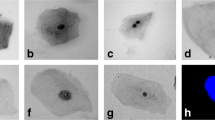
Abstract
The aim of this study was to evaluate the genotoxic effect of pesticides in exfoliated buccal cells of workers occupationally exposed in Guerrero, Mexico, using the comet assay and the micronucleus test. The study compared 111 agricultural workers in three rural communities (Arcelia 62, Ajuchitlan 13, and Tlapehuala 36), with 60 non-exposed individuals. All the participants were males. The presence of DNA damage was investigated in the exfoliated buccal cells of study participants with the comet assay and the micronucleus (MN) test; comet tail length was evaluated in 100 nuclei and 3000 epithelial cells of each individual, respectively; other nuclear anomalies such as nuclear buds, karyolysis, karyorrhexis, and binucleate cells were also evaluated. Study results revealed that the tail migration of DNA and the frequency of MN increased significantly in the exposed group, which also showed nuclear anomalies associated with cytotoxic or genotoxic effect. No positive correlation was noted between exposure time and tail length and micronuclei frequencies. No significant effect on genetic damage was observed as a result of age, smoking, and alcohol consumption. The MN and comet assay in exfoliated buccal cells are useful and minimally invasive methods for monitoring genetic damage in individuals exposed to pesticides. This study provided valuable data for establishing the possible risk to human health associated with pesticide exposure.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
AMIFAC. Asociación Mexicana de la Industria Fitosanitaria, A.C. (2015), México. http://amifac.org.mx/nosotros.html. Accessed Aug 10 2015.
Arbuckle TE, Lin Z, Mery LS (2001) An exploratory analysis of the effect of pesticide exposure on the risk of spontaneous abortion in an Ontario farm population. Environ Health Perspect 109(8):851–857. doi:10.1289/ehp.01109851
Ascarrunz ME, Tirado N, González AR, Cuti M, Cervantes R, Huichi O, Jors E (2006) Evaluación de riesgo genotóxico: biomonitorización de trabajadores agrícolas de Caranavi, Guanay, Palca y Mecapaca, expuestos a plaguicidas. Cuadernos Hosp Clin 51(2):1–15
Bejarano F (2015) Plaguicidas. Red de Acción sobre Plaguicidas y Alternativas en México (RAPAM). http://www.rachel.org/files/document/Pesticidas.htm. Accessed Aug 7 2015.
Benedetti D, Nunez E, Sarmento M, Porto C, Iochims dos Santos CE, Ferraz Dias J, da Silva J (2013) Genetic damage in soybean workers exposed to pesticides: evaluation with the comet and buccal micronucleus cytome assays. Mutat Res 752(1-2):28–33. doi:10.1016/j.mrgentox.2013.01.001
Bolognesi C, Creus A, Ostrosky-Wegman P, Marcos R (2011) Micronuclei and pesticide exposure. Mutagenesis 26(1):19–26. doi:10.1093/mutage/geq070
Bonassi S, Ugolini D, Kirsch-Volders M, Stromberg U, Vermeulen R, Tucker JD (2005) Human population studies with cytogenetic biomarkers: review of the literature and future prospectives. Environ Mol Mutagen 45(2-3):258–270. doi:10.1002/em.20115
Bonassi S, Znaor A, Ceppi M, Lando WP, Chang WP, Holland N, Kirsch-Volders M, Zieger E, Ban S, Barale R, Bigatti MP, Bolognesi C, Cebulska-Wasilewska A, Fabianova E, Fucic A, Hagmar L, Joksić G, Martell A, Migliore L, Mirkova E, Scarfi A, Zijno A, Norppa H, Fenech M (2007) An increased micronucleus frequency in peripheral blood lymphocytes predicts the risk of cancer in humans. Carcinogenesis 28(3):625–631. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgl177
Bonassi S, Biasotti B, Kirsch-Volders M, Knasmueller S, Zeiger E, Burgaz S, Fenech M (2009) State of the art survey of the buccal micronucleus assay—a first stage in the HUMNXL project initiative. Mutagenesis 24(4):295–302. doi:10.1093/mutage/gep019
