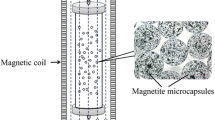
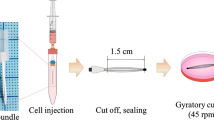
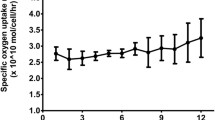
Abstract
An extracorporeal bioartificial liver (BAL) device containing viable hepatocytes has the potential to provide temporary hepatic support to liver failure patients, serving as a bridge to transplantation while awaiting a suitable donor. In some patients, providing temporary hepatic support may be sufficient to allow adequate regeneration of the host liver, thereby eliminating the need for a liver transplant. Although the BAL device is a promising technology for the treatment of liver failure, there are several technical challenges that must be overcome in order to develop systems with sufficient processing capacity and of manageable size. In this study, the authors describe the critical issues involved in developing a BAL device. They also discuss their experiences in hepatocyte culture optimization within the context of a microchannel flat-plate BAL device.









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- H or h:
-
Channel height (μm)
- C o :
-
Inlet oxygen concentration (nmol/cm3)
- Pe:
-
Peclèt number (no unit)
- Q :
-
Volumetric flow rate (mL/min)
- W :
-
Channel width (cm)
- D :
-
Oxygen diffusion coefficient (cm2/s)
- γ:
-
Cell seeding density (cells/cm2)
- Da:
-
Damköhler number (no unit)
- OUR (V max):
-
Oxygen uptake rate (nmol/s/106 cells)
- τ :
-
Shear stress (dyn/cm2)
References
Arias IM, Boyer JL, Chisari FV, Fausto N, Schacter D, Shafritz DA (2001) The liver: biology and pathobiology. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia
Ash SR (2001) Powdered sorbent liver dialysis and pheresis in treatment of hepatic failure. Ther Apher 5:404–416
Balis UJ, Behnia K, Bhatia SN, Sullivan SJ, Yarmush ML, Toner M (1999) Oxygen consumption characteristics of porcine hepatocytes. Metab Eng 1:49–62
Bhatia SN, Balis UJ, Yarmush ML, Toner M (1999) Effect of cell–cell interactions in preservation of cellular phenotype: cocultivation of hepatocytes and nonparenchymal cells. Faseb J 13:1883–1900
Carslaw HS, Jaeger JC (1959) Conduction of heat in solids. Oxford University Press, London
Catapano G (1996) Mass transfer limitations to the performance of membrane bioartificial liver support devices. Int J Artif Organs 19:18–35
Chan C, Berthiaume F, Nath BD, Tilles AW, Toner M, Yarmush ML (2004) Hepatic tissue engineering for adjunct and temporary liver support: critical technologies. Liver Transpl 10:1331–1342
Demetriou AA, Brown RS Jr, Busuttil RW, Fair J, McGuire BM, Rosenthal P, Am Esch JS II, Lerut J, Nyberg SL, Salizzoni M, Fagan EA, de Hemptinne B, Broelsch CE, Muraca M, Salmeron JM, Rabkin JM, Metselaar HJ, Pratt D, De La Mata M, McChesney LP, Everson GT, Lavin PT, Stevens AC, Pitkin Z, Solomon BA (2004) Prospective, randomized, multicenter, controlled trial of a bioartificial liver in treating acute liver failure. Ann Surg 239:660–667; discussion 667–670
Ellis AJ, Hughes RD, Wendon JA, Dunne J, Langley PG, Kelly JH, Gislason GT, Sussman NL, Williams R (1996) Pilot-controlled trial of the extracorporeal liver assist device in acute liver failure. Hepatology 24:1446–1451
Flendrig LM, la Soe JW, Jorning GG, Steenbeek A, Karlsen OT, Bovee WM, Ladiges NC, te Velde AA, Chamuleau RA (1997) In vitro evaluation of a novel bioreactor based on an integral oxygenator and a spirally wound nonwoven polyester matrix for hepatocyte culture as small aggregates. J Hepatol 26:1379–1392
Foy BD, Rotem A, Toner M, Tompkins RG, Yarmush ML (1994) A device to measure the oxygen-uptake rate of attached cells—importance in bioartificial organ design. Cell Transplantation 3:515–527
Gerlach JC, Encke J, Hole O, Muller C, Ryan CJ, Neuhaus P (1994) Bioreactor for a larger scale hepatocyte in-vitro perfusion. Transplantation 58:984–988
Hay PD, Veitch AR, Gaylor JD (2001) Oxygen transfer in a convection-enhanced hollow fiber bioartificial liver. Artif Organs 25:119–130
Hay PD, Veitch AR, Smith MD, Cousins RB, Gaylor JD (2000) Oxygen transfer in a diffusion-limited hollow fiber bioartificial liver. Artif Organs 24:278–288
Hu WS, Friend JR, Wu FJ, Sielaff T, Peshwa MV, Lazar A, Nyberg SL, Remmel RP, Cerra FB (1997) Development of a bioartificial liver employing xenogeneic hepatocytes. Cytotechnology 23:29–38
van de Kerkhove MP, Di Florio E, Scuderi V, Mancini A, Belli A, Bracco A, Dauri M, Tisone G, Di Nicuolo G, Amoroso P, Spadari A, Lombardi G, Hoekstra R, Calise F, Chamuleau RA (2002) Phase I clinical trial with the AMC-bioartificial liver Academic Medical Center. Int J Artif Organs 25:950–959
van de Kerkhove MP, Poyck PP, Deurholt T, Hoekstra R, Chamuleau RA, van Gulik TM (2005) Liver support therapy: an overview of the AMC-bioartificial liver research. Dig Surg 22:254–264. Epub 2005 Sep 2020
