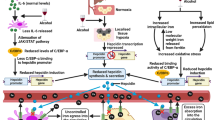
Abstract
The effect of duration of chronic treatment with fluoride (F, 50 mg/L as NaF) on the lipid profile, lipid droplets and triglycerides (TG) in liver was evaluated in mice with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) previously induced by hyperlipidic diet and in animals fed normocaloric diet. In addition, the effect of F administered for a short period (20 days) was evaluated on de novo lipogenesis, by nuclear magnetic resonance. GRP78, Apo-E, and sterol regulatory element-binding protein (SREBP) were quantified by Western blotting. Our data indicate that F interferes in lipid metabolism and lipid droplets, having a different action depending on the exposure time and type of diet administered. F improved lipid parameters and reduced steatosis only when administered for a short period of time (up to 20 days) to animals fed normocaloric diet. However, when NAFLD was already installed, lipid parameters were only slightly improved at 20 days of treatment, but no effect was observed on the degree of steatosis. In addition, lipid profile was in general impaired when the animals were treated with F for 30 days, regardless of the diet. Moreover, F did not alter de novo lipogenesis in animals with installed NAFLD. Furthermore, hyperlipidic diet increased F accumulation in the body. GRP78 increased, while Apo-E and SREBP decreased in the F-treated groups. Our results provide new insights on how F affects lipid metabolism depending on the available energy source.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Whitford GM (1996) The metabolism and toxicity of fluoride. Monogr Oral Sci 16 Rev 2:1–153
Buzalaf MA, Pessan JP, Honorio HM, ten Cate JM (2011) Mechanisms of action of fluoride for caries control. Monogr Oral Sci 22:97–114. https://doi.org/10.1159/000325151
Strunecka A, Patocka J, Blaylock RL, Chinoy NJ (2007) Fluoride interactions: from molecules to disease. Curr Signal Transduction Ther 2(3):190–213
Barbier O, Arreola-Mendoza L, Del Razo LM (2010) Molecular mechanisms of fluoride toxicity. Chem Biol Interact 188(2):319–333. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2010.07.011
Pereira HA, Leite Ade L, Charone S, Lobo JG, Cestari TM, Peres-Buzalaf C, Buzalaf MA (2013) Proteomic analysis of liver in rats chronically exposed to fluoride. PLoS One 8(9):e75343. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0075343
Carvalho JG, Leite Ade L, Peres-Buzalaf C, Salvato F, Labate CA, Everett ET, Whitford GM, Buzalaf MA (2013) Renal proteome in mice with different susceptibilities to fluorosis. PLoS One 8(1):e53261. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0053261
Kobayashi CA, Leite AL, Peres-Buzalaf C, Carvalho JG, Whitford GM, Everett ET, Siqueira WL, Buzalaf MA (2014) Bone response to fluoride exposure is influenced by genetics. PLoS One 9(12):e114343. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0114343
Kobayashi CA, Leite AL, Silva TL, Santos LD, Nogueira FC, Oliveira RC, Palma MS, Domont GB, Buzalaf MA (2009) Proteomic analysis of kidney in rats chronically exposed to fluoride. Chem Biol Interact 180(2):305–311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2009.03.009
Lima Leite A, Gualiume Vaz Madureira Lobo J, Barbosa da Silva Pereira HA, Silva Fernandes M, Martini T, Zucki F, Sumida DH, Rigalli A, Buzalaf MA (2014) Proteomic analysis of gastrocnemius muscle in rats with streptozotocin-induced diabetes and chronically exposed to fluoride. PLoS One 9(9):e106646. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0106646
Lobo JG, Leite AL, Pereira HA, Fernandes MS, Peres-Buzalaf C, Sumida DH, Rigalli A, Buzalaf MA (2015) Low-level fluoride exposure increases insulin sensitivity in experimental diabetes. J Dent Res 94(7):990–997. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022034515581186
Shanthakumari D, Srinivasalu S, Subramanian S (2004) Effect of fluoride intoxication on lipidperoxidation and antioxidant status in experimental rats. Toxicology 204(2–3):219–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2004.06.058
Dabrowska E, Letko R, Balunowska M (2006) Effect of sodium fluoride on the morphological picture of the rat liver exposed to NaF in drinking water. Adv Med Sci 51(Suppl 1):91–95
Dianat N, Steichen C, Vallier L, Weber A, Dubart-Kupperschmitt A (2013) Human pluripotent stem cells for modelling human liver diseases and cell therapy. Curr Gene Ther 13(2):120–132
