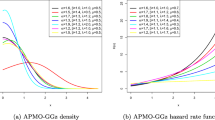
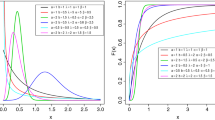
Abstract
In this paper we study some important aspects of the Kies distribution by deriving expressions for its percentile measures, raw moments, reliability measures etc. The maximum likelihood estimation of the parameters of the distribution have been discussed and the distribution has been fitted to certain real life data sets. The asymptotic behaviour of maximum likelihood estimators are also studied by using simulated data sets.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aarset, M.V.: How to identify bathtub hazard rate. IEEE Trans. Reliab. 36, 106–108 (1987)
Alam, M.: New solution and its impact on increasing, decreasing and bathtub shaped failure rate. Pak. J. Stat. Oper. Res. 5, 19–29 (2009)
Bebbington, M., Lai, C.D., Zitikis, R.: A flexible Weibull extension. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 92, 719–726 (2007)
Bebbington, M., Lai, C.D., Zitikis, R.: Modeling human mortality using mixtures of bathtub shaped failure distributions. J. Theor. Biol. 245, 528–538 (2007)
Bebbington, M., Lai, C.D., Zitikis, R.: Reduction in mean residual life in the presence of a constant competing risk. Appl. Stoch. Models Bus. Ind. 24, 51–63 (2008)
Carrasco, J.M.F., Edwin, M.M., Ortega, E.M.M., Cordeiro, G.M.: A generalized modified Weibull distribution for lifetime modeling. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 53, 450–462 (2008)
Efron, B., Tibshirani, R.: Statistical data analysis in the computer age. Science 253, 390–395 (1991)
Famoye, F., Lee, C., Olumolade, O.: The beta Weibull distribution. J. Stat. Theory Appl. 4(2), 121–136 (2005)
Gradshteyn, I.S., Ryhzik, I.M.: Tables of Integrals, Series and Products, 7th edn. Academic Press, New York (2007)
Gross, A.J., Clark, V.A.: Survival Distributions: Reliability Applications in the Biomedical Sciences. Wiley, New York (1975)
Gurvich, M.R., Dibenedetto, A.T., Rande, S.V.: A new statistical distribution for characterizing the random strength of brittle materials. J. Mater. Sci. 32, 2559–2564 (1997)
Hirose, H.: Maximum likelihood parameter estimation in the extended Weibull distribution and its applications to breakdown voltage estimation. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insulation 9(4), 524–536 (2002)
Karian, Z.A., Deudewicz, E.J.: Modern Statistical Systems and GPSS Simulations, 2nd edn. CRC Press, Florida (1999)
Kies, J.A.: The strength of glass performance. Naval Research Lab Report No. 5093, Washington, D.C. (1958)
Lai, C.D., Xie, M., Murthy, D.N.P.: A modified Weibull distribution. IEEE Trans. Reliab. 52(1), 33–37 (2003)
Lemonte, A.J.: A new exponential-type distribution with constant, decreasing, increasing, upside-down bathtub and bathtub-shaped failure rate function. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 62, 149–170 (2013)
Murthy, D.N.P., Xie, M., Jiang, R.: Weibull Models, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York (2004)
Nadarajah, S., Cordeiro, G.M., Ortega, M.M.: General results for the beta-modified Weibull distribution. J. Stat. Comput. Simul. (2011). doi:10.1080/00949651003796343
Reed, W.J.: A flexible parametric survival model which allows a bathtub shaped hazard rate function. J. Appl. Stat. 38(8), 1665–1680 (2011)
Rinne, H.: The Weibull Distribution A Handbook. Taylor and Francis Group, London (2009)
Schmid, F., Trede, M.: Simple tests for peakedness, fat tails and leptokurtosis based on quantiles. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 43, 1–12 (2003)
Singla, N., Jain, K., Sharma, S.K.: The beta generalized Weibull distribution: properties and applications. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 102, 5–15 (2012)
Xie, M., Tang, Y., Goh, T.N.: A modified Weibull extension with bathtub-shaped failure rate function. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 76, 279–285 (2002)
Zhang, T.L., Xie, M.: Failure data analysis with extended Weibull distribution. Commun. Stat. Simul. Comput. 36, 579–592 (2007)
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to express their gratitude to the Editor-in-Chief and both the anonymous referees for their valuable comments on an earlier version of the paper which greatly improved the quality and presentation of the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix
Appendix
The second order partial derivatives of the loglikelihood function \(\ell \) given in (58) with respect to the parameters a, b, \(\lambda \) and \(\beta \) are respectively
and
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Satheesh Kumar, C., Dharmaja, S.H.S. On some properties of Kies distribution. METRON 72, 97–122 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40300-013-0018-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40300-013-0018-8