Abstract
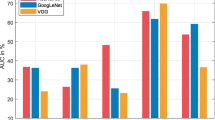
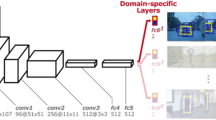
Convolutional neural networks (CNNs) have been applied in state-of-the-art visual tracking tasks to represent the target. However, most existing algorithms treat visual tracking as an object-specific task. Therefore, the model needs to be retrained for different test video sequences. We propose a branch-activated multi-domain convolutional neural network (BAMDCNN). In contrast to most existing trackers based on CNNs which require frequent online training, BAMDCNN only needs offline training and online fine-tuning. Specifically, BAMDCNN exploits category-specific features that are more robust against variations. To allow for learning category-specific information, we introduce a group algorithm and a branch activation method. Experimental results on challenging benchmark show that the proposed algorithm outperforms other state-of-the-art methods. What’s more, compared with CNN based trackers, BAMDCNN increases tracking speed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
BAI Y C, TANG M. Object tracking via robust multitask sparse representation [J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2014, 21(8): 909–913.
DALAL N, TRIGGS B. Histograms of oriented gradients for human detection [C]//International Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. San Diego, USA: IEEE, 2005: 886–893.
KALAL Z, MIKOLAJCZYK K, MATAS J. Trackinglearning-detection [J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2010, 6(1): 1–14.
NAM H, HAN B. Learning multi-domain convolutional neural networks for visual tracking [C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2016: 4293–4302.
WANG N Y, LI S Y, GUPTA A, et al. Transferring rich feature hierarchies for robust visual tracking [EB/OL]. (2017-02-22). https://arxiv.org/abs/1501.04587.
MA C, HUANG J B, YANG X K, et al. Hierarchical convolutional features for visual tracking [C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Boston, USA: IEEE, 2015: 3074–3082.
WANG L J, OUYANG W L, WANG X G, et al. Visual tracking with fully convolutional networks [C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Boston, USA: IEEE, 2015: 3119–3127.
MA C, XU Y, NI B B, et al. When correlation filters meet convolutional neural networks for visual tracking [J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2016, 23(10): 1454–1458.
CHEN K, TAO W B. Once for all: A two-flow convolutional neural network for visual tracking [EB/OL]. (2017-02-22). https://arxiv.org/abs/1604.07507.
LI H X, LI Y, PORIKLI F. Deeptrack: Learning discriminative feature representations online for robust visual tracking [J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2016, 25(4): 1834–1848.
CHATFIELD K, SIMONYAN K, VEDALDI A, et al. Return of the devil in the details: Delving deep into convolutional nets [EB/OL]. (2017-02-22). https://arxiv.org/abs/1405.3531.
JANWE N J, BHOYAR K K. Video key-frame extraction using unsupervised clustering and mutual comparison [J]. International Journal of Image Processing, 2016, 10(2): 73–84.
VEDALDI A, LENC K. MatConvNet: Convolutional neural networks for MATLAB [C]//Proceedings of the 23rd ACM International Conference on Multimedia. Brisbane, Australia: ACM, 2015: 689–692.
KRISTAN M, PFLUGFELDER R, LEONARDIS A, et al. The visual object tracking VOT2013 challenge results [C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops. Sydney, Australia: IEEE, 2013: 98–111.
KRIATAN M, PFLUGFELDER R, LEONARDIS A, et al. The visual object tracking VOT2014 challenge results [C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops. Paris, France: IEEE, 2014: 1–23.
KRISTAN M, MATAS J, LEONARDIS A, et al. The visual object tracking VOT2015 challenge results [C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops. Santiago, Chile: IEEE, 2015: 1–23.
WU Y, LIM J W, YANG M H. Object tracking benchmark [J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2015, 37(9): 1834–1848.
CHEN D P, YUAN Z J, WU Y, et al. Constructing adaptive complex cells for robust visual tracking [C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Sydney, Australia: IEEE, 2013: 1113–1120.
HARE S, GOLODETZ S, SAFFARI A, et al. Struck: Structured output tracking with kernels [J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2016, 38(10): 2096–2109.
HE S F, YANG Q X, LAU R W H, et al. Visual tracking via locality sensitive histograms [C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Oregon, Portland: IEEE, 2013: 2427–2434.
JIA X, LU H C, YANG M H. Visual tracking via adaptive structural local sparse appearance model [C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. RI, USA: IEEE, 2012: 1822–1829.
ZHONG W, LU H C, YANG M H. Robust object tracking via sparsity-based collaborative model [C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. RI, USA: IEEE, 2012: 1838–1845.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: the Innovation Action Plan Foundation of Shanghai (No. 16511101200))
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Y., Lu, R., Zou, Y. et al. Branch-Activated Multi-Domain Convolutional Neural Network for Visual Tracking. J. Shanghai Jiaotong Univ. (Sci.) 23, 360–367 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12204-018-1951-8
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12204-018-1951-8
Key words
- diesel
- convolutional neural network (CNN)
- category-specific feature
- group algorithm
- branch activation method