Abstract
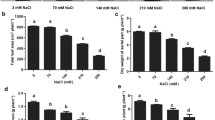
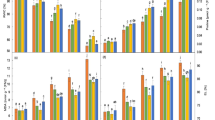
Sugar beet (Beta vulgaris L.) is a natrophilic species well adapted to salinity and water stress. To investigate the physiological impact of salt on osmotic stress response, in the present study, 3-week-old seedlings were treated with a series of additional external NaCl concentrations (5–150 mM). Seedlings were also subjected to 0 or 240 mM sorbitol in the presence or absence of 50 mM NaCl. It is clear that the addition of NaCl at a concentration of 50 mM in the medium was optimal for growth of sugar beet plants. Sorbitol-induced osmotic stress strongly reduced its growth and led to a significant decrease in shoot osmotic potential (Ψs), water content and K+ concentrations, whereas Na+ concentrations remained unchanged. The addition of 50 mM NaCl also mitigated the deleterious impact of osmotic stress on growth and reduced the shoot Ψs. Presence of NaCl in the medium, together with sorbitol, significantly increased the levels of Na+ and proline in both shoot and root, enhanced Na+ net uptake rate, and resulted in a decrease of K+ accumulation. These results suggest that the ability of NaCl to improve plant performance under osmotic stress may be due to its effect on osmotic adjustment through Na+ and proline accumulation.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DW:
-
Dry weight
- FW:
-
Fresh weight
- NHX:
-
Tonoplast Na+/H+ antiporter
- OA:
-
Osmotic adjustment
- RFW:
-
Root fresh weight
- SE:
-
Standard error
- WC:
-
Water content
- Ψs :
-
Osmotic potential
References
Adler G, Blumwald E, Bar-Zvi D (2010) The sugar beet gene encoding the sodium/proton exchanger 1 (BvNHX1) is regulated by a MYB transcription factor. Planta 232:187–195
Anschütz U, Becker D, Shabala S (2014) Going beyond nutrition: regulation of potassium homoeostasis as a common denominator of plant adaptive responses to environment. J Plant Physiol 171:670–687
Apse MP, Blumwald E (2007) Na+ transport in plants. FEBS Lett 581:2247–2254
Ashraf M, Foolad MR (2007) Roles of glycine betaine and proline in improving plant abiotic stress resistance. Environ Exp Bot 59:207–216
Bajji M, Kinet JM, Lutts S (1998) Salt stress effects on roots and leaves of Atriplex halimus L. and their corresponding callus cultures. Plant Sci 137:131–142
Barnabás B, Jäger K, Fehér A (2008) The effect of drought and heat stress on reproductive processes in cereals. Plant, Cell Environ 31:11–39
Bates LS, Waldren RP, Teare ID (1973) Rapid determination of free proline for water stress studies. Plant Soil 39:205–207
Ben Hassine A, Bouzid S, Lutts S (2010) Does habitat of Atriplex halimus L. affect plant strategy for osmotic adjustment? Acta Physiol Plant 32:325–331
Bhargava S, Sawant K (2013) Drought stress adaptation: metabolic adjustment and regulation of gene expression. Plant Breeding 132:21–32
Blum A, Munns R, Passioura JB, Turner NC, Sharp RE, Boyer JS, Nguyen HT, Hsiao TC (1996) Genetically engineered plants resistant to soil drying and salt stress: how to interpret osmotic relations? Plant Physiol 110:1051–1053
Blumwald E (2000) Sodium transport and salt tolerance in plants. Curr Opin Cell Biol 12:431–434
Blumwald E, Poole RJ (1985) Na+/H+ antiport in isolated tonoplast vesicles from storage tissue of Beta vulgaris. Plant Physiol 78:163–167
Blumwald E, Poole RJ (1987) Salt tolerance in suspension cultures of sugar beet-induction of Na+/H+ antiport activity at the tonoplast by growth in salt. Plant Physiol 83:884–887
Blumwald E, Cragoe EJ, Poole RJ (1987) Inhibition of Na+/H+ antiport activity in sugar beet tonoplast by analogs of amiloride. Plant Physiol 85:30–33
Cha-um S, Kirdmanee C (2009) Proline accumulation, photosynthetic abilities and growth characters of sugarcane (Saccharum officinarum L.) plantlets in response to iso-osmotic salt and water-deficit stress. Agric Sci China 8:51–58
