Abstract
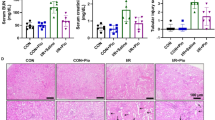
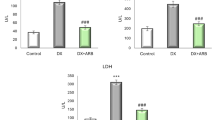
The present study was conducted to investigate the protective effects of hesperidin (HSP) against sodium arsenite (SA)-induced nephrotoxicity and hepatotoxicity in rats. Thirty-five male Sprague Dawley rats were divided into five groups as follows: control, HSP, SA, SA + HSP 100, and SA + HSP 200. Rats were orally gavaged with SA (10 mg/kg body weight) and HSP (100 and 200 mg/kg body weight) for 15 days. SA increased oxidative damage by decreasing antioxidant enzyme activities, such as catalase (CAT), superoxide dismutase (SOD), and glutathione peroxidase (GPx), and glutathione (GSH) level and increasing malondialdehyde (MDA) level in the kidney and liver tissues. In addition, it increased serum aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and alanine aminotransferase (ALT) activities and serum urea and creatinine levels. Furthermore, SA caused inflammation, apoptosis, and oxidative DNA damage by increasing tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB), interleukin-1β (IL-1β), cysteine aspartate-specific protease-3 (caspase-3), and 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG) levels in the kidney and liver tissues and by increasing liver p53 and kidney interleukin-6 (IL-6) expressions. In other words, HSP administration reduced apoptosis, oxidative stress, inflammation, and oxidative DNA damage significantly in SA-induced kidney and liver tissues depending on dose. In this study, it was seen that HSP showed a protective effect against SA-induced kidney and liver toxicity.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
El-Demerdash FM, Yousef MI, Radwan FME (2009) Ameliorating effect of curcumin on sodium arsenite-induced oxidative damage and lipid peroxidation in different rat organs. Food Chem Toxicol 47:249–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2008.11.013
Akanda MR, Tae HJ, Kim IS et al (2017) Hepatoprotective role of Hydrangea macrophylla against sodium arsenite-induced mitochondrial-dependent oxidative stress via the inhibition of MAPK/caspase-3 pathways. Int J Mol Sci 18:1482. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18071482
Saha S, Rashid K, Sadhukhan P et al (2016) Attenuative role of mangiferin in oxidative stress-mediated liver dysfunction in arsenic-intoxicated murines. BioFactors 42:515–532. https://doi.org/10.1002/biof.1276
Fouad AA, Al-Mulhim AS, Jresat I (2012) Telmisartan treatment attenuates arsenic-induced hepatotoxicity in mice. Toxicology 300:149–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2012.06.015
Dash M, Maity M, Dey A et al (2018) The consequence of NAC on sodium arsenite-induced uterine oxidative stress. Toxicol Reports 5:278–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxrep.2018.02.003
Adil M, Kandhare AD, Visnagri A, Bodhankar SL (2015) Naringin ameliorates sodium arsenite-induced renal and hepatic toxicity in rats: decisive role of KIM-1, caspase-3, TGF-β, and TNF-α. Ren Fail 37:1396–1407. https://doi.org/10.3109/0886022X.2015.1074462
Kim Y-J, Kim J-M (2015) Arsenic toxicity in male reproduction and development. Dev Reprod 19:167–180. https://doi.org/10.12717/DR.2015.19.4.167
Lin A, Zhang X, Zhu Y-G, Zhao F-J (2008) Arsenate-induced toxicity: effects on antioxidative enzymes and DNA damage in Vicia faba. Environ Toxicol Chem 27:413. https://doi.org/10.1897/07-266R.1
Gülçin İ (2012) Antioxidant activity of food constituents: an overview. Arch Toxicol 86:345–391. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-011-0774-2
Kandemir FM, Kucukler S, Eldutar E, et al (2017) Chrysin protects rat kidney from paracetamol-induced oxidative stress, inflammation, apoptosis, and autophagy: a multi-biomarker approach. Sci Pharm 85. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm85010004
Kandemir FM, Ozkaraca M, Küçükler S et al (2017) Preventive effects of hesperidin on diabetic nephropathy induced by streptozotocin via modulating TGF-β1 and oxidative DNA damage. Toxin Rev:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1080/15569543.2017.1364268