Yang KT, Lin C, Liu CW, Chen YC (2014) Effects of chicken-liver hydrolysates on lipid metabolism in a high-fat diet. Food Chem 160:148–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.03.052
Pereira HA, Dionizio AS, Fernandes MS, Araujo TT, Cestari TM, Buzalaf CP, Iano FG, Buzalaf MA (2016) Fluoride intensifies hypercaloric diet-induced ER oxidative stress and alters lipid metabolism. PLoS One 11(6):e0158121. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0158121
Asrih M, Jornayvaz FR (2014) Diets and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: the good and the bad. Clin Nutr 33(2):186–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnu.2013.11.003
Brunt EM, Tiniakos DG (2010) Histopathology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. World J Gastroenterol 16(42):5286–5296
Bugianesi E, Leone N, Vanni E, Marchesini G, Brunello F, Carucci P, Musso A, De Paolis P, Capussotti L, Salizzoni M, Rizzetto M (2002) Expanding the natural history of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: from cryptogenic cirrhosis to hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology 123(1):134–140
Palekar NA, Naus R, Larson SP, Ward J, Harrison SA (2006) Clinical model for distinguishing nonalcoholic steatohepatitis from simple steatosis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Liver Int 26(2):151–156. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1478-3231.2005.01209.x
Paschos P, Paletas K (2009) Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and metabolic syndrome. Hippokratia 13(1):9–19
Machado MV, Ravasco P, Jesus L, Marques-Vidal P, Oliveira CR, Proenca T, Baldeiras I, Camilo ME, Cortez-Pinto H (2008) Blood oxidative stress markers in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis and how it correlates with diet. Scand J Gastroenterol 43(1):95–102
Chlubek DPS (2003) Fluoride and oxidative stress. Fluoride 4:36
Bharti VK, Srivastava RS, Kumar H, Bag S, Majumdar AC, Singh G, Pandi-Perumal SR, Brown GM (2014) Effects of melatonin and epiphyseal proteins on fluoride-induced adverse changes in antioxidant status of heart, liver, and kidney of rats. Adv Pharmacol Sci 2014:532969. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/532969
Iano FG, Ferreira MC, Quaggio GB, Fernandes MS, Oliveira RC, Ximenes VF, Buzalaf MAR (2014) Effects of chronic fluoride intake on the antioxidant systems of the liver and kidney in rats. J Fluor Chem 168(0):212–217
Kammoun HL, Chabanon H, Hainault I, Luquet S, Magnan C, Koike T, Ferre P, Foufelle F (2009) GRP78 expression inhibits insulin and ER stress-induced SREBP-1c activation and reduces hepatic steatosis in mice. J Clin Invest 119(5):1201–1215. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI37007
Jo H, Choe SS, Shin KC, Jang H, Lee JH, Seong JK, Back SH, Kim JB (2013) Endoplasmic reticulum stress induces hepatic steatosis via increased expression of the hepatic very low-density lipoprotein receptor. Hepatology 57(4):1366–1377. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.26126
Miltonprabu S, Thangapandiyan S (2015) Epigallocatechin gallate potentially attenuates fluoride induced oxidative stress mediated cardiotoxicity and dyslipidemia in rats. J Trace Elem Med Biol 29:321–335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtemb.2014.08.015
Chiba FY, Garbin CAS, Mattera MSLC, Mota MSO, Pereira RF, Sumida DH (2015) Chronic treatment with a mild dose of Naf promotes dyslipidemia in rats. Fluoride 48(3):205–212
de Cassia Alves Nunes R, Chiba FY, Pereira AG, Pereira RF, de Lima Coutinho Mattera MS, Ervolino E, Louzada MJ, Buzalaf MA, Silva CA, Sumida DH (2016) Effect of sodium fluoride on bone biomechanical and histomorphometric parameters and on insulin signaling and insulin sensitivity in ovariectomized rats. Biol Trace Elem Res 173:144–153. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-016-0642-2
Reeves PG, Nielsen FH, Fahey GC Jr (1993) AIN-93 purified diets for laboratory rodents: final report of the American Institute of nutrition ad hoc writing committee on the reformulation of the AIN-76A rodent diet. J Nutr 123(11):1939–1951
Dunipace AJ, Brizendine EJ, Zhang W, Wilson ME, Miller LL, Katz BP, Warrick JM, Stookey GK (1995) Effect of aging on animal response to chronic fluoride exposure. J Dent Res 74(1):358–368. https://doi.org/10.1177/00220345950740011201
