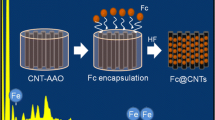
Abstract
A facile and convenient approach was proposed to highly fill carbon nanotubes with various nanoparticles, such as Fe3O4 and CoO. Furthermore, in the case of Fe3O4 and CoO nanoparticles, the effect of reaction conditions on the filling quality and confinement of CNTs on the size and morphology of NPs were explored. The encapsulation procedure in our work can provide a valuable guidance for filling a variety of NPs into hollow structure apart from CNTs. In addition, as a proof-of-concept demonstration, the magnetic properties of Fe3O4 in the absence and presence of CNTs were measured to indicate that magnetization and the blocking temperature of superparamagnetic Fe3O4 can be adjusted, which is due to the confinement effect of CNTs.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Iijima S (1991) Helical microtubules of graphitic carbon. Nature 354:56–58
Kay B, Kay HA, Won KS, Young PS, Jeong MM, Dong BJ, Seong LC (2001) Electrochemical properties of high-power supercapacitors using single-walled carbon nanotube electrodes. Adv Funct Mater 11:387–392
Heer WA, Chatelain A, Ugarte D (1995) A carbon nanotube field-emission electron source. Science 270:1179–1180
Kim P, Lieber CM (1999) Nanotube nanotweezers. Science 286:2148–2150
Singh R, Torti SV (2013) Carbon nanotubes in hyperthermia therapy. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 65:2045–2060
Deng Z, Jiang H, Hu Y, Liu Y, Zhang L, Liu H, Li C (2017) 3D ordered macroporous MoS2@C nanostructure for flexible Li-ion batteries. Adv Mater 29:1603020
Lim WQ, Gao Z (2016) Plasmonic nanoparticles in biomedicine. Nano Today 11(2):168–188
Li HH, Fu QQ, Xu L, Ma SY, Zheng YR, Liu XJ, Yu SH (2017) Highly crystalline PtCu nanotubes with three dimensional molecular accessible and restructured surface for efficient catalysis. Energy Environ Sci 10:1751–1756
Kong C, Du H, Chen L, Chen B (2017) Nanoscale MOF/organosilica membranes on tubular ceramic substrates for highly selective gas separation. Energy Environ Sci 10:1812–1819
Yu WJ, Hou PX, Zhang LL, Li F, Liu C, Cheng HM (2010) High coercivity of iron-filled carbon nanotubes synthesized on austenitic stainless steel. Chem Commun 46:8576–8578
Camilli L, Scarselli M, Gobbo SD, Castrucci P, Lamastra FR, Nanni F, Gautron E, Lefrant S, D’Orazio F, Lucari F, Crescenzi MD (2012) High coercivity of iron-filled carbon nanotubes synthesized on austenitic stainless steel. Carbon 50:718–721
Elías AL, Rodríguez-Manzo JA, McCartney MR, Golberg D, Zamudio A, Baltazar SE, López-Urías F, Muñoz-Sandoval E, Gu L, Tang CC, Smith DJ, Bando Y, Terrones H, Terrones D (2005) Production and characterization of single-crystal FeCo nanowires inside carbon nanotubes. Nano Lett 5:467–472
Wang D, Yang G, Ma Q, Wu M, Tan Y, Yoneyama Y, Tsubaki N (2012) Confinement effect of carbon nanotubes : copper nanoparticles filled carbon nanotubes for hydrogenation of methyl acetate. ACS Catal 2:1958–1966
Corio P, Santos AP, Santos PS, Temperini MLA, Brar VW, Pimenta MA, Dresselhaus MS (2004) Characterization of single wall carbon nanotubes filled with silver and with chromium compounds. Chem Phys Lett 383:475–480
Ugarte D, Chatelain A, Heer WA (1996) Nanocapillarity and chemistry in carbon nanotubes. Science 274:1897–1899
Zhang H, Song H, Chen X, Zhou J, Zhang H (2012) Preparation and electrochemical performance of SnO2@carbon nanotube core-shell structure composites as anode material for lithium-ion batteries. Electrochim Acta 59:160–167
Pan X, Fan Z, Chen W, Ding Y, Luo H, Bao X (2007) Enhanced ethanol production inside carbon-nanotube reactors containing catalytic particles. Nat Mater 6:507–511
Yang Z, Guo S, Pan X, Wang J, Bao X (2011) FeN nanoparticles confined in carbon nanotubes for CO hydrogenation. Energy Environ Sci 4:4500–4503
Ding Q, Liu D, Guo D, Yang F, Pang X, Che R, Zhou N, Xie J, Sun J, Huang Z, Gu N (2017) Shape-controlled fabrication of magnetite silver hybrid nanoparticles with high performance magnetic hyperthermia. Biomaterials 124:35–46
Revia RA, Zhang M (2016) Magnetite nanoparticles for cancer diagnosis, treatment, and treatment monitoring: recent advances. Mater Today 19:157–168
Wu L, Wu M, Lin X, Zhang X, Liu X, Liu J (2017) Magnetite nanocluster and paclitaxel-loaded charge-switchable nanohybrids for MR imaging and chemotherapy. J Mater Chem B 5:849–857
Tsang SC, Chen YK, Harris PJF, Green MLH (1994) A simple chemical method of opening and filling carbon nanotubes. Nature 372:159–162
Yu WJ, Hou PX, Li F, Liu C (2012) Improved electrochemical performance of Fe2O3 nanoparticles confined in carbon nanotubes. J Mater Chem 22:13756–13763
Costa PPMFJ, Sloan J, Rutherford T, Green MLH (2005) Encapsulation of RexOy clusters within single-walled carbon nanotubes and their in tubulo reduction and sintering to Re metal. Chem Mater 17:6579–6582
Dujardin BE, Ebbesen TW, Krishnan K, Treacy MMJ (1998) Wetting of single shell carbon nanotubes. Adv Mater 10:1472–1475
Ebbesen W (1996) Wetting, filling and decorating carbon nanotubes. J Phys Chem Solids 57:951–955
Seo WS, Shim JH, Oh SJ, Lee EK, Hur NH, Park JT (2005) Phase- and size-controlled synthesis of hexagonal and cubic CoO nanocrystals. J Am Chem Soc 127:6188–6189
An K, Lee N, Park J, Kim SC, Wang H, Park JG, Kim JY, Park JH, Han MJ, Yu J, Hyeon T (2006) Synthesis, characterization, and self-assembly of pencil-shaped CoO nanorods. J Am Chem Soc 128:9753–9760
Chen S, Wu G, Sha M, Huang S (2007) Transition of ionic liquid [bmim][PF6] from liquid to high-melting-point crystal when confined in multiwalled carbon nanotubes. J Am Chem Soc 129:2416–2417
Funding
We acknowledge financial support from by the financial supports of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21601144), Xi’an science and technology project-Engineering program of University and Institute talents servicing Enterprise (2017085CG/RC048(XBDX006)) and the Natural Science Foundation of Shaanxi Province (No. 2017JM2025).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 28360 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Diao, J., Wang, G., Ma, S. et al. A facile and convenient approach to fill carbon nanotubes with various nanoparticles. Ionics 25, 3079–3085 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-019-02841-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-019-02841-9