Abstract
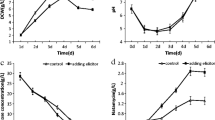
Syringin production and related secondary metabolism enzyme activities in suspension cultures of Saussurea medusa treated with different elicitors (yeast extract, chitosan and Ag+) were investigated. All elicitors enhanced syringin production, and the optimal feeding protocol was the combined addition of 1.5% (v/v) yeast extract, 0.2 g l−1 chitosan and 75 μM Ag+ at the 15th day of the cell culture. The highest syringin production reached 741.9 mg l−1, which was 3.6−fold that of the control. The glucose−6-phosphate dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.49), phenylalanine ammonia lyase (EC 4.3.1.5) and peroxidase (EC 1.11.1.7) activities increased significantly after elicitor treatment. The maximum enzyme activities were obtained when the treatment time was 6 h.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 6BA:
-
6-Benzylaminopurine
- DTT:
-
Dithiotreitol
- G6PDH:
-
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase
- NAA:
-
α-Naphthaleneacetic acid
- PAL:
-
Phenylalanine ammonia lyase
- POD:
-
Peroxidase
- PPP:
-
Pentose phosphate pathway
- PVPP:
-
Polyvinyl polypyrrolidone
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
References
Chen FJ, Yang YG, Zhao DX (1999) Advance in studies of species, habitats distribution and chemical composition of snow lotuses (Saussurea) in China. Chin Bull Bot 16:561–566
Debnam PM, Emes MJ (1999) Subcellular distribution of enzymes of the oxidative pentose phosphate pathway in root and leaf tissues. J Exp Bot 50:1653–1661
Fahrendorf T, Ni W, Shorroosh BS, Dixon RA (1995) Stress responses in alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). XIX. Transcriptional activation of oxidative pentose phosphate pathway genes at the onset of the isoflavanoid phytoalexin response. Plant Mol Biol 28:885–900
Hammerschmidt R, Kuc J (1982) Lignification as a mechanism for induced systemic resistance in cucumber. Physiol Plant Pathol 20:61–71
Komaraiah P, Naga Amrutha R, Kavi Kishor PB, Ramakrishna SV (2002) Elicitor enhanced production of plumbagin in suspension cultures of Plumbago rosea L. Enzyme Microb Technol 3:634–639
Koukol J, Conn EE (1961) The metabolism of aromatic and properties of the phenylalanine deaminase of Hordeum vulgare. J Biol Chem 236:2692–2698
Luo J, He GY (2004) Optimization of elicitors and precursors for paclitaxel production in cell suspension culture of Taxus chinensis in the presence of nutrient feeding. Process Biochem 39:1073–1079
Mehdy MC (1994) Active oxygen species in plant defense against pathogens. Plant Physiol 105:467–472
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bio assays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15:473–497
Pan Z, Wang H, Zhong J (2000) Scale-up study on suspension cultures of Taxus chinensis cells for production of taxane diterpene. Enzyme Microb Technol 27:714–723
Rajendran L, Suvarnalatha G, Ravishankar GA, Venkataraman LV (1994) Enhancement of anthocyanin production in callus cultures of Daucus carota L., under the influence of fungal elicitors. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 42:227–231
Savitha BC, Thimmaraju R, Bhagyalakshmi N, Ravishankar GA (2006) Different biotic and abiotic elicitors influence betalain production in hairy root cultures of Beta vulgaris in shake-flask and bioreactor. Process Biochem 41:50–60
Thoma I, Loeffler C, Sinha AK, Gupta M, Krischke M, Steffan B (2003) Cyclopentenone isoprostanes induced by reactive oxygen species trigger defense gene activation and phytoalexin accumulation in plants. Plant J 34:363–375
Yang ZJ, Tong SQ, Chu JJ, Sheng LQ, Chen G (2004) Preparative isolation and purification of syringin and edgeworoside C from Edgeworthia chrysantha Lindl by high-speed counter-current chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1043:329–332
Yu ZZ, Fu CX, Han YS, Li YX, Zhao DX (2006) Salicylic acid enhances jaceosidin and syringin production in cell cultures of Saussurea medusa. Biotechnol Lett 28:1027–1031
Yuan XF, Wang Q, Zhao B, Wang YC (2002) Improved cell growth and total flavonoids of Saussurea medusa on solid culture medium supplemented with rare earth elements. Biotechnol Lett 24:1889–1892
Zhang CZ, Wu JY (2003) Ethylene inhibitors enhance elicitor-induced paclitaxel production in suspension cultures of Taxus spp. cells. Enzyme Microb Technol 32:71–77
Zhao DX, Fu CX, Han YS, Lu DP (2005a) Effects of elicitation on jaceosidin and hispidulin production in cell suspension cultures of Saussurea medusa. Process Biochem 40:739–745
Zhao J, Davis LC, Verpoorte R (2005b) Elicitor signal transduction leading to production of plant secondary metabolites. Biotechnol Adv 23:283–333
Acknowledgment
This research is supported by Directional Project of Knowledge Innovation Engineering, CAS (KGCX2-SW−506).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, C., Zhao, B., Ou, Y. et al. Elicitor-enhanced syringin production in suspension cultures of Saussurea medusa . World J Microbiol Biotechnol 23, 965–970 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-006-9321-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-006-9321-3