Taslimi P, Caglayan C, Gulcin İ (2017) The impact of some natural phenolic compounds on carbonic anhydrase, acetylcholinesterase, butyrylcholinesterase, and α-glycosidase enzymes: an antidiabetic, anticholinergic, and antiepileptic study. J Biochem Mol Toxicol 31:e21995. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbt.21995
Mishra K (2013) Structure-activity relationship of antioxidative property of hesperidin. Int J Pharm Erud 2:40
Hamdy SM, Shabaan AM, Abdel Latif AKM et al (2017) Protective effect of hesperidin and tiger nut against acrylamide toxicity in female rats. Exp Toxicol Pathol 69:580–588. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etp.2017.05.004
Ahmad ST, Arjumand W, Nafees S (2012) Hesperidin alleviates acetaminophen induced toxicity in Wistar rats by abrogation of oxidative stress, apoptosis and inflammation. Toxicol Lett 208:149–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2011.10.023
Placer ZA, Cushman LL, Johnson BC (1966) Estimation of product of lipid peroxidation (malonyl dialdehyde) in biochemical systems. Anal Biochem 16:359–364. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(66)90167-9
Aebi H (1983) Catalase. Methods Enzym Anal 3:273
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Sun Y, Oberley LW, Li Y (1988) A simple method for clinical assay of superoxide dismutase. Clin Chem 34:497–500
Lawrence RA, Burk RF (1976) Glutathione peroxidase activity in selenium-deficient rat liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 71:952–958. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-291X(76)90747-6
Sedlak J, Lindsay RH (1968) Estimation of total, protein-bound, and nonprotein sulfhydryl groups in tissue with Ellman’s reagent. Anal Biochem 25:192–205
Majhi CR, Khan S, Leo MDM et al (2011) Effects of acetaminophen on reactive oxygen species and nitric oxide redox signaling in kidney of arsenic-exposed rats. Food Chem Toxicol 49:974–982. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2011.01.003
Yousef MI, El-Demerdash FM, Radwan FME (2008) Sodium arsenite induced biochemical perturbations in rats: ameliorating effect of curcumin. Food Chem Toxicol 46:3506–3511. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.FCT.2008.08.031
Brunati AM, Pagano MA, Bindoli A, Rigobello MP (2010) Thiol redox systems and protein kinases in hepatic stellate cell regulatory processes. Free Radic Res 44:363–378. https://doi.org/10.3109/10715760903555836
Mershiba SD, Dassprakash MV, Saraswathy SD (2013) Protective effect of naringenin on hepatic and renal dysfunction and oxidative stress in arsenic intoxicated rats. Mol Biol Rep 40:3681–3691. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-012-2444-8
Flora SJS (2011) Arsenic-induced oxidative stress and its reversibility. Free Radic Biol Med 51:257–281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2011.04.008
Maiti S, Chatterjee AK (2001) Effects on levels of glutathione and some related enzymes in tissues after an acute arsenic exposure in rats and their relationship to dietary protein deficiency. Arch Toxicol 75:531–537
Flora SJS, Chouhan S, Kannan GM et al (2008) Combined administration of taurine and monoisoamyl DMSA protects arsenic induced oxidative injury in rats. Oxidative Med Cell Longev 1:39–45
Mishra D, Mehta A, Flora SJS (2008) Reversal of arsenic-induced hepatic apoptosis with combined administration of DMSA and its analogues in guinea pigs: role of glutathione and linked enzymes. Chem Res Toxicol 21:400–407. https://doi.org/10.1021/tx700315a
Shi H, Shi X, Liu KJ (2004) Oxidative mechanism of arsenic toxicity and carcinogenesis. Mol Cell Biochem 255:67–78. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:MCBI.0000007262.26044.e8
Kirici M, Turk C, Caglayan C, Kirici M (2017) Toxic effects of copper sulphate pentahydrate on antioxidant enzyme activities and lipid peroxidation of freshwater fish Capoeta umbla (Heckel, 1843) tissues. Appl Ecol Environ Res 15:1685–1696
Ogun M, Ozcan A, Karaman M et al (2016) Oleuropein ameliorates arsenic induced oxidative stress in mice. J Trace Elem Med Biol 36:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtemb.2016.03.006
