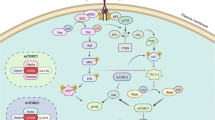
Summary
Lovastatin is a 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase inhibitor. Its inhibitory action on HMG-CoA reductase leads to depletion of isoprenoids, which inhibits post-translational modification of RAS. In this study, we investigated the effect of combining lovastatin with gefitinib on gefitinib-resistant human non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cell lines with K-Ras mutations. Antitumor effects were measured by growth inhibition and 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay. Effects on apoptosis were determined by flow cytometry, DNA fragmentation, and immunoblots. Protein levels of RAS, AKT/pAKT, and RAF/ERK1/2 in cancer cells were analyzed by immunoblot. Compared with gefitinib alone, a combination of gefitinib with lovastatin showed significantly enhanced cell growth inhibition and cytotoxicity in gefitinib-resistant A549 and NCI-H460 human NSCLC cells. In addition, lovastatin combination treatment significantly increased gefitinib-related apoptosis, as determined by fluorescence microscopy and flow cytometric analysis. These effects correlated with up-regulation of cleaved caspase-3, poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP), and Bax and down-regulation of Bcl-2. The combination of lovastatin and gefitinib effectively down-regulated RAS protein and suppressed the phosphorylation of RAF, ERK1/2, AKT, and EGFR in both cell lines. Taken together, these results suggest lovastatin can overcome gefitinib resistance, in NSCLC cells with K-Ras mutations, by down regulation of RAS protein, which leads to inhibition of both RAF/ERK and AKT pathways.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fukuoka M, Yano S, Giaccone G, Tamura T, Nakagawa K, Douillard JY et al (2003) Multi-institutional randomized phase II trial of gefitinib for previously treated patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (The IDEAL 1 Trial). J Clin Oncol 21:2237–46. doi:10.1200/JCO.2003.10.038
Lee DH, Han JY, Kim HT, Lee JS (2006) Gefitinib is of more benefit in chemotherapy-naive patients with good performance status and adenocarcinoma histology: retrospective analysis of 575 Korean patients. Lung Cancer 53:339–45. doi:10.1016/j.lungcan.2006.05.015
Janne PA, Johnson BE (2006) Effect of epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase domain mutations on the outcome of patients with non-small cell lung cancer treated with epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Clin Cancer Res 12:4416s–20s. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-0555
Eberhard DA, Johnson BE, Amler LC, Goddard AD, Heldens SL, Herbst RS et al (2005) Mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor and in KRAS are predictive and prognostic indicators in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer treated with chemotherapy alone and in combination with erlotinib. J Clin Oncol 23:5900–9. doi:10.1200/JCO.2005.02.857
Wennerberg K, Rossman KL, Der CJ (2005) The Ras superfamily at a glance. J Cell Sci 118:843–6. doi:10.1242/jcs.01660
Istvan ES, Deisenhofer J (2001) Structural mechanism for statin inhibition of HMG-CoA reductase. Science 292:1160–4. doi:10.1126/science.1059344
Mantha AJ, Hanson JE, Goss G, Lagarde AE, Lorimer IA, Dimitroulakos J (2005) Targeting the mevalonate pathway inhibits the function of the epidermal growth factor receptor. Clin Cancer Res 11:2398–407. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-1951
Demierre MF, Higgins PD, Gruber SB, Hawk E, Lippman SM (2005) Statins and cancer prevention. Nat Rev Cancer 5:930–42. doi:10.1038/nrc1751
Chou TC, Motzer RJ, Tong Y, Bosl GJ (1994) Computerized quantitation of synergism and antagonism of taxol, topotecan, and cisplatin against human teratocarcinoma cell growth: a rational approach to clinical protocol design. J Natl Cancer Inst 86:1517–24
Engelman JA, Janne PA, Mermel C, Pearlberg J, Mukohara T, Fleet C et al (2005) ErbB-3 mediates phosphoinositide 3-kinase activity in gefitinib-sensitive non-small cell lung cancer cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:3788–93. doi:10.1073/pnas.0409773102
