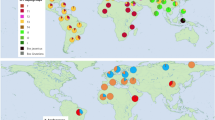
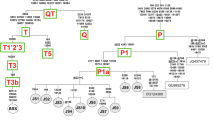
Abstract
The time around 4000 BP marks a key stage from the Late Neolithic to the Early Bronze Age in China. During the time, sheep and cattle husbandry saw rapid development under the Qijia Culture in the Gansu-Qinghai region and also became more common in the Central Plains and Inner Mongolia. In this study, we performed ancient DNA analysis on sheep and cattle remains from four archaeological sites (Changning, Shimao, Taosi and Dashanqian) in northern China, and we obtained mtDNA D-loop fragments (overlapping 271 bp for sheep and overlapping 294 bp for cattle) from 22 of 26 sheep and 44 of 52 cattle remains. The mtDNA haplogroup data reveal that all the sheep DNA samples belong to sub-haplogroups A or B, and all the cattle DNA samples belong to haplogroup T3 or T4. The identification of these common haplogroups again confirms that the ancestors of these early sheep and cattle must have been introduced from outside China, likely from the Near East. The more detailed comparison of haplogroups also indicates potential intensified trade and cultural exchanges between different regions. Furthermore, this study also provides new ancient DNA data for better understanding the origins and spread of sheep and cattle in ancient China.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achilli, A., A. Olivieri, M. Pellecchia, C. Uboldi, L. Colli, N. Al-Zahery, M. Accetturo, M. Pala, B.H. Kashani, U.A. Perego, V. Battaglia, S. Fornarino, J. Kalamati, M. Houshmand, R. Negrini, O. Semino, M. Richards, V. Macaulay, L. Ferretti, H.J. Bandelt, P. Ajmone-Marsan, and A. Torroni. 2008. Mitochondrial genomes of extinct aurochs survive in domestic cattle. Current Biology 18 (4): R157–R158.
Ajmone-Marsan, P., J.F. Garcia, and J.A. Lenstra. 2010. On the origin of cattle: How aurochs became cattle and colonized the world. Evolutionary Anthropology 19 (4): 148–157.
Bollongino, R., J. Burger, A. Powell, M. Mashkour, J.D. Vigne, and M.G. Thomas. 2012. Modern taurine cattle descended from small number of near-eastern founders. Molecular Biology and Evolution 29 (9): 2101–2104.
Cai, D., Z. Tang, H. Yu, L. Han, X. Ren, X. Zhao, H. Zhu, and H. Zhou. 2011. Early history of Chinese domestic sheep indicated by ancient DNA analysis of bronze age individuals. Journal of Archaeological Science 38 (4): 896–902.
Cai, D., Y. Sun, Z. Tang, S. Hu, W. Li, X. Zhao, H. Xiang, and H. Zhou. 2014. The origins of Chinese domestic cattle as revealed by ancient DNA analysis. Journal of Archaeological Science 41: 423–434.
Cai, D., N. Zhang, S. Zhu, Q. Chen, L. Wang, X. Zhao, X. Ma, T.C.A. Roylee, H. Zhou, and D.Y. Yang. 2018. Ancient DNA reveals evidence of abundant aurochs (Bos primigenius) in Neolithic Northeast China. Journal of Archaeological Science 98: 72–80.
Dai, Yingxin 戴应新 1977. Shaanxi Shenmu xian Shimao Longshan wen hua yi zhi diao cha 陕西神木县石峁龙山文化遗址调查 (Survey of the Shimao site in Shenmu County, Shaanxi Province). Kao gu 考古 1977.03: 154–157, 172, 217–220.
Demirci, S., B.E. Koban, N.D. Dagtas, E. Piskin, A. Engin, F. Ozer, E. Yuncu, S.A. Dogan, and I. Togan. 2013. Mitochondrial DNA diversity of modern, ancient and wild sheep (Ovis gmelinii anatolica) from Turkey: New insights on the evolutionary history of sheep. PLoS One 8 (12): e81952.
Flad, R. 傅罗文, Jing Yuan 袁靖, and Shuicheng Li 李水城 2009. Lun Zhongguo Ganqing di qu xin shi qi shi dai jia yang dong wu de lai yuan ji te zheng 论中国甘青地区新石器时代家养动物的来源及特征 (On the source and features of Neolithic domestic animals in the Gansu and Qinghai region, China). Kao gu 考古 2009.5: 80–86.