Chaves MM, Maroco JP, Pereira JS (2003) Understanding plant responses to drought-from genes to the whole plant. Funct Plant Biol 30:239–264
DaCosta M, Huang B (2006) Osmotic adjustment associated with variation in bent grass tolerance to drought stress. J Am Soc Hortic Sci 131:338–344
Errabii T, Gandonou CB, Essalmani H, Abrini J, Idaomar M, Senhaji NS (2007) Effect of NaCl and mannitol induced stress on sugarcane (Saccharum sp.) callus cultures. Acta Physiol Plant 29:95–102
Flowers TJ, Läuchli A (1983) Sodium versus potassium: Substitution and compartmentation. In: Läuchli A, Bieleski RL (eds) Encyclopedia of plant physiology, new series. Springer, Berlin, pp 651–681
Ghoulam C, Foursy A, Fares K (2002) Effects of salt stress on growth, inorganic ions and proline accumulation in relation to osmotic adjustment in five sugar beet cultivars. Environ Exp Bot 47:39–50
Glenn EP, Brown JJ (1998) Effects of soil salt levels on the growth and water use efficiency of Atriplex canescens (Chenopodiaceae) varieties in drying soil. Am J Bot 85:10–16
Gong JM, Waner DA, Horie T, Li SL, Horie R, Abid KB, Schroeder JI (2004) Microarray-based rapid cloning of an ion accumulation deletion mutant in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:15404–15409
Hessinia K, Martínez JP, Gandour M, Albouchi A, Soltani A, Abdelly C (2009) Effect of water stress on growth, osmotic adjustment, cell wall elasticity and water-use efficiency in Spartina alterniflora. Environ Exp Bot 67:312–319
Kusaka M, Ohta M, Fujimura T (2005) Contribution of inorganic components to osmotic adjustment and leaf folding for drought tolerance in pearl millet. Physiol Plant 125:474–489
Liu HL, Wang QQ, Yu MM, Zhang YY, Wu YB, Zhang HX (2008) Transgenic salt-tolerant sugar beet (Beta vulgaris L.) constitutively expressing an Arabidopsis thaliana vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter gene, AtNHX3, accumulates more soluble sugar but less salt in storage roots. Plant, Cell Environ 31:1325–1334
Ma Q, Yue LJ, Zhang JL, Wu GQ, Bao AK, Wang SM (2012) Sodium chloride improves the photosynthesis and water status in succulent xerophyte Zygophyllum xanthoxylum. Tree Physiol 32:4–13
Maathuis FJM, Sanders D (2001) Sodium uptake in Arabidopsis roots is regulated by cyclic nucleotides. Plant Physiol 127:1617–1625
Maggio A, Reddy MP, Joly RJ (2000) Leaf gas exchange and solute accumulation in the halophyte Salvadora persica grown at moderate salinity. Environ Exp Bot 44:31–38
Martínez JP, Ledent JF, Bajji M, Kinet JM, Lutts S (2003) Effect of water stress on growth, Na+ and K+ accumulation and water use efficiency in relation to osmotic adjustment in two populations of Atriplex halimus L. Plant Growth Regul 41:63–73
Martínez JP, Lutts S, Schanck A, Bajji M, Kinet JM (2004) Is osmotic adjustment required for water-stress resistance in the Mediterranean shrub Atriplex halimus L.? J Plant Physiol 161:1041–1051
Martínez JP, Kinet JM, Bajji M, Lutts S (2005) NaCl alleviates polyethylene glycol-induced water stress in the halophyte species Atriplex halimus L. J Exp Bot 419:2421–2431
McDowell N, Pockman WT, Allen CD, Breshears DD, Cobb N, Kolb T, Plaut J, Sperry J, West A, Williams DG, Yepez EA (2008) Mechanisms of plant survival and mortality during drought: why do some plants survive while others succumb to drought? New Phytol 178:719–739
Ming DF, Pei ZF, Naeem MS, Gong HJ, Zhou WJ (2012) Silicon alleviates PEG-induced water-deficit stress in upland rice seedlings by enhancing osmotic adjustment. J Agron Crop Sci 198:14–26
Pantoja O, Dainty J, Blumwald E (1990) Tonoplast ion channels from sugar-beet cell-suspensions. Inhibition by amiloride and its analogs. Plant Physiol 94:1788–1794
Patakas A, Nikolaou N, Zioziou K, Radoglou K, Noitsakis B (2002) The role of organic solute and ion accumulation in osmotic adjustment in drought-stressed grapevines. Plant Sci 163:361–367
