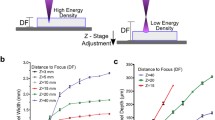
Abstract
Micromilling is a proven method for prototyping microfluidic devices; however, high overhead costs, large machine footprints, an esoteric software stack, and nonstandard device bonding protocols may be hampering the widespread adoption of micromilling in the greater microfluidics community. This research exploits a free design-to-device software chain and uses it to explore the applicability of a new class of inexpensive, desktop micromills for fabricating microfluidic devices out of polycarbonate. We present an analysis framework for stratifying micromill’s spatial accuracy and surface quality. Utilizing this we concluded milling geometries directly on the substrate is advantageous to making molds out of the substrate, in terms of accuracy and minimum feature size. Moreover, we proposed a general procedure to calculate feedrate and spindle-speed for any sub-millimeter endmill based on a recommended load percentage. We also established stepover is the major parameter in determining the surface quality rather than spindle-speed and feedrate, showing low-cost mills are able to deliver high-quality surface finishes. Ultimately, we clarified the suitability of low-cost micromills and a cost-efficient assembly method in the field of microfluidics by demonstrating rate- and size-controlled microfluidic droplet generation.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aubin J, Prat L, Xuereb C, Gourdon C (2009) Effect of microchannel aspect ratio on residence time distributions and the axial dispersion coefficient. Chem Eng Process Process Intensif 48(1):554–559
Ayoib A, Hashim U, Arshad MM, Thivina V (2016) Soft lithography of microfluidics channels using su-8 mould on glass substrate for low cost fabrication. In: 2016 IEEE EMBS conference on biomedical engineering and sciences (IECBES). IEEE, pp 226–229
Bahrami M, Yovanovich M, Culham J (2006) Pressure drop of fully-developed, laminar flow in microchannels of arbitrary cross-section. J Fluids Eng 128(5):1036–1044
Barbier V, Tatoulian M, Li H, Arefi-Khonsari F, Ajdari A, Tabeling P (2006) Stable modification of pdms surface properties by plasma polymerization: application to the formation of double emulsions in microfluidic systems. Langmuir 22(12):5230–5232
Beebe DJ, Mensing GA, Walker GM (2002) Physics and applications of microfluidics in biology. Ann Rev Biomed Eng 4(1):261–286
Brower K, White AK, Fordyce PM (2017) Multi-step variable height photolithography for valved multilayer microfluidic devices. J Vis Exp (119):e55276–e55276
Chen PC, Pan CW, Lee WC, Li KM (2014) Optimization of micromilling microchannels on a polycarbonate substrate. Int J Precis Eng Manuf 15(1):149–154
Dittrich PS, Schwille P (2003) An integrated microfluidic system for reaction, high-sensitivity detection, and sorting of fluorescent cells and particles. Anal Chem 75(21):5767–5774
Eddings MA, Johnson MA, Gale BK (2008) Determining the optimal pdms-pdms bonding technique for microfluidic devices. J Micromech Microeng 18(6):067001
Guckenberger DJ, de Groot TE, Wan AM, Beebe DJ, Young EW (2015) Micromilling: a method for ultra-rapid prototyping of plastic microfluidic devices. Lab Chip 15(11):2364–2378
Harper CA (2000) Modern plastics handbook: handbook. McGraw-Hill Professional, New York
Huang H, Densmore D (2014) Fluigi: microfluidic device synthesis for synthetic biology. ACM J Emerg Technol Comput Syst (JETC) 11(3):26
Jankowski P, Ogonczyk D, Kosinski A, Lisowski W, Garstecki P (2011) Hydrophobic modification of polycarbonate for reproducible and stable formation of biocompatible microparticles. Lab Chip 11(4):748–752
Kang JH, Kim YC, Park JK (2008) Analysis of pressure-driven air bubble elimination in a microfluidic device. Lab Chip 8(1):176–178
Kintses B, Hein C, Mohamed MF, Fischlechner M, Courtois F, Lainé C, Hollfelder F (2012) Picoliter cell lysate assays in microfluidic droplet compartments for directed enzyme evolution. Chem Biol 19(8):1001–1009
Lashkaripour A, Abouei Mehrizi A, Rasouli M, Goharimanesh M (2015) Numerical study of droplet generation process in a microfluidic flow focusing. J Comput Appl Mech 46(2):167–175
Lashkaripour A, Abouei Mehrizi A, Rasouli M, Goharimanesh M, Razavi Bazaz S (2018) Size-controlled droplet generation in a microfluidic device for rare dna amplification by optimizing its effective parameters. J Mech Med Biol 18(1):1850002