Bonassi S, Coskun E, Ceppi M, Lando C, Bolognesi C, Burgaz S, Holland N, Kirsh-Volders M, Knasmueller S, Zeiger E, Carnesoltas D, Cavallo D, da Silva J, de Andrade VM, Cackmak Demircigil G, Dominguez Odio A, Donmez-Altuntas H, Gattas G, Giri A, Giri S, Gómez-Meda B, Gómez-Arroyo S, Hadjidekova V, Haveric A, Kamboj M, Kurteshi K, Martino-Roth MG, Montero-Montoya R, Nersesyan A, Pastor-Benito S, Favero Salvadori DM, Shaposhnikova A, Stopper H, Thomas P, Torres-Bugarín O, Singh Yadav A, Zúñiga González G, Fenech M (2011) The human micronucleus project on exfoliated buccal cells (HUMNXL): the role of life-style, host factors, occupational exposures, health status, and assay protocol. Mutat Res 728(3):88–97. doi:10.1016/j.mrrev.2011.06.005
Bortoli de Moura GM, Barbieri de Azevedo M, Basso da Silva L (2009) Cytogenetic biomonitoring of Brazilian workers exposed to pesticides: micronucleus analysis in buccal cells of soybean growers. Mutat Res 675(1-3):1–4. doi:10.1016/j.mrgentox.2009.01.001
Castillo-Cadena J, Tenorio-Vieyra LE, Quintana-Carabia AI, García-Fabila MM, Ramírez-San Juan E, Madrigal-Bujaidar E (2006) Determination of DNA damage in floriculturists exposed to mixtures of pesticides. J Biomed Biotechnol 2:1–12. doi:10.1155/JBB/2006/97896
Da Silva J, Moraes R, Heuser VD, Andrade VM, Silva FR, Kvitko K, Emmel V, Rohr P, Bordin DL, Andreazza C, Salvador M, Henriques JA, Erdtmann B (2008) Evaluation of genetic damage in a Brazilian population exposed to pesticides and its correlation with polymorphisms in metabolizing genes. Mutagenesis 23(5):415–422. doi:10.1093/mutage/gen031
Ergene S, Çelik A, Çavaş T, Kaya F (2007) Genotoxic biomonitoring study of population residing in pesticide contaminated regions in Gösku delta: micronucleus, chromosomal aberrations and sister chromatid exchanges. Environ Int 33(7):877–885. doi:10.1016/j.envint.2007.04.003
Fairbairn DW, Olive PL, O’Neill KL (1995) The comet assay: a comprehensive review. Mutat Res 339(1):37–59. doi:10.1016/0165-1110(94)00013-3v
Garaj-Vrhovac V, Zeljezic D (2000) Evaluation of DNA damage in workers occupationally exposed to pesticides using single-cell gel electrophoresis (SCGE) assay pesticide genotoxicity revealed by comet assay. Mutat Res 469(2):279–285. doi:10.1016/S1383-5718(00)00092-9
Garaj-Vrhovac V, Zeljezic D (2001) Cytogenetic monitoring of Croatian population occupationally exposed to a complex mixture of pesticides. Toxicology 165(2-3):153–162. doi:10.1016/S0300-483X(01)00419-X
Garry FG, Harkins M, Lybimov A, Erickson L, Long L (2002) Reproductive outcomes in the women of the Red River Valley of the north. 1. The spouses of pesticide applicators: pregnancy loss, age at menarche, and exposures to pesticides. J Toxicol Environ Health Part A 65(11):769–786. doi:10.1080/00984100290071333
Gómez-Arroyo S, Díaz-Sánchez Y, Meneses-Pérez MA, Villalobos-Pietrini R, De León-Rodríguez J (2000) Cytogenetic biomonitoring in a Mexican floriculture worker group exposed to pesticides. Mutat Res 466(1):117–124. doi:10.1016/S1383-5718(99)00231-4
Grover P, Danadevi K, Mahboob M, Rozati R, Banu BS, Rahman MF (2003) Evaluation of genetic damage in workers employed in pesticide production utilizing the comet assay. Mutagenesis 18(2):201–205. doi:10.1093/mutage/18.2.201
Holland N, Bolognesi C, Kirsch-Volders M, Bonassi S, Zeiger E, Knasmueller S, Fenech M (2008) The micronucleus assay in human buccal cells as a tool for biomonitoring DNA damage: the HUMN project perspective on current status and knowledge gaps. Mutat Res 659(1-2):93–108. doi:10.1016/j.mrrev.2008.03.007
IARC International Agency for Research on Cancer (2006) Lion France.