Shabala S, Shabala L (2011) Ion transport and osmotic adjustment in plants and bacteria. Biomol Concepts 2:407–419
Slama I, Ghnaya T, Messedi D, Hessini K, Labidi N, Savoure A, Abdelly C (2007) Effect of sodium chloride on the response of the halophyte species Sesuvium portulacastrum grown in mannitol-induced water stress. J Plant Res 120:291–299
Subbarao GV, Wheeler RM, Stutte GW, Levine LH (1999) How far can sodium substitute for potassium in red beet? J Plant Nutr 22:1745–1761
Subbarao GV, Wheeler RM, Levine LH, Stutte GW (2001) Glycinbetaine accumulation, ionic and water relations of red beet at contrasting levels of sodium supply. J Plant Physiol 158:67–776
Sucre B, Suárez N (2011) Effect of salinity and PEG-induced water stress on water status, gas exchange, solute accumulation, and leaf growth in Ipomoea pes-caprae. Environ Exp Bot 70:192–203
Taylor CB (1996) Proline and water deficit: ups, downs, ins, and outs. Plant Cell 8:1221–1224
Wakeel A, Abd-El-Motagally F, Steffens D, Schubert S (2009) Sodium induced calcium deficiency in sugar beet during substitution of potassium by sodium. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 172:254–260
Wakeel A, Hanstein S, Pitann B, Schubert S (2010) Hydrolytic and pumping activity of H+-ATPase from leaves of sugar beet (Beta vulgaris L.) as affected by salt stress. J Plant Physiol 167:725–731
Wakeel A, Faroop M, Qadir M, Schubert S (2011) Potassium substitution by sodium in plants. Crit Rev Plant Sci 30:401–413
Wang BS, Lüttge U, Ratajczak R (2001) Effects of salt treatment and osmotic stress on V-ATPase and V-PPase in leaves of the halophyte Suaeda salsa. J Exp Bot 365:2355–2365
Wang SM, Wan CG, Wang YR, Chen H, Zhou ZY, Fu H, Sosebee RE (2004) The characteristics of Na+, K+ and free proline distribution in several drought-resistant plants of the Alxa Desert, China. J Arid Environ 56:525–539
Wang SM, Zhang JL, Flowers TJ (2007) Low-affinity Na+ uptake in the halophyte Suaeda maritime. Plant Physiol 145:559–571
Wang CM, Zhang JL, Liu XS, Li Z, Wu GQ, Cai JY, Flowers TJ, Wang SM (2009) Puccinellia tenuiflora maintains a low Na+ level under salinity by limiting unidirectional Na+ influx resulting in a high selectivity for K+ over Na+. Plant, Cell Environ 32:486–496
Wu GQ, Liang N, Feng RJ, Zhang JJ (2013) Evaluation of salinity tolerance in seedlings of sugar beet (Beta vulgaris L.) cultivars using proline, soluble sugars and cation accumulation criteria. Acta Physiol Plant 35:2665–2694
Xia T, Apse MP, Aharon GS, Blumwald E (2002) Identification and characterization of a NaCl-inducible vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter in Beta vulgaris. Physiol Plant 116:206–212
Yue LJ, Ma Q, Li SX, Zhou XR, Wu GQ, Bao AK, Zhang JL, Wang SM (2012) NaCl stimulates growth and alleviates water stress in the xerophyte Zygophyllum xanthoxylum. J Arid Environ 87:153–160
Zhang J, Nguyen H, Blum A (1999) Genetic analysis of osmotic adjustment in crop plants. J Exp Bot 50:291–302
Zhang ZJ, Li HZ, Zhou WJ, Takeuchi Y, Yoneyama K (2006) Effect of 5-aminolevulinic acid on development and salt tolerance of potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) microtubers in vitro. Plant Growth Regul 49:27–34
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31260294) and the Natural Science Foundation of Gansu Province, China (Grant No. 1208RJZA238). We thank Prof. Suo-Min Wang’s lab at Lanzhou University for kindly providing the facility for osmotic potential measurement. We are also grateful to the anonymous reviewers for their valuable suggestions and comments on the initial version of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, GQ., Feng, RJ., Liang, N. et al. Sodium chloride stimulates growth and alleviates sorbitol-induced osmotic stress in sugar beet seedlings. Plant Growth Regul 75, 307–316 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-014-9954-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-014-9954-4