Moura LP, Figueredo GA, Bertolini NO, Ceccato M, Pereira JR, Sponton AC, de Mello MA (2012) Dietary restriction, caloric value and the accumulation of hepatic fat. Lipids Health Dis 11:2. https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-511X-11-2
WHO (2004) Fluoride in drinking water. Background document for development of - WHO Guidelines for Drinking-water Quality. http://www.who.int/water_sanitation_health/dwq/chemicals/fluoride.pdf
Taves DR (1968) Separation of fluoride by rapid diffusion using hexamethyldisiloxane. Talanta 15(9):969–974
Luna LG (1968) Manual of the histologic staining methods of the armed force imtituli of pathology. 3 edn
Friedewald WT, Levy RI, Fredrickson DS (1972) Estimation of the concentration of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in plasma, without use of the preparative ultracentrifuge. Clin Chem 18(6):499–502
Folch J, Lees M, Sloane Stanley GH (1957) A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem 226(1):497–509
Christie WW (1982) Preparation of lipid extracts from tissues. Lipid analysis
Silva AM, Martins F, Jones JG, Carvalho R (2011) 2H2O incorporation into hepatic acetyl-CoA and de novo lipogenesis as measured by Krebs cycle-mediated 2H-enrichment of glutamate and glutamine. Magn Reson Med 66(6):1526–1530. https://doi.org/10.1002/mrm.22955
Jones JG, Fagulha A, Barosa C, Bastos M, Barros L, Baptista C, Caldeira MM, Carvalheiro M (2006) Noninvasive analysis of hepatic glycogen kinetics before and after breakfast with deuterated water and acetaminophen. Diabetes 55(8):2294–2300. https://doi.org/10.2337/db06-0304
Duarte JA, Carvalho F, Pearson M, Horton JD, Browning JD, Jones JG, Burgess SC (2014) A high-fat diet suppresses de novo lipogenesis and desaturation but not elongation and triglyceride synthesis in mice. J Lipid Res 55(12):2541–2553. https://doi.org/10.1194/jlr.M052308
Yan YX, Gong YW, Guo Y, Lv Q, Guo C, Zhuang Y, Zhang Y, Li R, Zhang XZ (2012) Mechanical strain regulates osteoblast proliferation through integrin-mediated ERK activation. PLoS One 7(4):e35709. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0035709
Mahley RW, Rall SC Jr (2000) Apolipoprotein E: far more than a lipid transport protein. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet 1:507–537. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.genom.1.1.507
Sun L, Gao Y, Zhang W, Liu H, Sun D (2014) Effect of high fluoride and high fat on serum lipid levels and oxidative stress in rabbits. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 38(3):1000–1006. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2014.10.010
Miller RF, Phillips PH (1955) The enhancement of the toxicity of sodium fluoride in the rat by high dietary fat. J Nutr 56(4):447–454
Buttner W, Muhler JC (1958) The retention of fluoride by the skeleton, liver, heart and kidney as a function of dietary fat intake in the rat. J Nutr 65(2):259–266
Vijayran M, Manuja N, Chaudhary S, Sinha A, Chaitra TR (2014) Co-relation of body mass index, dental caries and periodontal status with fluorosis in different high fluoridated areas of Haryana state, India. Indian J Dent Res 25(6):722–728. https://doi.org/10.4103/0970-9290.152174
Liu G, Ye Q, Chen W, Zhao Z, Li L, Lin P (2015) Study of the relationship between the lifestyle of residents residing in fluorosis endemic areas and adult skeletal fluorosis. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 40(1):326–332. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2015.06.022
Daugherity EK, Balmus G, Al Saei A, Moore ES, Abi Abdallah D, Rogers AB, Weiss RS, Maurer KJ (2012) The DNA damage checkpoint protein ATM promotes hepatocellular apoptosis and fibrosis in a mouse model of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Cell Cycle 11(10):1918–1928. https://doi.org/10.4161/cc.20259
Umarani V, Muvvala S, Ramesh A, Lakshmi BV, Sravanthi N (2015) Rutin potentially attenuates fluoride-induced oxidative stress-mediated cardiotoxicity, blood toxicity and dyslipidemia in rats. Toxicol Mech Methods 25(2):143–149. https://doi.org/10.3109/15376516.2014.1003359
Zhou BH, Zhao J, Liu J, Zhang JL, Li J, Wang HW (2015) Fluoride-induced oxidative stress is involved in the morphological damage and dysfunction of liver in female mice. Chemosphere 139:504–511. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.08.030
Gregor MF, Hotamisligil GS (2011) Inflammatory mechanisms in obesity. Annu Rev Immunol 29:415–445. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-immunol-031210-101322