Kandemir FM, Küçükler S, Çağlayan C (2017) Beneficial effects of silymarin and naringin against methotrexate-induced hepatotoxicity in rats. Bil Derg 12:167–177. https://doi.org/10.17094/ataunivbd.347970
El-Maraghy SA, Rizk SM, El-Sawalhi MM (2009) Hepatoprotective potential of crocin and curcumin against iron overload-induced biochemical alterations in rat. Afr J Biochem Res 3:215–221
Pari L, Karthikeyan A, Karthika P, Rathinam A (2015) Protective effects of hesperidin on oxidative stress, dyslipidaemia and histological changes in iron-induced hepatic and renal toxicity in rats. Toxicol Reports 2:46–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxrep.2014.11.003
Kandemir FM, Yildirim S, Kucukler S et al (2018) Therapeutic efficacy of zingerone against vancomycin-induced oxidative stress, inflammation, apoptosis and aquaporin 1 permeability in rat kidney. Biomed Pharmacother 105:981–991. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.06.048
Jagadeesan G, Bharathi E (2014) In vivo restoration of hepatic and nephro protective potential of hesperidin and ellagic acid against mercuric chloride intoxicated rats. Biomed Aging Pathol 4:219–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomag.2014.01.008
Roussel RR, Barchowsky A (2000) Arsenic inhibits NF-κB-mediated gene transcription by blocking IκB kinase activity and IκBα phosphorylation and degradation. Arch Biochem Biophys 377:204–212. https://doi.org/10.1006/ABBI.2000.1770
Benzer F, Kandemir FM, Kucukler S et al (2018) Chemoprotective effects of curcumin on doxorubicin-induced nephrotoxicity in Wistar rats: by modulating inflammatory cytokines, apoptosis, oxidative stress and oxidative DNA damage. Arch Physiol Biochem 0:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1080/13813455.2017.1422766
Kandemir FM, Kucukler S, Caglayan C et al (2017) Therapeutic effects of silymarin and naringin on methotrexate-induced nephrotoxicity in rats: biochemical evaluation of anti-inflammatory, antiapoptotic, and antiautophagic properties. J Food Biochem 41:e12398. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfbc.12398
Jing H, Shen G, Wang G et al (2012) MG132 alleviates liver injury induced by intestinal ischemia/reperfusion in rats: involvement of the AhR and NFκB pathways. J Surg Res 176:63–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jss.2011.09.001
Ruiz-Ramos R, Lopez-Carrillo L, Rios-Perez AD et al (2009) Sodium arsenite induces ROS generation, DNA oxidative damage, HO-1 and c-Myc proteins, NF-κB activation and cell proliferation in human breast cancer MCF-7 cells. Mutat Res Toxicol Environ Mutagen 674:109–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mrgentox.2008.09.021
Eldutar E, Kandemir FM, Kucukler S, Caglayan C (2017) Restorative effects of Chrysin pretreatment on oxidant-antioxidant status, inflammatory cytokine production, and apoptotic and autophagic markers in acute paracetamol-induced hepatotoxicity in rats: an experimental and biochemical study. J Biochem Mol Toxicol 31:e21960. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbt.21960
Donnahoo KK, Shames BD, Harken AH, Meldrum DR (1999) Review article: the role of tumor necrosis factor in renal ischemia-reperfusion injury. J Urol 162:196–203. https://doi.org/10.1097/00005392-199907000-00068
Bae Y, Lee S, Kim S-H (2011) Chrysin suppresses mast cell-mediated allergic inflammation: involvement of calcium, caspase-1 and nuclear factor-κB. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 254:56–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2011.04.008
Adil M, Visnagri A, Shiva Kuma V et al (2014) Protective effect of naringin on sodium arsenite induced testicular toxicity via modulation of biochemical perturbations in experimental rats. Pharmacologia 5:222–234. https://doi.org/10.5567/pharmacologia.2014.222.234
Bali İ, Bilir B, Emir S et al (2016) The effects of melatonin on liver functions in arsenic-induced liver damage. Ulus cerrahi Derg 32:233–237. https://doi.org/10.5152/UCD.2015.3224