Guo, J., L.X. Du, Y.H. Ma, W.J. Guan, H.B. Li, Q.J. Zhao, X. Li, and S.Q. Rao. 2005. A novel maternal lineage revealed in sheep (Ovis aries). Animal Genetics 36 (4): 331–336.
Han, Lu 韩璐, Dawei Cai 蔡大伟, Huixin Yu 于慧鑫, Xiaolei Zhang 张小雷, Hui Zhou 周慧, Hong Zhu 朱泓 2009. Neimenggu chun qiu zhan guo shi qi gu mian yang xian li ti DNA fen xi 内蒙古春秋战国时期古绵羊线粒体DNA分析 (Mitochondrial DNA analysis of ancient sheep in Inner Mongolia during the spring and autumn and the warring states period). Zi ran ke xue jin zhan 自然科学进展 2009.10: 1049–1055.
Helmer, D., L. Gourichon, H. Monchot, J. Peters, and M. Sana Segui. 2005. Identifying early domestic cattle from pre-pottery Neolithic sites on the middle Euphrates using sexual dimorphism. In The first steps of animal domestication: New Archaeozoological approaches, ed. J.D. Vigne, 86–95. Oxford: Oxbow Books.
Hiendleder, S., K. Mainz, Y. Plante, and H. Lewalski. 1998. Analysis of mitochondrial DNA indicates that domestic sheep are derived from two different ancestral maternal sources: No evidence for contributions from urial and argali sheep. Journal of Heredity 89 (2): 113–120.
Hou, Guangliang 侯光良, Fenggui Liu 刘峰贵, Cuihua Liu 刘翠华, Xiuqi Fang 方修绮 2009. Zhong quan xin shi Gan qing di qu gu wen hua bian qian de huan jing qu dong 中全新世甘青地区古文化变迁的环境驱动 (Prehistorical cultural transition in the in Gansu-Qinghai region forced by environmental change during the mid-Holocene). Di li xue bao 地理学报 2009.01: 53–58.
Lv, F. H., W. F. Peng, J. Yang, Y. X. Zhao, W. R. Li, M. J. Liu, Y. H. Ma, Q. J. Zhao, G. L. Yang, F. Wang, J. Q. Li, Y. G. Liu, Z. Q. Shen, S. G. Zhao, E. Hehua, N. A. Gorkhali, V. S. Farhad, M. Muladno, A. N. Naqvi, J. Tabell, T. Iso-Touru, M. W. Bruford, J. Kantanen, J. L. Han, , and M. H. Li (2015). “Mitogenomic meta-analysis identifies two phases of migration in the history of eastern Eurasian sheep.” Molecular Biology and Evolution 32 (10): 2515–2533.
Mannen, H., M. Kohno, Y. Nagata, S. Tsuji, D.G. Bradley, J.S. Yeo, D. Nyamsamba, Y. Zagdsuren, M. Yokohama, K. Nomura, and T. Amano. 2004. Independent mitochondrial origin and historical genetic differentiation in north eastern Asian cattle. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution 32 (2): 539–544.
Meadows, J.R.S., I. Cemal, O. Karaca, E. Gootwine, and J.W. Kijas. 2006. Five ovine mitochondrial lineages identified from sheep breeds of the near east. Genetics 175 (3): 1371–1379.
Pedrosa, S., M. Uzun, J. J. Arranz, B. Gutierrez-Gil, F. San Primitivo, and Y., Bayon (2005). “Evidence of three maternal lineages in near eastern sheep supporting multiple domestication events.” Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences 272 (1577): 2211–2217.
Shao, Huiqiu 邵会秋 2009. Dong xi fang wen hua zao qi de peng zhuang yu rong he: Cong Xinjiang shi qian shi qi wen hua ge ju de yan jin tan qi 东西方文化早期的碰撞与融合——从新疆史前时期文化格局的演进谈起 (Collision and fusion of early eastern and Western cultures: Based on the evolution of cultural patterns in prehistoric times in Xinjiang ). She hui ke xue zhan xian 社会科学战线 2009.09: 146–150.
Song, Yanping 宋燕平 2009. Qijia wen hua jing ji xing tai tan tao 齐家文化经济形态探讨 (Discussion on the economic pattern of the Qijia Culture). Si chou zhi lu 丝绸之路 165 (20): 9–10.
Stiner, M.C., H. Buitenhuis, G. Duru, S.L. Kuhn, S.M. Mentzer, N.D. Munro, N. Pollath, J. Quade, G. Tsartsidou, and M. Ozbasaran. 2014. A forager-herder trade-off, from broad-spectrum hunting to sheep management at Asikli Hoyuk, Turkey. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 111 (23): 8404–8409.
Troy, C.S., D.E. MacHugh, J.F. Bailey, D.A. Magee, R.T. Loftus, P. Cunningham, A.T. Chamberlain, B.C. Sykes, and D.G. Bradley. 2001. Genetic evidence for near eastern origins of European cattle. Nature 410 (6832): 1088–1091.
Wang, Lixin 王立新 2007. Dashanqian yi zhi fa jue zi liao suo fan ying de Xiajiadian xia ceng wen hua de jing ji xing tai yu huan jing bei jing 大山前遗址发掘资料所反映的夏家店下层文化的经济形态与环境背景 (The economic pattern and environmental context of the lower Xiajiadian culture reflected by the excavation data of the Dashanqian site). Bian jiang kao gu yan jiu 边疆考古研究 2007.00: 350–357.
Yang, D.Y., B. Eng, J.S. Waye, J.C. Dudar, and S.R. Saunders. 1998. Technical note: Improved DNA extraction from ancient bones using silica-based spin columns. American Journal of Physical Anthropology 105 (4): 539–543.
Yuan, Jing 袁靖, Yunping Huang 黄蕴平, Mengfei Yang 杨梦菲, Peng Lü 吕鹏, Yang Tao 陶洋, and Jie Yang 杨杰 2007. Gong yuan qian 2500 nian - gong yuan qian 1500 nian Zhongyuan di qu dong wu kao gu xue yan jiu: yi Taosi, Wangchenggang, Xinzhai he Erlitou wei li 公元前2500年~公元前1500年中原地区动物考古学研究—以陶寺、王城岗、新砦和二里头遗址为例 (Animal archaeological study in the Zhongyuan region from 2500 to 1500 BC based on the examples of the Taosi, Wangchenggang, Xinzhai, and Erlitou sites). In Zhongguo She Hui Ke Xue Yuan Kao Gu Yan Jiu Suo Kao Guo Ke Ji Zhong Xin 中国社会科学院考古研究所考古科技中心 (editor), Ke ji kao gu (di er ji) 科技考古(第二辑) (Archaeological Sciences, vol. 2), pp. 12–34. Beijing: Ke xue chu ban she.
Zeder, M.A. 2008. Domestication and early agriculture in the Mediterranean Basin: Origins, diffusion, and impact. PNAS 105 (33): 11597–11604.
Zhang, Zhongpei 张忠培 1987. Qijia wen hua yan jiu (xia) 齐家文化研究(下) Research on the Qijia culture (part 2) . Kao gu xue bao 考古学报 1987.02: 153–176.
Zhao, Z.J., 赵志军 2015. Xiao mai chuan ru zhong guo de yan jiu 小麦传入中国的研究Archaeobotanic data for the study of the spread of wheat into China. Na fang wen wu 南方文物 2015. 3, 44–52.
Zhao, Chunyan 赵春燕, Jing Yuan 袁靖, and Nu He 何努 2011. Shanxi sheng Xiangfen xian Taosi yi zhi chu tu dong wu ya you zhi de si tong wei su bi zhi fen xi 山西省襄汾县陶寺遗址出土动物牙釉质的锶同位素比值分析 (strontium isotope analysis of archaeological fauna tooth enamel from the Taosi site, Xiangfen County, Shanxi Province). Di si ji yan jiu 第四纪研究 2011.01: 22–28.
Zhao, Chunyan 赵春燕, Peng Lü 吕鹏, Jing Yuan 袁靖, and Yanming Fang 方燕明 2012. Henan Yuzhou shi Wadian yi zhi chu tu dong wu yi cun de yuan su he si tong wei su bi zhi fen xi 河南禹州市瓦店遗址出土动物遗存的元素和锶同位素比值分析 (Element and strontium isotope analysis of archaeological fauna from the Wadian site, Yuzhou City, Henan Province).” Kao gu 考古 2012.11: 89–96.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by the Major Projects of the National Social Science Foundation of China [17ZDA221] and SSHRC Canada Partnership Development Grant [DY].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cai, D., Zhang, N., Shao, X. et al. New ancient DNA data on the origins and spread of sheep and cattle in northern China around 4000 BP. asian archaeol 2, 51–57 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41826-018-0018-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41826-018-0018-z