Abstract
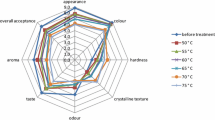
Infrared (IR) heating method against rice weevils (Sitophilus oryzae) in an egg stage was investigated. A kinetic model was developed to describe insect mortality in a temperature range of 40–60 °C. Effects of IR heating temperature (50–60 °C) and exposure time (1–3 min) on insect mortality and quality attributes of the treated rice were evaluated. The optimized condition obtained by means of the response surface method was used to analyze rice quality before and after IR treatment with storage. The results showed that the 0.5th-order thermal death kinetic equation was the most suitable model, and the S. oryzae eggs had less heat tolerance than the adults and some other species. Mortality achieved 100 % after 2 min for all temperatures. Both IR heating parameters significantly affected the treated milled rice qualities. The minimal changes in rice quality before and after storage could be obtained using optimized temperature and exposure time of 53.6 °C and 1.2 min, respectively.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alfaifi, B., Tang, J. M., Jiao, Y., Wang, S. J., Rasco, B., Jiao, S. S., & Sablani, S. (2014). Radio frequency disinfestation treatments for dried fruit: model development and validation. Journal of Food Engineering, 120, 268–276.
Aluja, M., Diaz-Fleischer, F., Arredondo, J., Valle-Mora, J., & Rull, J. (2010). Effect of cold storage on larval and adult Anastrepha ludens (Diptera: Tephritidae) viability in commercially ripe, artificially infested Persea Americana ‘Hass’. Journal of Economic Entomology, 103, 2000–2008.
AOAC. (1995). Official methods of analysis (16th ed.). Washington, DC: Association of official Agricultural Chemists.
Armstrong, J. W., & Follet, P. A. (2007). Hot-water immersion quarantine treatment against Mediterranean fruit fly and oriental fruit fly (Diptera: Tephritidae) eggs and larvae in litchi and longan fruit exported from Hawaii. Journal of Economic Entomology, 100, 1091–1097.
Armstrong, J. W., Tang, J., & Wang, S. (2009). Thermal death kinetics of Mediterranean, Malaysian, melon, and oriental fruit fly (Diptera: Tephritidae) eggs and third instar. Journal of Economic Entomology, 102, 522–532.
Ben-Ialli, A., Méot, J.-M., Bohuon, P., & Collignan, A. (2009). Survival kinetics of Ephestia kuehniella eggs during 46–75°C heat treatment. Journal of Stored Products Research, 45, 206–211.
Carocho, M., Antonio, A. L., Barreira, J. C., Rafalski, A., Bento, A., & Ferreira, I. C. (2014). Validation of gamma and electron beam irradiation as alternative conservation technology for European chestnuts. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 7(7), 1917–1927.
Cnossen, A. G., & Siebenmorgen, T. J. (2000). The glass transition temperature concept in rice drying and tempering: effect on milling quality. Transactions of the ASAE, 43(6), 1661–1667.
Cnossen, A. G., Jiménez, M. J., & Siebenmorgen, T. J. (2003). Rice fissuring response to high drying and tempering temperatures. Journal of Food Engineering, 59, 61–69.
Ding, C., Khir, R., Pan, Z., Zhang, J., Tu, K., & El-Mashad, H. (2015a). Effect of infrared and conventional drying methods on physicochemical characteristics of stored white rice. Cereal Chemistry, 92(5), 441–448.
Ding, C., Khir, R., Pan, Z., Zhao, L., Tu, K., El-Mashad, H., & McHugh, T. H. (2015b). Improvement in shelf life of rough and brown rice using infrared radiation heating. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 8, 1149–1159.
Ding, C., Khir, R., Pan, Z., Wood, D. E., Tu, K., El-Mashad, H., & Berrios, J. (2016). Improvement in storage stability of infrared-dried rough rice. Food and Bioprocess Technoogy, 9, 1010–1020.
Duangkhamchan, W., & Siriamornpun, S. (2015). Quality attributes and anthocyanin content of rice coated by purple-corn cob extract as affected by coating conditions. Food and Bioproducts Processing, 96, 171–179.
Follett, P. A. (2008). Effect of irradiation on Mexican leafroller (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae) development and reproduction. Journal of Economic Entomology, 101, 710–715.