Kisby GE, Muniz JF, Scherer J, Lasarev MR, Koshy M, Kow YW, McCauley L (2009) Oxidative stress and DNA damage in agricultural workers. J Agromedecine 14(2):206–214. doi:10.1080/10599240902824042
Koifman S, Koifman RJ, Meyer A (2002) Human reproductive system disturbances and pesticide exposure in Brazil. Cad Saúde Púb, Rio de Janeiro Brazil 18(2):435–445. doi:10.1590/S0102-311X2012001000019
Martínez-Valenzuela C, Gómez-Arroyo S, Villalobos-Pietrini R, Waliszewski S, Calderón-Segura ME, Félix-Gastélum R, Álvarez-Torres A (2009) Genotoxic biomonitoring of agricultural workers exposed to pesticides in the north of Sinaloa state, Mexico. Environ Int 35(8):1155–1159. doi:10.1016/j.envint.2009.07.010
Möller P (2006) The alkaline comet assay: towards validation in biomonitoring of DNA damaging exposures. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 98(4):336–345. doi:10.1111/j.1742-7843.2006.pto_167.x
Muniz JF, McCauley L, Scherer J, Lasarev M, Kaoshy M, Kow YW, Nazar-Stewart V, Kisby GE (2008) Biomarkers of oxidative stress and DNA damage in agricultural workers: a pilot study. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 227(1):97–107. doi:10.1016/j.taap.2007.10.027
Muñoz Aristizábal AF (2009) Evaluación del daño en el ADN en dos poblaciones colombianas de agricultores y floricultores. Actualidad y Divulgación Científica 12(1):7–16
Östling O, Johanson KJ (1984) Microelectrophoretic study of radiation-induced DNA damages in individual mammalian cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 123(1):291–298. doi:10.1016/0006-291X(84)90411-X
Paiva CG, Cabral IO, Soares BM, Sombra CML, Ferreira JRO, Moares MO, Cavalcanti BC, Pessoa C (2011) Biomonitoring of rural workers exposed to a complex mixture of pesticides in the municipalities of Tianguá and Ubajara (Ceará state, Brazil): genotoxic and cytogenetic studies. Environ Mol Mutagen 52(6):492–501. doi:10.1002/em.20647
Pastor S, Creus A, Parrón T, Cebulska-Wasilewska A, Siffel C, Piperakis S, Marcos R (2003) Biomonitoring of four European populations occupationally exposed to pesticides: use of micronuclei as biomarkers. Mutagenesis 18(3):249–258. doi:10.1093/mutage/18.3.249
Paz-y-Miño C, Sánchez ME, Arévalo M, Muñoz MJ, Witte T, Oleas De-la-Carrera G, Leone PE (2007) Evaluation of DNA damage in an Ecuadorian population exposed to glyphosate. Genet Mol Biol 30(2):456–460. doi:10.1590/S1415-47572007000300026
Peralta L, Mañas F, Gentile N, Bosch B, Méndez A, Aiassa D (2011) Evaluación del daño genético en pobladores de Marcos Juárez expuestos a plaguicidas: estudio de un caso en Córdoba, Argentina. Diálogos-Universidad Nacional de San Luis-Facultad de Ciencias Humanas 2(1):7–26
Petrelli G, Figá-Talamanca I, Tropeano R, Tangucci M, Cini C, Aquilani S, Gasperini L, Meli P (2000) Reproductive male-mediated risk: spontaneous abortion among wives of pesticide applicators. Eur J Epidemiol 16(4):391–393. doi:10.1023/A:1007630610911
Ramírez V, Cuenca P (2002) Daño del ADN en trabajadoras expuestas a plaguicidas en Limón, Costa Rica. Rev Biol Trop 50(2):507–518
Remor AL, Caprini Totti C, Alves Moreira D, Pimentel Dutra G, Dahlström Heuser V, Boeira JM (2009) Occupational exposure of farm workers to pesticides: biochemical parameters and evaluation of genotoxicity. Environ Int 35(2):273–278. doi:10.1016/j.envint.2008.06.011
Rojas A, Ojeda M, Barraza X (2000) Congenital malformations and pesticide exposure. Rev Med Chil 128(4):399–404. doi:10.4067/S0034-98872000000400006
Sailaja N, Chandrasekhar M, Rekhadevi P, Mahboob M, Rahman M, Saleha B, Vuyyuri B, Danadevi K, Hussain S, Grover P (2006) Genotoxic evaluation of workers employed in pesticide production. Mutat Res 609(1):74–80. doi:10.1016/j.mrgentox.2006.06.022
