Abstract
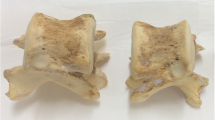
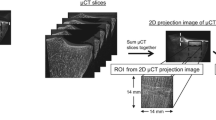
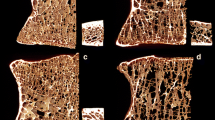
Bone microarchitecture of the iliac bone is used to characterize the properties of bone tissue in osteoporosis, particularly in pharmacological studies. Trabecular bone is known to be heterogeneous media. For a few years, the analysis of three-dimensional (3-D) bone microarchitecture has been based on micro-computed tomography (micro-CT). To assess the interindividual variability (inter-indVar) and the intrasample variability (intra-sampVar) of iliac crest biopsies, we used a Bordier needle trephine in 35 postmenopausal female cadavers (mean age, 74.4 ± 10.4 years). Finally, we had at our disposal 32 individual iliac crests to assess the inter-indVar and 21 oriented specimens to assess the intra-sampVar. All the samples were chemically defatted, and the images were performed with a desktop micro-CT with a voxel size of 10.77 μm. We measured trabecular bone parameters: bone volume/tissue volume (BV/TV %), trabecular thickness and spacing (Tb. Th*, Tb.Sp* μm), bone surface/bone volume (BS/BV, 1/mm), the trabecular number (Tb.N, 1/mm), structure model index (SMI), trabecular pattern factor (Tb.Pf), and degree of anisotropy (DA). We also measured cortical bone parameters: cortical thickness (Cort.Th), porosity (PoV/TV), and pore diameter (Po.Dm). For the inter-indVar, we analyzed a fixed volume of interest corresponding to 119.8 mm3 centered on each iliac crest. To assess the intra-sampVar, we divided the whole trabecular volume into three equal height parts (external, middle, internal). BV/TV, Tb.N, and PoV/TV were negatively correlated with age and Tb.Sp* and SMI were positively correlated. The mean difference of absolute individual variations in percentage with the middle area used as a reference, comparatively to external and internal areas, ranged from 6.6% (Tb.Sp*) to 27.8% (BV/TV), except Tb.Pf, which showed large variability. There was no difference between external and internal areas, with a tendency for lower values of BV/TV, Tb.Th*, and Tb.N in the middle of the iliac crest and higher values of Tb.Sp* and BS/BV. The evaluation of bone microarchitecture of iliac crest samples on micro-CT images is reliable. The heterogeneity of bone inside the iliac crest is noticeable as leading to analyzing the largest possible quantity of bone, with standardized location, according to cortex but without any assumption of orientation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
NIH Consensus (2000) Osteoporosis prevention, diagnosis, and therapy. NIH Consensus Statement 17:1–45
Parfitt AM, Mathews CH, Villanueva AR, Kleerekoper M, Frame B, Rao DS (1983) Relationships between surface, volume, and thickness of iliac trabecular bone in aging and in osteoporosis. Implications for the microanatomic and cellular mechanisms of bone loss. J Clin Invest 72:1396–1409
Aaron JE, Makins NB, Sagreiya K (1987) The microanatomy of trabecular bone loss in normal aging men and women. Clin Orthop Relat Res 215:260–271
Podenphant J, Gotfredsen A, Nilas L, Norgaard H, Braendstrup O (1986) Iliac crest biopsy: representativity for the amount of mineralized bone. Bone (NY) 76:427–430
Mosekilde L, Viidik A, Mosekilde L (1985) Correlation between the compressive strength of iliac and vertebral trabecular bone in normal individuals. Bone (NY) 65:291–295
Oleksik A, Ott SM, Vedi S, Bravenboer N, Compston J, Lips P (2000) Bone structure in patients with low bone mineral density with or without vertebral fractures. J Bone Miner Res 15: 1368–1375
Dalle Carbonare L, Arlot ME, Chavassieux PM, Roux JP, Portero NR, Meunier PJ (2001) Comparison of trabecular bone microarchitecture and remodeling in glucocorticoid-induced and postmenopausal osteoporosis. J Bone Miner Res 16:97–103
Chappard D, Legrand E, Basle MF, Fromont P, Racineux JL, Rebel A, Audran M (1996) Altered trabecular architecture induced by corticosteroids: a bone histomorphometric study. J Bone Miner Res 1:676–685
Parisien M, Cosman F, Mellish RW, Schnitzer M, Nieves J, Silverberg SJ, Shane E, Kimmel D, Recker RR, Bilezikian JP (1995) Bone structure in postmenopausal hyperparathyroid, osteoporotic, and normal women. J Bone Miner Res 10:1393–1399
Eriksen EF, Melsen F, Sod E, Barton I, Chines A (2002) Effects of long-term risedronate on bone quality and bone turnover in women with postmenopausal osteoporosis. Bone (NY) 31:620–625
Dufresne TE, Chmielewski PA, Manhart MD, Johnson TD, Borah B (2003) Risedronate preserves bone architecture in early postmenopausal women in 1 year as measured by three-dimensional microcomputed tomography. Calcif Tissue Int 73:423–432
Borah B, Dufresne TE, Chmielewski PA, Johnson TD, Chines A, Manhart MD (2004) Risedronate preserves bone architecture in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis as measured by three-dimensional microcomputed tomography. Bone (NY) 34:736–746