Gujral, H. S., & Kumar, V. (2003). Effect of accelerated aging on the physicochemical and textural properties of brown and milled rice. Journal of Food Engineering, 59, 117–121.
Hallman, G. J., Wang, S., & Tang, J. (2005). Reaction orders for thermal mortality of third instars of Mexican fruit fly (Diptera: Tephritidae). Journal of Economic Entomology, 97, 1540–1546.
Hansen, J., Heidt, M., Watkins, M., Drake, S., Tang, J., & Wang, S. (2005). Evaluation of radio frequency—hot water treatments for postharvest control of codling moth in ‘Bing’ sweet cherries. HortTechnology, 15(3), 613–616.
Hou, L., Johnson, J. A., & Wang, S. (2016). Radio frequency heating for postharvest control of pests in agricultural products: a review. Postharvest Biology and Technology, 113, 106–118.
Hsu, R. J.-C., Chen, H.-J., Lu, S., & Chiang, W. (2015). Effects of cooking, retrogradation and drying on starch digestibility in instant rice making. Journal of Cereal Science, 65, 154–161.
ISO 11747:2012 (E) (2012). Rice—determination of rice kernel resistance to extrusion after cooking. International Standard Organization, 1–5.
Jian, F., Jayas, D. S., White, N. D., Fields, P. G., & Howe, N. (2015). An evaluation of insect expulsion from wheat samples by microwave treatment for disinfestation. Biosystems Engineering, 130, 1–12.
Jiao, S., Johnson, J. A., Tang, J., Mattinson, D. S., Fellman, J. K., Davenport, T. L., & Wang, S. (2013). Tolerance of codling moth, and apple quality associated with low pressure/low temperature treatments. Postharvest Biology and Technology, 85, 136–140.
Khamis, M., Subramanyam, B., Dogan, H., Flinn, P. W., & Gwirtz, J. A. (2011). Effects of flameless catalytic infrared radiation on Sitophilus oryzae (L.) life stages. Journal of Stored Products Research, 47, 173–178.
Khir, R., Pan, Z., Salim, A., Hartsough, B. R., & Mohamed, S. (2011). Moisture diffusivity of rough rice under infrared radiation drying. LWT--Food Science and Technology, 44, 1126–1132.
Laohavanich, J., & Wongpichet, S. (2009). Drying characteristics and milling quality aspects of paddy dried with gas-fired infrared. Journal of Food Process Engineering, 32, 442–461.
Li, H. B., Shi, L., Lu, M. X., Wang, J. J., & Du, Y. Z. (2011). Thermal tolerance of Frankliniella occidentalis: effects of temperature, exposure time, and gender. Journal of Thermal Biology, 36(7), 437–442.
Moss, J. I., & Chan, H. T. (1993). Thermal death kinetics of Caribbean fruit fly (Diptera: Tephritidae) embryos. Journal of Economic Entomology, 86, 1162–1166.
Neven, L. G., & Rehfield-Ray, L. (2006). Combined heat and controlled atmosphere quarantine treatments for control of western cherry fruit fly in sweet cherries. Journal of Economic Entomology, 99, 658–663.
Pan, Z., Khir, R., Godfrey, L. D., Lewis, R., Thompson, J. F., & Salim, A. (2008). Feasibility of simultaneous rough rice drying and disinfestations by infrared radiation heating and rice milling quality. Journal of Food Engineering, 84, 469–479.
Pan, Z., Khir, R., Bett-Garber, K. L., Champagne, E. T., Thompson, J. F., Salim, A., Hartsough, B. R., & Mohamed, S. (2011). Drying characteristics and quality of rough rice under infrared radiation heating. Transactions of the ASABE, 54(1), 203–210.
Rajendran, S., & Sriranjini, V. (2008). Plant products as fumigants for stored-product insect control. Journal of Stored Products Research, 44, 126–135.
Ronsse, F., Pieters, J. G., & Dewettinck, K. (2009). Modeling heat and mass transfer in batch top-spray fluidized bed coating processes. Powder Technology, 190, 170–175.
Samtani, J. B., Gilbert, C., Ben Webber, J., Subbarao, K. V., Goodhue, R. E., & Fennimore, S. A. (2012). Effect of steam and solarisation treatments on pest control, strawberry yield, and economic returns relative to methyl bromide fumigation. HortScience, 47, 64–70.
