K et al (2020) Genome-wide R-loop landscapes during cell differentiation and reprogramming. Cell Rep 32(1):107870. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2020.107870
Xu W, Li K, Li S, Hou Q, Zhang Y, Liu K et al (2020) The R-loop atlas of Arabidopsis development and responses to environmental stimuli. Plant Cell 32(4):888–903. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.19.00802
Yang X, Liu QL, Xu W, Zhang YC, Yang Y, Ju LF et al (2019) m(6)A promotes R-loop formation to facilitate transcription termination. Cell Res 29(12):1035–1038. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41422-019-0235-7
Gan H, Serra-Cardona A, Hua X, Zhou H, Labib K, Yu C et al (2018) The Mcm2-Ctf4-polalpha axis facilitates parental histone H3-H4 transfer to lagging strands. Mol Cell 72(1):140–51.e3. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2018.09.001
Yu C, Gan H, Serra-Cardona A, Zhang L, Gan S, Sharma S et al (2018) A mechanism for preventing asymmetric histone segregation onto replicating DNA strands. Science 361(6409):1386–1389. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aat8849
Ginno PA, Lott PL, Christensen HC, Korf I, Chedin F (2012) R-loop formation is a distinctive characteristic of unmethylated human CpG island promoters. Mol Cell 45(6):814–825. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2012.01.017
Sanz LA, Chedin F (2019) High-resolution, strand-specific R-loop mapping via S9.6-based DNA-RNA immunoprecipitation and high-throughput sequencing. Nat Protoc 14(6):1734–1755. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41596-019-0159-1
Wahba L, Costantino L, Tan FJ, Zimmer A, Koshland D (2016) S1-DRIP-seq identifies high expression and polyA tracts as major contributors to R-loop formation. Genes Dev 30(11):1327–1338. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.280834.116
Dumelie JG, Jaffrey SR (2017) Defining the location of promoter associated R-loops at near-nucleotide resolution using bisDRIP-seq. eLife 6:39. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.28306
Chen JY, Zhang X, Fu XD, Chen L (2019) R-ChIP for genome-wide mapping of R-loops by using catalytically inactive RNASEH1. Nat Protoc 14(5):1661–1685. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41596-019-0154-6
Wang K, Wang H, Li C, Yin Z, Xiao R, Li Q et al (2021) Genomic profiling of native R loops with a DNA-RNA hybrid recognition sensor. Sci Adv 7(8):eabe3516. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.abe3516
Boguslawski SJ, Smith DE, Michalak MA, Mickelson KE, Yehle CO, Patterson WL et al (1986) Characterization of monoclonal-antibody to DNA.RNA and its application to immunodetection of hybrids. J Immunol Methods 89(1):123–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-1759(86)90040-2
Konig F, Schubert T, Langst G (2017) The monoclonal S9.6 antibody exhibits highly variable binding affinities towards different R-loop sequences. PLoS One 12(6):e0178875. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0178875
Phillips DD, Garboczi DN, Singh K, Hu Z, Leppla SH, Leysath CE (2013) The sub-nanomolar binding of DNA-RNA hybrids by the single-chain Fv fragment of antibody S9.6. J Mol Recognit 26(8):376–381. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmr.2284
Langmead B, Salzberg SL (2012) Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat Methods 9(4):357–359. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.1923
Li H, Handsaker B, Wysoker A, Fennell T, Ruan J, Homer N et al (2009) The Sequence Alignment/Map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 25(16):2078–2079. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btp352
Quinlan AR, Hall IM (2010) BEDTools: a flexible suite of utilities for comparing genomic features. Bioinformatics 26(6):841–842. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btq033
Ramirez F, Dundar F, Diehl S, Gruning BA, Manke T (2014) deepTools: a flexible platform for exploring deep-sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res 42(Web Server issue):W187–W191. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gku365
Thorvaldsdottir H, Robinson JT, Mesirov JP (2013) Integrative Genomics Viewer (IGV): high-performance genomics data visualization and exploration. Brief Bioinform 14(2):178–192. https://doi.org/10.1093/bib/bbs017
Zhang Y, Liu T, Meyer CA, Eeckhoute J, Johnson DS, Bernstein BE et al (2008) Model-based analysis of ChIP-Seq (MACS). Genome Biol 9(9):R137. https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2008-9-9-r137
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant nos. 91740105, 31822028, and 91940306 to Q. Sun and 32071437 and 31900302 to W. Xu) and the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (2016YFA0500800). W. Xu was supported by the postdoctoral fellowships from Tsinghua-Peking Joint Center for Life Sciences. The Sun Lab is supported by Tsinghua-Peking Joint Center for Life Sciences and the 1000 Young Talent Program of China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Xu, W., Li, K., Li, Q., Li, S., Zhou, J., Sun, Q. (2022). Quantitative, Convenient, and Efficient Genome-Wide R-Loop Profiling by ssDRIP-Seq in Multiple Organisms. In: Aguilera, A., Ruzov, A. (eds) R-Loops . Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 2528. Humana, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-2477-7_29
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-2477-7_29
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-0716-2476-0
Online ISBN: 978-1-0716-2477-7
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols