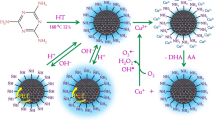
Abstract
The current study reports a facile, single step microwave assisted synthesis of nitrogen, oxygen-doped carbon quantum dots (NCQDs) with high quantum yield (~36%). The synthesized NCQDs with an average size of 4 nm demonstrate many fold increase in the intensity of photoluminescence (PL) over the undoped carbon quantum dots (CQDs). UV–Vis absorption peak exhibits a red shift of 26 nm for NCQDs with respect to pristine CQDs. The spectral shift was further confirmed by density functional theory based calculations. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy measurements reveal the graphitic nature and significantly high nitrogen doping of NCQDs (38.2%). The NCQDs exhibited excitation dependent PL behaviour in the visible region with maximum emission peak recorded at 415 nm with optimum excitation wavelength of 340 nm. The remarkably enhanced PL properties of NCQDs have been employed as fluorescent probe for sensitive and selective sensing of Cu2+ ions. The Cu2+ quenches the fluorescence intensity of NCQDs due to its high binding affinity towards N and O containing functional groups in quantum dots. The NCQDs render a simple, reliable and sensitive detection of Cu2+ ions with limit of detection as low as 1.8 µM.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ananthanarayanan A, Wang X, Routh P et al (2014) Facile synthesis of graphene quantum dots from 3D graphene and their application for Fe3+ sensing. Adv Funct Mater 24:3021–3026. doi:10.1002/adfm.201303441
Badiye A, Kapoor N, Khajuria H (2013) Copper toxicity: a comprehensive study. Res J Recent Sci 2:58–67
Bao L, Zhang Z, Tian Z et al (2011) Electrochemical tuning of luminescent carbon nanodots: from preparation to luminescence mechanism. Adv Mater 23:5801–5806. doi:10.1002/adma.201102866
Belli SL, Zirino A (1993) behavior and calibration of the Copper(II) ion-selective electrode in high chloride media and marine waters. Anal Chem 65:2583–2589
Chaudhary S, Kumar S, Kaur B, Mehta SK (2016) Potential prospects for carbon dots as a fluorescence sensing probe for metal ions. RSC Adv 6:90526–90536. doi:10.1039/C6RA15691F
De B, Karak N (2013) A green and facile approach for the synthesis of water soluble fluorescent carbon dots from banana juice. RSC Adv 3:8286–8290. doi:10.1039/c3ra00088e
Dong Y, Pang H, Bin Yang H et al (2013) Carbon-based dots Co-doped with nitrogen and sulfur for high quantum yield and excitation-independent emission. Angew Chemie 52:7800–7804. doi:10.1002/anie.201301114
Etienne M, Bessiere J, Walcarius A (2001) Voltammetric detection of copper(II) at a carbon paste electrode containing an organically modified silica. Sens Actuators B Chem 76:531–538. doi:10.1016/S0925-4005(01)00614-1
Fang B, Liang Y, Chen F (2014) Highly sensitive and selective determination of cupric ions by using N, N’-bis(salicylidene)-o-phenylenediamine as fluorescent chemosensor and related applications. Talanta 119:601–605. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2013.11.066
Farajzadeh MA, Bahram M, Mehr BG, Jönsson JA (2008) Optimization of dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction of copper (II) by atomic absorption spectrometry as its oxinate chelate: application to determination of copper in different water samples. Talanta 75:832–840. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2007.12.035
Geng J, Li M, Wu L et al (2012) Liberation of copper from amyloid plaques: making a risk factor useful for Alzheimer’ s disease treatment. J Med Chem 55:9146–9155
Gu J, Hu MJ, Guo QQ et al (2014) High-yield synthesis of graphene quantum dots with strong green photoluminescence. RSC Adv 4:50141–50144. doi:10.1039/C4RA10011E
Hu C, Liu Y, Yang Y et al (2013) One-step preparation of nitrogen-doped graphenequantum dots from oxidized debris of graphene oxide. J Mater Chem B 1:39–42. doi:10.1039/C2TB00189F
Janegitz BC, Marcolino-Junior LH, Campana-Filho SP et al (2009) Anodic stripping voltammetric determination of copper(II) using a functionalized carbon nanotubes paste electrode modified with crosslinked chitosan. Sens Actuators B Chem 142:260–266. doi:10.1016/j.snb.2009.08.033
Kohn W, Sham LJ (1965) Self-consistent equations including exchange and correlation effects. Phys Rev 140:A1133–A1138. doi:10.1103/PhysRev.140.A1133
Koval IA, Gamez P, Belle C et al (2006) Synthetic models of the active site of catechol oxidase: mechanistic studies. Chem Soc Rev 35:814–840. doi:10.1039/b516250p
Kresse G, Furthmüller J (1996) Efficiency of ab initio total energy calculations for metals and semiconductors using a plane-wave basis set. Comput Mater Sci 6:15–50. doi:10.1016/0927-0256(96)00008-0
Kresse G, Hafner J (1994) Ab initio molecular-dynamics simulation of the liquid-metal-amorphous-semiconductor transition in germanium. Phys Rev B Condens Matter 49:14251–14269
Li J, Duan C, Gu Z, Wang D (1998) Linear optical properties and multiphoton absorption of alkali halides calculated from first principles. Phys Rev B 57:2222–2228. doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.57.2222
Li D, Müller MB, Gilje S et al (2008) Processable aqueous dispersions of graphene nanosheets. Nat Nanotechnol 3:101–105. doi:10.1038/nnano.2007.451
Li Z, Zhang L, Wang L et al (2011) Highly sensitive and selective fluorescent sensor for Zn2+/Cu2+ and new approach for sensing Cu2+ by central metal displacement. Chem Commun 47:5798–5800. doi:10.1039/c1cc10696a
