Abstract
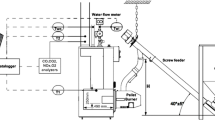
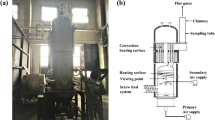
Wood pellets are a kind of solid biomass energy and a renewable energy source. Made by compressing sawdust, wood pellets have a higher energy density than split firewood and wood chips. In 2007, the new and renewable energy (NRE) portion was 2.4% with respect to total primary energy in Korea. The Korean government wants to increase the new and renewable energy (NRE) portion up to 6.1% by 2020 [1]. To achieve this target, the government has been establishing some policies, such as incentive policy, NRE mandatory use for public building and renewable portfolio standard (RPS) and so on. To supply wood pellets as fuel for the combustion chamber of a wood pellet boiler, most domestic wood pellet boilers put a constant volume by using an auger type fuel feed system. In an auger system as fuel feeding, there is the possibility of changing energy input due to the different density of wood pellets even in a constant volume flow rate of wood pellets. If fuel input rate is changed without any correction of air flow rate for combustion, the condition of combustion in a wood pellet boiler can be deteriorated. We have developed an air-fuel control system for a domestic wood pellet boiler by using flue gas oxygen concentration measurement and a PID controller. To measure O2 concentration of flue gas, a wide band O2 sensor was adopted. We changed fuel input from 100% to 50% by artificial manipulation to confirm the control system. The O2 concentration in flue gas can be controlled to be 8.5% ± 1% without significant change of CO and NOx concentration.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Korea energy management corporation, Overview of New and Renewable Energy in Korea 2010 (2010).
European committee for standardization, EN 303-5 Heating boilers for solid fuels, hand and automatically stoked, with a nominal heat output up to 300 kW, European Standard (1991).
Korea forest research institute, Wood pellet standard in Korea (2009).
Pellet-Zentralheisungen und pelletofen, Bundesmini-sterium fur Ernashrung, Landwirtschaft und Verb-raucherschutz.
S. B. Kang, J. J. Kim and K. S. Choi, Performance test and flue gas characteristics of domestic wood pellet boilers, Proceeding of SAREK 2009 Winter Annual Conference (2009) 569–573.
E. F. Kristensen and J. K. Kristensen, Development and test of small-scale batch-fired straw boilers in Denmark, Biomass & Bioenergy, 26 (2004) 561–569.
A. Žandeckis, L. Timma, D. Blumberga, C. Rochas and M. Rosa, Solar and pellet combisystem for apartment buildings: Heat losses and efficiency improvements of the pellet boiler, Applied Energy (2012).
Korean Agency for Technology and Standards, KS B 6205 Land boilers — heating balancing, Korea Standard (2008).
Korean Agency for Technology and Standards, KS B 8109 Gas burning hot water boiler, Korea Standard (2011).
F. P. Incropera and D. P. DeWitt, Introduction to heat transfer, Wiley, New York (1996).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Sae Byul Kang received Ph.D. degree in Mechanical Engineering from Seoul National University in 2003. Now he is working at Korea Institute of Energy Research (KIER) Energy Efficiency Department. Dr. Kang’s research interests are development of woody biomass boiler such as wood pellet and wood chip boiler, combustion control of boiler for optimum combustion and program development for smart pad and smart phone.
Jong Jin Kim received master degree in Mechanical Engineering from Inha University in 1981. Now he is working at Korea Institute of Energy Research (KIER) Energy Efficiency Department. Mr. Kim’s research interests are development of woody biomass boiler such as wood pellet and wood chip boiler, industrial boiler system, calculation program development for industrial boiler and certification code development for solid biomass boiler.
Kyu Sung Choi received master degree in Mechanical Engineering from Kongju National University in 2003. Now he is working at Korea Institute of Energy Research (KIER) Energy Efficiency Department. Mr. Choi’s research interests are development of woody biomass boiler such as wood pellet and wood chip boiler, industrial boiler system and test for certification.
Bong Suk Sim received master degree in Mechanical Engineering from Kyungpook National University in 2012. Now he is working at Korea Institute of Energy Research (KIER) Energy Efficiency Department. Mr. Sim’s research interests are development of woody biomass boiler such as wood pellet and wood chip boiler, and CFD analysis for industrial boiler system.
Hong Young Oh received master degree in Environmental Engineering from Hanbat National University in 2011. Now he is working at Korea Institute of Energy Research (KIER) Energy Efficiency Department. Mr. Oh’s research interests are development of woody biomass boiler such as wood pellet and wood chip boiler, and control system development for wood pellet boiler system.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kang, S.B., Kim, J.J., Choi, K.S. et al. Development of an air fuel control system for a domestic wood pellet boiler. J Mech Sci Technol 27, 1701–1706 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-013-0419-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-013-0419-x