Abstract
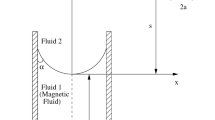
To analytically determine liquid depth and velocity, we formulated a theoretical a capillary flow. The coupling effects of viscous force (Fv), capillary force (Fs), and electromagnetic force (Fm) were considered during the modeling process. Periodical electromagnetic force facilitates capillary flow in hydrophilic conditions, and velocity vibration synchronizes with electromagnetic force. A sufficiently high electromagnetic force was required for ensuring the upward movement of liquid front in hydrophobic conditions. Liquid depth was increased with the increase in magnetic field, damping factor, and angular frequency. The velocity peak was positively related to \(\mid \cos\theta \mid\) and magnified with the increase in damping factor and angular frequency in hydrophilic conditions. However, variations in velocity in hydrophobic conditions experienced an initial forward instantaneous peak and became consistent with that of hydrophilic conditions because of electromagnetic force.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- B :
-
Magnetic induction intensity
- B 0 :
-
Peak of magnetic induction
- F :
-
Total force
- F s :
-
Capillary force
- F v :
-
Total viscous force
- F m :
-
Electromagnetic force
- h :
-
Liquid depth
- P :
-
Pressure
- R :
-
Radius
- t :
-
Time
- v :
-
Flow velocity
- \(\overline{v}\) :
-
Average velocity
- r, z :
-
Coordinate directions
- γ :
-
Viscous shearing force
- θ :
-
Contact angle
- τ :
-
Damping factor
- σ :
-
Surface tension
- ω :
-
Angular frequency
- μ :
-
Magnetic permeability
- η :
-
Dynamic viscosity
References
Y Xiao, F Z Yang and R Pitchumani J. Colloid Interface Sci. 298 880 (2006)
W R Jong, T H Kuo, S W Ho, H H Chiu and S H Peng Int. Commun. Heat Mass 34 186 (2007)
A Bandopadhyay, U Ghosh and S Chakraborty Phys. Rev. E 89 053024 (2014)
S Chakraborty and D Paul J. Phys. D 39 5364 (2006)
K Zhang, Z Shi, H Xia, K Wang, G Liu, G Qiao and J Yang Ceram. Int. 42 996 (2015)
J M Zeng, H X Zhu and J Y Kong Adv. Mat. Res. 634 1914 (2013)
M Sanchez, J Rams and A Urena Compos. Part A–Appl. S. 41 1605 (2010)
T Matsunaga, K Matsuda, T Hatayama, K Shinozaki and M Yoshida Compos. Part A–Appl. S. 38 1902 (2007)
P K Rohatgi, V Tiwari and N Gupta J. Mater. Sci. 41 7232 (2006)
R M Andrews and A Mortensen Mater. Sci. Eng. A Struct. 144 165 (1991)
K Cui, Z L Zhao, S Chen, J J Gao and L F Wei Appl. Phys. Lett. 111 224103 (2017)
E W Washburn Phys. Rev. 17 273 (1921)
S Levin, P Reed and J Watson Colloid Interface Sci. 3 403 (1976)
D Quere Europhys. Lett. 39 533 (1997)
N Fries and M Dreyer J. Colloid Interface Sci. 320 259 (2008)
P R Waghmare and S K Mitra Microfluid Nanofluid 12 53 (2012)
S Chakraborty Anal. Chim. Acta 605 175 (2007)
G H Tang, X F Li, Y L He and W Q Tao J. Non-Newton Fluid 157 133 (2009)
W Ritchie Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. 122 279 (1832)
C P Tso and K Sundaravadivelu J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 34 3522 (2001)
B Lequesne IEEE Trans. Magn. 26 1107 (1990)
D Wattiaux and O Verlinden Exp. Mech. 51 1459 (2011)
Acknowledgements
The work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51374173) and Natural Science Basic Research Plan in Shanxi Province of China (2018JM5082).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cui, K., Zhao, Z., Chen, S. et al. Capillary flows along microchannels in the presence of magnetic field. Indian J Phys 93, 213–219 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12648-018-1261-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12648-018-1261-x