Ola MS, Nawaz M, Ahsan H (2011) Role of Bcl-2 family proteins and caspases in the regulation of apoptosis. Mol Cell Biochem 351:41–58. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-010-0709-x
Othman MS, Safwat G, Aboulkhair M, Abdel Moneim AE (2014) The potential effect of berberine in mercury-induced hepatorenal toxicity in albino rats. Food Chem Toxicol 69:175–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2014.04.012
Wang B, Xiao Z, Ko HL, Ren E-C (2010) The p53 response element and transcriptional repression. Cell Cycle 9:870–879. https://doi.org/10.4161/cc.9.5.10825
Chen J, Wang J, Li H et al (2016) p53 activates miR-192-5p to mediate vancomycin induced AKI. Sci Rep 6:38868. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep38868
Chou R-H, Huang H (2002) Restoration of p53 tumor suppressor pathway in human cervical carcinoma cells by sodium arsenite. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 293:298–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0006-291X(02)00212-7
Vogt BL, Rossman TG (2001) Effects of arsenite on p53, p21 and cyclin D expression in normal human fibroblasts—a possible mechanism for arsenite’s comutagenicity. Mutat Res 478:159–168
Ueno M, Masutani H, Arai RJ et al (1999) Thioredoxin-dependent redox regulation of p53-mediated p21 activation. J Biol Chem 274:35809–35815
Benzer F, Kandemir FM, Ozkaraca M, et al (2018) Curcumin ameliorates doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity by abrogation of inflammation, apoptosis, oxidative DNA damage, and protein oxidation in rats. J Biochem Mol Toxicol 32. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/jbt.22030
Kaygusuzoglu E, Caglayan C, Kandemir FM et al (2018) Zingerone ameliorates cisplatin-induced ovarian and uterine toxicity via suppression of sex hormone imbalances, oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis in female Wistar rats. Biomed Pharmacother 102:517–530. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.03.119
Banerjee N, Banerjee M, Ganguly S et al (2008) Arsenic-induced mitochondrial instability leading to programmed cell death in the exposed individuals. Toxicology 246:101–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2007.12.029
Cetin AA, Çetin A, Çiftçi O, Otlu A (2016) Protective effect of hesperidin on oxidative and histological liver damage following carbon tetrachloride administration in Wistar rats. Arch Med Sci 12:486–493. https://doi.org/10.5114/aoms.2015.49484
Sahu BD, Kuncha M, Sindhura GJ, Sistla R (2013) Hesperidin attenuates cisplatin-induced acute renal injury by decreasing oxidative stress, inflammation and DNA damage. Phytomedicine 20:453–460. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2012.12.001
Pan H, Zhang L, Guo M et al (2010) The oxidative stress status in diabetes mellitus and diabetic nephropathy. Acta Diabetol 47:71–76. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-009-0128-1
Caglayan C, Temel Y, Kandemir FM et al (2018) Naringin protects against cyclophosphamide-induced hepatotoxicity and nephrotoxicity through modulation of oxidative stress, inflammation, apoptosis, autophagy, and DNA damage. Environ Sci Pollut Res:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2242-5
Sinha D, Roy M (2011) Antagonistic role of tea against sodium arsenite-induced oxidative DNA damage and inhibition of DNA repair in Swiss Albino mice. J Environ Pathol Toxicol Oncol 30:311–322. https://doi.org/10.1615/JEnvironPatholToxicolOncol.v30.i4.40
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Unit of Scientific Research Projects of the University of Ağrı İbrahim Çeçen (Project number ECZF.17.002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that there is no any conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Turk, E., Kandemir, F.M., Yildirim, S. et al. Protective Effect of Hesperidin on Sodium Arsenite-Induced Nephrotoxicity and Hepatotoxicity in Rats. Biol Trace Elem Res 189, 95–108 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-018-1443-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-018-1443-6