Simoniello MF, Kleinsorge EC, Carballo MA (2010) Evaluación bioquímica de trabajadores rurales expuestos a pesticidas. Medicina (Buenos Aires) 70(6):489–498
Singh NP, McCoy MT, Tice RR, Schneider EL (1988) A simple technique for quantitation of low levels of DNA damage in individual cells. Exp Cell Res 175(1):184–191. doi:10.1016/0014-4827(88)90265-0
Speit G, Hartmann A (2006) The comet assay: a sensitive genotoxicity test for the detection of DNA damage and repair. Methods Mol Biol 314:275–286. doi:10.1385/1-59259-973-7:275
Stich HF (1987) Micronucleated exfoliated cells as indicators for genotoxic damage and as markers in chemo-prevention trials. J Nutr Growth Cancer 4(5):9–18. doi:10.1016/0091-7435(89)90044-3
Stich HF, Rosin MP (1984) Micronuclei in exfoliated human cells as a tool for studies in cancer risk and cancer intervention. Cancer Lett 22(3):241–253. doi:10.1016/0304-3835(84)90159-9
Tas S, Lauwerys R, Lyson D (1996) Occupational hazard for male reproductive system. Crit Rev Toxicol 26(3):261–307. doi:10.1136/oem.58.10.635
Thomas P, Holland N, Bolognesi C, Kirsch-Volders M, Bonassi S, Zieger E, Knasmueller S, Fenech M (2009) Buccal micronucleus cytome assay. Nat Protoc 4(6):825–837. doi:10.1038/nprot.2009.53
Tice RR, Agurell E, Anderson D, Burlinson B, Hartmann A, Kobayashi H, Miyamae Y, Rojas E, Ryu JC, Sasaki YF (2000) Single cell/comet assay: guidelines for in vitro and in vivo genetic toxicology testing. Environ Mol Mutagen 35(3):206–221. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1098-2280(2000)
Tolbert PE, Shy CM, Allen JM (1992) Micronuclei and other nuclear anomalies in buccal smears: methods development. Mutat Res 271(1):69–77. doi:10.1016/0165-1161(92)90033-I
Ünderğer Ü, Başaran N (2002) Assessment of DNA damage in workers occupationally exposed to pesticide mixtures by the alkaline comet assay. Arch Toxicol 76(3):430–436. doi:10.1007/s00204-002-0355-5
WHO (World Health Organization) (2010) The WHO recommended classification of pesticides by hazard and guidelines to classification 2009. International Program on Chemical Safety (IPCS) & World Health Organization (WHO), Geneva
Wilhelm CM, Kunz AC, Basso da Siva L (2015) Assessment of DNA damage in floriculturists in southern Brazil. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22(11):8182–8189. doi:10.1007/s11356-014-3959-4
Zeljezic D, Garaj-Vrhovac V (2001) Chromosomal aberration and single cell gel electrophoresis (comet) assay in the longitudinal risk assessment of occupational exposure to pesticides. Mutagenesis 16(4):359–363. doi:10.1093/mutage/16.4.359
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr. Stefano Bonassi for his comments and suggestions, María Luisa Vargas Torres and Liliana Sánchez Estrada for their technical assistance, the physician Andrés Palacios for the medical attention extended to the agricultural workers, and Claudio Amescua for his editing assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
This study was performed in accordance with the principles stated in the Declaration of Helsinki. All participants were informed regarding the study and they accepted the idea of taking part in it. They subsequently signed the document in which they agreed to complete a standardized questionnaire with personal data related to age; time of exposure, habits such as smoking and alcohol consumption, drugs, and diets; the type of work performed; and protective measures used.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Carbajal-López, Y., Gómez-Arroyo, S., Villalobos-Pietrini, R. et al. Biomonitoring of agricultural workers exposed to pesticide mixtures in Guerrero state, Mexico, with comet assay and micronucleus test. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 2513–2520 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5474-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5474-7