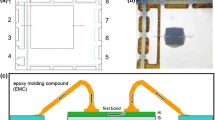
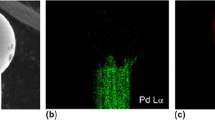
Abstract
Copper wires are increasingly used to replace gold wires in wire-bonding technology owing to their better electrical properties and lower cost. However, not many studies have been conducted on electromigration-induced failure of Cu wedge bonds on Al metallization. In this study, we investigated the failure mechanism of Cu-Al wedge bonds under high current stressing from 4 × 104 A/cm2 to 1 × 105 A/cm2 at ambient temperature of 175°C. The resistance evolution of samples during current stressing and the microstructure of the joint interface between the Cu wire and Al-Si bond pad were examined. The results showed that abnormal crack formation accompanying significant intermetallic compound growth was observed at the second joint of the samples, regardless of the direction of electric current for both current densities of 4 × 104 A/cm2 and 8 × 104 A/cm2. We propose that this abnormal crack formation at the second joint is mainly due to the higher temperature induced by the greater Joule heating at the second joint for the same current stressing, because of its smaller bonded area compared with the first joint. The corresponding fluxes induced by the electric current and chemical potential difference between Cu and Al were calculated and compared to explain the failure mechanism. For current density of 1 × 105 A/cm2, the Cu wire melted within 0.5 h owing to serious Joule heating.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
W. Wu, M. Held, P. Jacob, P. Scacco, and A. Birolini, in Power Semiconductor Devices and ICs, Proceedings of 1995 International Symposium, (IEEE, 1995), pp. 443–448.
H. Xu, C. Liu, V.V. Silberschmidt, S.S. Pramana, T.J. White, Z. Chen, and V.L. Acoff, Intermetallics 19, 1808 (2011).
N.J. Noolu, N.M. Murdeshwar, K.J. Ely, J.C. Lippold, and W.A. Baeslack, J. Mater. Res. 19, 1374 (2004).
H.T. Orchard and A.L. Greer, J. Electron. Mater. 35, 1961 (2006).
E. Zin, N. Michael, S.H. Kang, K.H. Oh, U. Chul, J.S. Cho, J.T. Moon, and C.U. Kim, Electronic Components and Technology Conference, (IEEE, 2009), pp. 943.
H.J. Kim, J.Y. Lee, K.W. Paik, K.W. Koh, J. Won, S. Choe, and Y.J. Park, IEEE Trans. Compon. Packag. Technol. 26, 367 (2003).
H. Xu, C. Liu, V.V. Silberschmidt, S.S. Pramana, T.J. White, Z. Chen, and V.L. Acoff, Acta Mater. 59, 5661 (2011).
C.J. Hang, C.Q. Wang, M. Mayer, Y.H. Tian, Y. Zhou, and H.H. Wang, Microelectron. Reliab. 48, 416 (2008).
Standard, MIL-STD-883G Method 2011.7.
B. Senthil Kumar, S. Mohandass, Ramkumar Malliah, M. Li, K.Y. Song, James, Electronics Packaging Technology Conference (IEEE, 2010), pp. 859–867.
F.W. Wulff, C.D. Breach, and D. Stephan, Electronics Packaging Technology Conference (IEEE, 2004), pp. 348–353.
F.W. Wulff, C.D. Breach, and D. Stephan, Proceedings of SEMICON Conference (2005).
Y. Tian, C. Wang, I. Lum, M. Mayer, J.P. Jung, and Y. Zhou, J. Mater. Process. Technol. 208, 179 (2008).
I. Lum, J.P. Jung, and Y. Zhou, Metall. Mater. Trans. A A36, 1279 (2005).
Y. Takahashi and S. Matsusaka Dhes, Sci. Technol. 17, 435 (2003).
J. Chen, D. Degryse, and P. Ratchev, IEEE Trans. Compon. Packag. Technol. 27, 539 (2004).
C.F. Yu, C.M. Chan, L.C. Chan, and K.C. Hsieh, Microelectron. Reliab. 51, 119 (2011).
M.Y. Guo, C.K. Lin, C. Chen, and K.N. Tu, Intermetallics 29, 155 (2012).
C. Chen, H.-Y. Hsiao, Y.-W. Chang, F.-Y. Ouyang, and K.N. Tu, Mater. Sci. Eng. R 73, 85 (2012).
K.N. Tu, Electronic Thin-Film Reliability (New York, NY: Cambridge University Press, 2010).
W.F. Gale and T.C. Totemeier, Smithells Metals Reference Book (Oxford, UK: Elsevier Butterworth-Heinemann, 2004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, TH., Lin, YM. & Ouyang, FY. Joule-Heating-Induced Damage in Cu-Al Wedge Bonds Under Current Stressing. J. Electron. Mater. 43, 270–276 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-013-2790-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-013-2790-x