Mazariegos GV, Kramer DJ, Lopez RC, Shakil AO, Rosenbloom AJ, DeVera M, Giraldo M, Grogan TA, Zhu Y, Fulmer ML, Amiot BP, Patzer JF (2001) Safety observations in phase I clinical evaluation of the Excorp Medical Bioartificial Liver Support System after the first four patients. ASAIO J 47:471-475
O’Grady JG, Gimson AE, O’Brien CJ, Pucknell A, Hughes RD, Williams R (1988) Controlled trials of charcoal hemoperfusion and prognostic factors in fulminant hepatic failure. Gastroenterology 94:1186–1192
Park J, Berthiaume F, Toner M, Yarmush ML, Tilles AW (2005) Microfabricated grooved substrates as platforms for bioartificial liver reactors. Biotechnol Bioeng 90:632–644
Pascher A, Sauer IM, Hammer C, Gerlach JC, Neuhaus P (2002) Extracorporeal liver perfusion as hepatic assist in acute liver failure: a review of world experience. Xenotransplantation 9:309–324
Patzer IJ, Lopez RC, Zhu Y, Wang ZF, Mazariegos GV, Fung JJ (2002) Bioartificial liver assist devices in support of patients with liver failure. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int 1:18–25
Peng CA, Palsson BO (1996) Determination of specific oxygen uptake rates in human hematopoietic cultures and implications for bioreactor design. Ann Biomed Eng 24:373–381
Rifai K, Ernst T, Kretschmer U, Bahr MJ, Schneider A, Hafer C, Haller H, Manns MP, Fliser D (2003) Prometheus–a new extracorporeal system for the treatment of liver failure. J Hepatol 39:984–990
Rotem A, Toner M, Bhatia S, Foy BD, Tompkins RG, Yarmush ML (1994) Oxygen is a factor determining in-vitro tissue assembly—effects on attachment and spreading of hepatocytes. Biotechnol Bioeng 43:654–660
Rotem A, Toner M, Tompkins RG, Yarmush ML (1992) Oxygen-uptake rates in cultured rat hepatocytes. Biotechnol Bioeng 40:1286–1291
Sauer IM, Kardassis D, Zeillinger K, Pascher A, Gruenwald A, Pless G, Irgang M, Kraemer M, Puhl G, Frank J, Muller AR, Steinmuller T, Denner J, Neuhaus P, Gerlach JC (2003) Clinical extracorporeal hybrid liver support-phase I study with primary porcine liver cells. Xenotransplantation 10:460–469
Smithson JE, Neuberger JM (1999) Acute liver failure. Overview. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 11:943–947
Stange J, Hassanein TI, Mehta R, Mitzner SR, Bartlett RH (2002) The molecular adsorbents recycling system as a liver support system based on albumin dialysis: a summary of preclinical investigations, prospective, randomized, controlled clinical trial, and clinical experience from 19 centers. Artif Organs 26:103–110
Stefanovich P, Matthew HWT, Toner M, Tompkins RG, Yarmush ML (1996) Extracorporeal plasma perfusion of cultured hepatocytes: effect of intermittent perfusion on hepatocyte function and morphology. J Surg Res 66:57–63
Taguchi K, Matsushita M, Takahashi M, Uchino J (1996) Development of a bioartificial liver with sandwiched-cultured hepatocytes between two collagen gel layers. Artif Organs 20:178–185
Tilles AW, Balis UJ, Baskaran H, Yarmush ML, Toner M (2001a) Internal membrane oxygenation removes substrate oxygen limitations in a small-scale flat-plate hepatocyte bioreactor. In: Ohshima N (eds) International symposium on tissue engineering for therapeutic use 5. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 59–71
Tilles AW, Baskaran H, Roy P, Yarmush ML, Toner M (2001b) Effects of oxygenation and flow on the viability and function of rat hepatocytes cocultured in a microchannel flat-plate bioreactor. Biotechnol Bioeng 73:379–389
Uchino J, Tsuburaya T, Kumagai F, Hase T, Hamada T, Komai T, Funatsu A, Hashimura E, Nakamura K, Kon T (1988) A hybrid bioartificial liver composed of multiplated hepatocyte monolayers. ASAIO Trans 34:972–977
Watanabe FD, Mullon CJ, Hewitt WR, Arkadopoulos N, Kahaku E, Eguchi S, Khalili T, Arnaout W, Shackleton CR, Rozga J, Solomon B, Demetriou AA (1997) Clinical experience with a bioartificial liver in the treatment of severe liver failure A phase I clinical trial. Ann Surg 225:484–494
Yarmush ML, Dunn JCY, Tompkins RG (1992a) Assessment of artificial liver support technology. Cell Transplant 1:323–341
Yarmush ML, Toner M, Dunn JCY, Rotem A, Hubel A, Tompkins RG (1992b) Hepatic tissue engineering - Development of critical technologies. Ann N Y Acad Sci 665:238–252
Acknowledgments
This work was partially supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health (K08 DK66040) and (R01 DK43371). The microfabrication was performed at the BioMicroElectroMechanical Systems (BioMEMS) Resource Center at the Massachusetts General Hospital funded by the National Institutes of Health (P41 EB02503).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, J., Toner, M., Yarmush, M.L. et al. Microchannel bioreactors for bioartificial liver support. Microfluid Nanofluid 2, 525–535 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-006-0095-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-006-0095-6