Li Y, Zhao Y, Cheng H et al (2012) Nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots with oxygen-rich functional groups. J Am Chem Soc 134:15–18. doi:10.1021/ja206030c
Liu H, Ye T, Mao C (2007) Fluorescent carbon nanoparticles derived from candle soot. Angew Chemie 46:6473–6475. doi:10.1002/anie.200701271
Liu S, Tian J, Wang L et al (2012) Hydrothermal treatment of grass: a low-cost, green route to nitrogen-doped, carbon-rich, photoluminescent polymer nanodots as an effective fluorescent sensing platform for label-free detection of Cu(II) ions. Adv Mater 24:2037–2041. doi:10.1002/adma.201200164
Liu J, Liu X, Luo H, Gao Y (2014) One-step preparation of nitrogen-doped and surface passivated carbon quantum dots with high qantum yield and excellent optical properties. RSC Adv 4:7648–7654. doi:10.1039/c3ra47577h
Ma Z, Ming H, Huang H et al (2012) One-step ultrasonic synthesis of fluorescent N-doped carbon dots from glucose and their visible-light sensitive photocatalytic ability. New J Chem 36:861. doi:10.1039/c2nj20942j
Osredkar J, Natasa S (2011) Copper and zinc, biological role and significance of copper/zinc imbalance. J Clin Toxicol 3:1–18. doi:10.4172/2161-0495.S3-001
Perdew JP, Wang Y (1992) Accurate and simple analytic representation of the electron-gas correlation energy. Phys Rev B 45:13244–13249. doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.45.13244
Perdew J, Chevary J, Vosko S et al (1992) Atoms, molecules, solids, and surfaces: applications of the generalized gradient approximation for exchange and correlation. Phys Rev B Condens Matter 46:6671–6687
Shirley D (1972) High-resolution X-Ray photoemission spectrum of the valence bands of gold. Phys Rev B 5:4709–4714. doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.5.4709
Singh AK, Mehtab S, Jain AK (2006) Selective electrochemical sensor for copper (II) ion based on chelating ionophores. Anal Chim Acta 575:25–31. doi:10.1016/j.aca.2006.05.076
Sun H, Wu L, Wei W, Qu X (2013a) Recent advances in graphene quantum dots for sensing. Mater Today 16:433–442. doi:10.1016/j.mattod.2013.10.020
Sun H, Gao N, Wu L et al (2013b) Highly photoluminescent amino-functionalized graphene quantum dots used for sensing copper ions. Chem A Eur J 19:13362–13368. doi:10.1002/chem.201302268
Tanuma S, Powell CJ, Penn DR (1994) Calculations of electron inelastic mean free paths. V. Data for 14 organic compounds over the 50–2000 eV range. Surf Interface Anal 21:165–176. doi:10.1002/sia.740210302
Viguier RFH, Hulme AN (2006) A sensitized europium complex generated by micromolar concentrations of Copper (I): toward the detection of Copper (I) in biology. J Am Chem Soc 128:11370–11371
Wei W, Xu C, Wu L et al (2014) Non-enzymatic-browning-reaction: a versatile route for production of nitrogen-doped carbon dots with tunable multicolor luminescent display. Sci Rep 4:3564. doi:10.1038/srep03564
Wu D, Chen Z, Huang G, Liu X (2014) ZnSe quantum dots based fluorescence sensors for Cu2+ ions. Sens Actuators A Phys 205:72–78. doi:10.1016/j.sna.2013.10.020
Xu M, He G, Li Z et al (2014) A green heterogeneous synthesis of N-doped carbon dots and their photoluminescence applications in solid and aqueous states. Nanoscale 6:10307–10315. doi:10.1039/c4nr02792b
Yeh JJ, Lindau I (1985) Atomic subshell photoionization cross sections and asymmetry parameters: 1 ≤ Z ≤ 103. At Data Nucl Data Tables 32:1–155. doi:10.1016/0092-640X(85)90016-6
Zhang R, Chen W (2014) Nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dots: facile synthesis and application as a “turn-off” fluorescent probe for detection of Hg2+ ions. Biosens Bioelectron 55:83–90. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2013.11.074
Zhang Y-L, Wang L, Zhang H-C et al (2013) Graphitic carbon quantum dots as a fluorescent sensing platform for highly efficient detection of Fe3+ ions. RSC Adv 3:3733. doi:10.1039/c3ra23410j
Zhang X, Liu D, Li L, You T (2015) Direct electrochemistry of glucose oxidase on novel free-standing nitrogen-doped carbon nanospheres@carbon nanofibers composite film. Sci Rep 5:9885. doi:10.1038/srep09885
Zhou L, Lin Y, Huang Z et al (2012) Carbon nanodots as fluorescence probes for rapid, sensitive, and label-free detection of Hg2+ and biothiols in complex matrices. Chem Commun (Camb) 48:1147–1149. doi:10.1039/c2cc16791c
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the financial support of CAS program of the Department of Zoology for the completion of the present work. Authors also acknowledge Biophysics Laboratory, Department of Physics for extending their characterization facility. Authors would also like to acknowledge the financial support from SERB, India (Project code-EMR/2016/007720). Authors would also like to acknowledge the Erasmus Mundus for a doctoral fellowship, Carl Tryggers Stiftelse for Vetenskaplig Forskning (CTS) & Swedish Research Council (VR) for financial support. SNIC, HPC2N and UPPMAX are acknowledged for providing computing time.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, V., Kumar, V., Yadav, U. et al. Sensitive and selective detection of copper ions using low cost nitrogen doped carbon quantum dots as a fluorescent sensing plateform. ISSS J Micro Smart Syst 6, 109–117 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41683-017-0011-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41683-017-0011-1