Singh, B., Chakkal, S. K., & Ahuja, N. (2006). Formulation and optimization of controlled release mucoadhesive tablets of atenolol using response surface methodology. AAPS PharmSciTech, 7, 19–28.
Suhem, K., Matan, N., Nisoa, M., & Matan, N. (2013). Low pressure radio frequency plasma effects on the mould control, physical quality, nutritional value, mineral content and trace element content of brown rice snack bars. Journal of Food and Nutrition Research, 52(2), 87–94.
Tulyathan, V., Srisupattarawanich, N., & Suwanagul, A. (2008). Effect of rice flour coating on 2-acetyl-1-pyrroline and n-hexanal in brown rice cv. Jao Ham Supanburi during storage. Postharvest Biology and Technology, 47, 367–372.
Wang, S.-J., & Tang, J.-M. (2004). Radio frequency heating: a new potential means of post-harvest pest control in nuts and dry products. Journal of Zhejiang University Science, 5(10), 1169–1174.
Wang, S., Ikediala, J. N., Tang, J., Hansen, J. D., Mitcham, E., Mao, R., & Swanson, B. (2001a). Radio frequency treatments to control codling moth in in-shell walnuts. Postharvest Biology and Technology, 22, 29–38.
Wang, S., Tang, J., & Cavalieri, R. (2001b). Modeling fruit internal heating rates for hot air and hot water treatments. Postharvest Biology and Technology, 22, 257–270.
Wang, S., Tang, J., Johnson, J. A., & Cavalieri, R. P. (2013). Heating uniformity and differential heating of insects in almonds associated with radio frequency energy. Journal of Stored Products Research, 55, 15–20.
Wang, B., Khir, R., Pan, Z., El-Mashad, H., Atungulu, G. G., Ma, H., McHugh, T. H., Qu, W., & Wu, B. (2014). Effective disinfection of rough rice using infrared radiation heating. Journal of Food Protection, 77(9), 1538–1545.
Wangspa, W., Chanbang, Y., & Vearasilp, S. (2015). Radio frequency heat treatment for controlling rice weevil in rough rice cv. Khao Dawk Mali 105. Chiang Mai University Journal of Natural Sciences, 14(2), 189–197.
Wongpornchai, S., Dumri, K., Jongkaewwattana, S., & Siri, B. (2004). Effects of drying methods and storage time on the aroma and milling quality of rice (Oryzae sativa L.) cv. Khao Dawk Mali 105. Food Chemistry, 87, 407–414.
Yadav, D. N., Anand, T., Sharma, M., & Gupta, R. (2014). Microwave technology for disinfestation of cereals and pulses: an overview. Journal of Food Science and Technology, 51(12), 3568–3576.
Yan, R., Huang, Z., Zhu, H., Johnson, J. A., & Wang, S. (2014). Thermal death kinetics of adult Sitophilus oryzae and effects of heating rate on thermotolerance. Journal of Stored Products Research, 59, 231–236.
Zhao, S., Qiu, C., Xiong, S., & Cheng, X. (2007a). A thermal lethal model of rice weevils subjected to microwave irradiation. Journal of Stored Products Research, 43, 430–434.
Zhao, S., Xiong, S., Qiu, C., & Xu, Y. (2007b). Effect of microwaves on rice quality. Journal of Stored Products Research, 43, 496–502.
Zhou, L., & Wang, S. (2016). Verification of radio frequency heating uniformity and Sitophilus oryzae control in rough, brown, and milled rice. Journal of Stored Products Research, 65, 40–47.
Zhou, L., Ling, B., Zheng, A., Zhang, B., & Wang, S. (2015). Developing radio frequency technology for postharvest insect control in milled rice. Journal of Stored Products Research, 62, 22–31.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Faculty of Technology, Mahasarakham University, for financial support. Thanks are also given to the Research and Researcher for Industry (RRI) (No. MSD5710045). The authors also thank Asst. Prof. Dr. Perayot Kangkan for his advice on the 2-acetyl-1-pyrroline analysis and Seri Rungruenag Kit Rice Mill for financial and material support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Duangkhamchan, W., Phomphai, A., Wanna, R. et al. Infrared Heating as a Disinfestation Method Against Sitophilus oryzae and Its Effect on Textural and Cooking Properties of Milled Rice. Food Bioprocess Technol 10, 284–295 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-016-1813-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-016-1813-z