Janmaat ML, Rodriguez JA, Gallegos-Ruiz M, Kruyt FA, Giaccone G (2006) Enhanced cytotoxicity induced by gefitinib and specific inhibitors of the Ras or phosphatidyl inositol-3 kinase pathways in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Int J Cancer 118:209–14. doi:10.1002/ijc.21290
Aggarwal BB, Takada Y (2005) Pro-apototic and anti-apoptotic effects of tumor necrosis factor in tumor cells. Role of nuclear transcription factor NF-kappaB. Cancer Treat Res 126:103–27
Engelman JA, Janne PA (2008) Mechanisms of acquired resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res 14:2895–9. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-2248
Campbell SL, Khosravi-Far R, Rossman KL, Clark GJ, Der CJ (1998) Increasing complexity of Ras signaling. Oncogene 17:1395–413. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1202174
Yarden Y, Sliwkowski MX (2001) Untangling the ErbB signaling network. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2:127–37. doi:10.1038/35052073
Rodriguez-Viciana P, Warne PH, Dhand R, Vanhaesebroeck B, Gout I, Fry MJ et al (1994) Phosphatidylinositol-3-OH kinase as a direct target of Ras. Nature 370:527–32. doi:10.1038/370527a0
Okudela K, Hayashi H, Ito T, Yazawa T, Suzuki T, Nakane Y et al (2004) K-ras gene mutation enhances motility of immortalized airway cells and lung adenocarcinoma cells via Akt activation: possible contribution to non-invasive expansion of lung adenocarcinoma. Am J Pathol 164:91–100
Pao W, Wang TY, Riely GJ, Miller VA, Pan Q, Ladanyi M et al (2005) KRAS mutations and primary resistance of lung adenocarcinomas to gefitinib or erlotinib. PLoS Med 2:e17. doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.0020017
Massarelli E, Varella-Garcia M, Tang X, Xavier AC, Ozburn NC, Liu DD et al (2007) KRAS mutation is an important predictor of resistance to therapy with epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in non-small-cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res 13:2890–6. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-3043
Linardou H, Dahabreh IJ, Kanaloupiti D, Siannis F, Bafaloukos D, Kosmidis P et al (2008) Assessment of somatic k-RAS mutations as a mechanism associated with resistance to EGFR-targeted agents: a systematic review and meta-analysis of studies in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer and metastatic colorectal cancer. Lancet Oncol 9:962–72. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(08)70206-7
Reuter CW, Morgan MA, Bergmann L (2000) Targeting the Ras signaling pathway: a rational, mechanism-based treatment for hematologic malignancies? Blood 96:1655–69
Cemeus C, Zhao TT, Barrett GM, Lorimer IA, Dimitroulakos J (2008) Lovastatin enhances gefitinib activity in glioblastoma cells irrespective of EGFRvIII and PTEN status. J Neurooncol 90:9–17. doi:10.1007/s11060-008-9627-0
Laezza C, Fiorentino L, Pisanti S, Gazzerro P, Caraglia M, Portella G et al (2008) Lovastatin induces apoptosis of k-ras-transformed thyroid cells via inhibition of ras farnesylation and by modulating redox state. J Mol Med 86:1341–51. doi:10.1007/s00109-008-0396-1
Ogunwobi OO, Beales IL (2008) Statins inhibit proliferation and induce apoptosis in Barrett’s esophageal adenocarcinoma cells. Am J Gastroenterol 103:825–37. doi:10.1111/j.1572-0241.2007.01773.x
Wong WW, Dimitroulakos J, Minden MD, Penn LZ (2002) HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors and the malignant cell: the statin family of drugs as triggers of tumor-specific apoptosis. Leukemia 16:508–19. doi:10.1038/sj.leu.2402476
Chan KK, Oza AM, Siu LL (2003) The statins as anticancer agents. Clin Cancer Res 9:10–9
Kawata S, Yamasaki E, Nagase T, Inui Y, Ito N, Matsuda Y et al (2001) Effect of pravastatin on survival in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. A randomized controlled trial. Br J Cancer 84:886–91. doi:10.1054/bjoc.2000.1716
Acknowledgment
This study was supported by a grant from the National Cancer Center 0810130-2.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
In Hae Park and Jae In Jung have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, I.H., Kim, J.Y., Jung, J.I. et al. Lovastatin overcomes gefitinib resistance in human non-small cell lung cancer cells with K-Ras mutations. Invest New Drugs 28, 791–799 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-009-9319-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-009-9319-4