Lee K, Dornfeld DA (2004) A study of surface roughness in the micro-end-milling process
Luo Y, Yu F, Zare RN (2008) Microfluidic device for immunoassays based on surface plasmon resonance imaging. Lab Chip 8(5):694–700
Mian A, Driver N, Mativenga P (2011) Estimation of minimum chip thickness in micro-milling using acoustic emission. Proc Inst Mech Eng B J Eng Manuf 225(9):1535–1551
Mogi K, Sugii Y, Yamamoto T, Fujii T (2014) Rapid fabrication technique of nano/microfluidic device with high mechanical stability utilizing two-step soft lithography. Sens Actuators B Chem 201:407–412
Mukhopadhyay R (2007) When PDMS isn't the best. Anal Chem 79(9):3248–3253
Ogonczyk D, Wegrzyn J, Jankowski P, Dabrowski B, Garstecki P (2010) Bonding of microfluidic devices fabricated in polycarbonate. Lab Chip 10(10):1324–1327
Pansare VB, Sharma SB (2013) Chip load sensitive performance in micro-face milling of engineering materials. J Braz Soc Mech Sci Eng 35(3):285–291
Prentner S, Allen DM, Larcombe L, Marson S, Jenkins K, Saumer M (2010) Effects of channel surface finish on blood flow in microfluidic devices. Microsyst Technol 16(7):1091–1096
Rasouli M, Abouei Mehrizi A, Lashkaripour A (2015) Numerical study on low reynolds mixing oft-shaped micro-mixers with obstacles. Transp Phenom Nano Micro Scales 3(2):68–76
Sackmann EK, Fulton AL, Beebe DJ (2014) The present and future role of microfluidics in biomedical research. Nature 507(7491):181–189
Silva R, Bhatia S, Densmore D (2016) A reconfigurable continuous-flow fluidic routing fabric using a modular, scalable primitive. Lab Chip 16(14):2730–2741
Silva R, Dow P, Dubay R, Lissandrello C, Holder J, Densmore D, Fiering J (2017) Rapid prototyping and parametric optimization of plastic acoustofluidic devices for blood-bacteria separation. Biomed Microdevices 19(3):70
Solutions H (2016) Helical machining guidebook. Helical Solutions, LLC, Gorham
Squires TM, Quake SR (2005) Microfluidics: fluid physics at the nanoliter scale. Rev Mod Phys 77(3):977
Stone HA, Stroock AD, Ajdari A (2004) Engineering flows in small devices: microfluidics toward a lab-on-a-chip. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 36:381–411
Tang J, Guo H, Zhao M, Yang J, Tsoukalas D, Zhang B, Liu J, Xue C, Zhang W (2015) Highly stretchable electrodes on wrinkled polydimethylsiloxane substrates. Sci Rep 5(16):527
Thorsen T, Roberts RW, Arnold FH, Quake SR (2001) Dynamic pattern formation in a vesicle-generating microfluidic device. Phys Rev Lett 86(18):4163
Tirandazi P, Hidrovo CH (2017) Liquid-in-gas droplet microfluidics; experimental characterization of droplet morphology, generation frequency, and monodispersity in a flow-focusing microfluidic device. J Micromech Microeng 27(7):075020
Tsao CW, DeVoe DL (2009) Bonding of thermoplastic polymer microfluidics. Microfluid Nanofluid 6(1):1–16
Ward T, Faivre M, Abkarian M, Stone HA (2005) Microfluidic flow focusing: drop size and scaling in pressure versus flow-rate-driven pumping. Electrophoresis 26(19):3716–3724
Whitesides GM (2006) The origins and the future of microfluidics. Nature 442(7101):368–373
Wu N, Zhu Y, Brown S, Oakeshott J, Peat T, Surjadi R, Easton C, Leech P, Sexton B (2009) A pmma microfluidic droplet platform for in vitro protein expression using crude e. coli s30 extract. Lab Chip 9(23):3391–3398
Yen DP, Ando Y, Shen K (2016) A cost-effective micromilling platform for rapid prototyping of microdevices. Technology 4(04):234–239
Acknowledgements
We like to thank Mohammadreza Rasouli from Biomat’X research laboratories at McGill University who provided a detailed pricing information on photolithography. We also like to thank Christopher Rodriguez and Sarah Nemsick for the image processing of the microfluidic droplet generation and graphic design, respectively. This work was supported by the NSF Living Computing Project Award \(\#1522074\) and NSF CAREER Award \(\#1253856\).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary material 2 (mp4 3623 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lashkaripour, A., Silva, R. & Densmore, D. Desktop micromilled microfluidics. Microfluid Nanofluid 22, 31 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-018-2048-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-018-2048-2