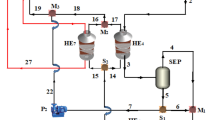
Abstract
Further utilization of waste heat produced by power plant system will increase the efficiency of the whole power plant system. The Kalina Cycle offers alternative solution to generate additional power from waste heat or from low temperature geothermal resources. The modeling application on energy system is used to study the basic design of thermal system, which uses Kalina Cycle for further utilization of geothermal brine water. If this geothermal brine water were not used in the Kalina Cycle, it would be reinjected to the geothermal reservoir and its remaining energy content would have been wasted. The study of this process is done by Cycle Tempo 5.0 simulation software, to obtain the data of efficiency, energy and exergy that could be generated from the heat source. An ammonia-water mixture is used as a working fluid on Kalina cycle system (KCS) 34. In order to obtain the maximum power output and maximum efficiency, the system will be optimized on the mass fraction of working fluid and also on the turbine output pressure. The result of the study shows that the maximum efficiency and power output are achieved at 78% ammonia-water mixture.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. A. Mlcak, Kalina Cycle Concepts for Low Temperature Geothermal. Journal of Geothermal Resources Council Transaction. 26 (2002) 712.
T. J. Kotas, The Exergy Method of Thermal Plant Analysis, Krieger Publishing Company, Florida (1995).
J. Ahrendts, Reference States, Energy, Vol. 5, (1980) 667–677.
Cycle Tempo 5.0 TU Delft (Delft University of Technology), The Netherlands, (2002).
H. Mlcak, M. Mirolli, H. Hjartarson and M. Ralph, Notes from the North: a Report on the Debut Year of the 2 MW Kalina Cycle® Geothermal Power Plant in Húsavík, Iceland, USA, April (2002).
REFPROP 8, Reference Fluid Thermodynamic and Transport Properties, Standard Reference Database 23 NIST (2007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Nasruddin is a faculty member of Mechanical Engineering Department University of Indonesia. He received his Bachelor degree from the same university. He then obtained Master of Engineering (MEng.) from K.U. Leuven (Belgium). He received Doktor der Ingenieurwissenschaften (Dr.-Ing.) from RWTH Aachen University (Germany) in 2005. He has more than 13 years of experiences in lecture and research in engineering thermodynamics. He is a member of ASHRAE.
Rama Usvika received his Engineer degree in Mechanical Engineering from the University of Indonesia in 1996. He then obtained MSc degree in Energy and Environmental Engineering from Ecole des Mines de Nantes (France) in 2005. Mr. Rama currently serves as Engineering Manager for Power Generation projects at PT. Rekayasa Industri, Indonesia’s premier Engineering & Construction company. He has more than 12 years of experiences in engineering, procurement, construction and commissioning of In-dustrial Process and Power plants. He is a member of ASME, the author and co-author of several papers on Power and Energy topics.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nasruddin, Usvika, R., Rifaldi, M. et al. Energy and exergy analysis of kalina cycle system (KCS) 34 with mass fraction ammonia-water mixture variation. J Mech Sci Technol 23, 1871–1876 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-009-0617-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-009-0617-8