Kim E, Choi Y, Jang J, Park T (2013) Carvacrol protects against hepatic steatosis in mice fed a high-fat diet by enhancing SIRT1-AMPK signaling. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2013:290104–290110. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/290104
Buzalaf MA, Whitford GM (2011) Fluoride metabolism. Monogr Oral Sci 22:20–36. https://doi.org/10.1159/000325107
Melcrova A, Pokorna S, Pullanchery S, Kohagen M, Jurkiewicz P, Hof M, Jungwirth P, Cremer PS, Cwiklik L (2016) The complex nature of calcium cation interactions with phospholipid bilayers. Sci Rep 6:38035. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep38035
Rapold RA, Wueest S, Knoepfel A, Schoenle EJ, Konrad D (2013) Fas activates lipolysis in a Ca2+-CaMKII-dependent manner in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J Lipid Res 54(1):63–70. https://doi.org/10.1194/jlr.M028035
Delgado TC, Pinheiro D, Caldeira M, Castro MM, Geraldes CF, Lopez-Larrubia P, Cerdan S, Jones JG (2009) Sources of hepatic triglyceride accumulation during high-fat feeding in the healthy rat. NMR Biomed 22(3):310–317. https://doi.org/10.1002/nbm.1327
Strable MS, Ntambi JM (2010) Genetic control of de novo lipogenesis: role in diet-induced obesity. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 45(3):199–214. https://doi.org/10.3109/10409231003667500
Leavens KF, Easton RM, Shulman GI, Previs SF, Birnbaum MJ (2009) Akt2 is required for hepatic lipid accumulation in models of insulin resistance. Cell Metab 10(5):405–418. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2009.10.004
Oosterveer MH, van Dijk TH, Tietge UJ, Boer T, Havinga R, Stellaard F, Groen AK, Kuipers F, Reijngoud DJ (2009) High fat feeding induces hepatic fatty acid elongation in mice. PLoS One 4(6):e6066. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0006066
Lee WN, Bassilian S, Ajie HO, Schoeller DA, Edmond J, Bergner EA, Byerley LO (1994) In vivo measurement of fatty acids and cholesterol synthesis using D2O and mass isotopomer analysis. Am J Phys 266(5 Pt 1):E699–E708
Brunengraber DZ, McCabe BJ, Kasumov T, Alexander JC, Chandramouli V, Previs SF (2003) Influence of diet on the modeling of adipose tissue triglycerides during growth. Am J Phys Endocrinol Metab 285(4):E917–E925. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.00128.2003
Fon Tacer K, Rozman D (2011) Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: focus on lipoprotein and lipid deregulation. J Lipids 2011:783976. https://doi.org/10.1155/2011/783976
Kockx M, Dinnes DL, Huang KY, Sharpe LJ, Jessup W, Brown AJ, Kritharides L (2012) Cholesterol accumulation inhibits ER to Golgi transport and protein secretion: studies of apolipoprotein E and VSVGt. Biochem J 447(1):51–60. https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20111891
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Dr. Leandro Pereira de Moura for the help with the preparation of the hyperlipidic diet and Dr. José Roberto Bosqueiro for the help with obtaining the animals.
Funding
We thank Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (FAPESP) for the concession of a Master scholarship to the first author (grant number 2013/25756-0 and 2015/10988-9).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Dionizio A, Pereira HABS, and Buzalaf MAR conceived the experiments. Dionizio A, Pereira HABS, Nogueira FN, and Carvalho, RA conducted the experiments. Dionizio A, Pereira HABS, Araujo TT, Sabino-Arias IT. Fernandes MS. Oliveira KA. Nogueira FN, Carvalho, RA, Raymundo FS, and Cestari TM participated in the research experiments. Dionizio A, Pereira HABS, and Buzalaf MAR drafted the article and analyzed and interpreted the results. All authors reviewed and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All experimental protocols were approved by the Ethics Committee for Animal Experiments of Bauru Dental School, University of São Paulo (protocol: 001/2014; 008/2015).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic Supplementary Material
ESM 1
(PDF 125 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dionizio, A., Pereira, H.A.B.S., Araujo, T.T. et al. Effect of Duration of Exposure to Fluoride and Type of Diet on Lipid Parameters and De Novo Lipogenesis. Biol Trace Elem Res 190, 157–171 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-018-1542-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-018-1542-4