Jiang Y, Zhao JJ, Mitlak BH, Wang O, Genant HK, Eriksen EF (2003) Recombinant human parathyroid hormone (1–34) [teriparatide] improves both cortical and cancellous bone structure. J Bone Miner Res 18:1932–1941
Muller R, Koller B, Hildebrand T, Laib A, Gionollini S, Rüegsegger P (1996) Resolution dependency of microstructural properties of cancellous bone based on three dimensional μ-tomography. Technol Health Care 4:113–119
Peyrin F, Salome M, Cloetens P, Laval-Jeantet AM, Ritman E, Ruegsegger P (1998) MicroCT examinations of trabecular bone samples at different resolutions: 14, 7 and 2 micron level Technol Health Care 6:391–401
Parfitt AM, Drezner MK, Glorieux FH, Kanis JA, Malluche H, Meunier PJ, Ott SM, Recker RR (1987) Bone histomorphometry: standardization of nomenclature, symbols, and units. Report of the ASBMR Histomorphometry Nomenclature Committee. J Bone Miner Res 2:595–610
Serra J (1982) Image Analysis and Mathematical Morphology. Academic Press, New York, p 104
Muller R, Van Campenhout H, Van Damme B, Van Der Perre G, Dequeker J, Hildebrand T, Ruegsegger P (1998) Morphometric analysis of human bone biopsies: a quantitative structural comparison of histological sections and microcomputed tomography. Bone (NY) 23:59–66
Chappard D, Retailleau-Gaborit N, Legrand E, Basle MF, Audran M (2005) Comparison insight bone measurements by histomorphometry and microCT. J Bone Miner Res 20:1177–1184
Muller R (2003) Bone microarchitecture assessment: current and future trends. Osteoporos Int 14(suppl 5):89–99
van Rietbergen B, Majumdar S, Pistoia W, Newitt DC, Kothari M, Laib A, Ruegsegger P (1998) Assessment of cancellous bone mechanical properties from micro-FE models based on micro-CT, pQCT and MR images. Technol Health Care 6:413–420
Uchiyama T, Tanizawa T, Muramatsu H, Endo N, Takahashi HE, Hara T (1999) Three-dimensional microstructural analysis of human trabecular bone in relation to its mechanical properties. Bone (NY) 25:487–491
Recker R, Masarachia P, Santora A, Howard T, Chavassieux P, Arlot M, Rodan G, Wehren L, Kimmel D (2005) Trabecular bone microarchitecture after alendronate treatment of osteoporotic women. Curr Med Res Opin. 21:185–194. Erratum in: Curr Med Res Opin 21:324
Dempster DW, Cosman F, Kurland ES, Zhou H, Nieves J, Woelfert L, Shane E, Plavetic K, Muller R, Bilezikian J, Lindsay R (2001) Effects of daily treatment with parathyroid hormone on bone microarchitecture and turnover in patients with osteoporosis: a paired biopsy study. J Bone Miner Res 16:1846–1853
Amling M, Herden S, Posl M, Hahn M, Ritzel H, Delling G (1996) Heterogeneity of the skeleton: comparison of the trabecular microarchitecture of the spine, the iliac crest, the femur, and the calcaneus. J Bone Miner Res 11:36–4
Parisien MV, McMahon D, Pushparaj N, Dempster DW (1988) Trabecular architecture in iliac crest bone biopsies: infra-individual variability in structural parameters and changes with age. Bone (NY) 9:289–295
Podenphant J, Gotfredsen A, Nilas L, Norgard H, Braendstrup O, Christiansen C (1986) Iliac crest biopsy: an investigation on certain aspects of precision and accuracy. Bone Miner 1:279–287
Chappard C, Basillais A, Benhamou L, Bonassie A, Brunet-Imbault B, Bonnet N, Peyrin F (2006) Comparison of synchrotron radiation and conventional x-ray microcomputed tomography for assessing trabecular bone microarchitecture of human femoral heads. Med Phys 33:3568–3577
Lorensen WE, Cline HE (1987) Marching cubes: a high resolution 3D surface construction algorithm. Computer Graphics 21(suppl 1):7–12
Ulrich D, Van Rietbergen B, Laib A, Ruegsegger P (1999) The ability of three dimensional structural indices to reflect mechanical aspects of trabecular bone. Bone (NY) 25:55–60
Hildebrand T, Rüegsegger P (1997) A new method for the model independent assessment of thickness in three dimensional images. J Microsc 185:67–75
Whitehouse WJ (1974) The quantitative morphology of anisotropic trabecular bone. J Microsc 101:153–156
Hildebrand T, Rüegsegger P (1997) Quantification of bone microarchitecture with the structure model index. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Eng 1:15–23
Hahn M, Vogel M, Pompesius-Kempa M, Delling G (1992) Trabecular bone pattern factor: a new parameter for simple quantification of bone microarchitecture. Bone (NY) 13:327–330
Dufresne T (1998) Segmentation techniques for analysis of bone by three-dimensional computed tomographic imaging. Technol Health Care 6:351–359
Basillais A, Bensamoun S, Chappard C, Brunet-Imbault B, Lemineur G III, Ilharreborde B, Ho Ba Tho MC, Benhamou CL (2007) Three dimensional characterization of cortical bone microstructure by micro-computed tomography: validation with ultrasound and microscopic measurements. J Orthop Sci 12:141–148
Gluer CC, Blake G, Lu Y, Blunt BA, Jergas M, Genant HK (1995) Accurate assessment of precision errors: how to measure the reproducibility of bone densitometry techniques. Osteoporos Int 5:262–270
Akhter MP, Lappe JM, Davies KM, Recker RR (2007) Transmenopausal changes in the trabecular bone structure. Bone (NY) 41:111–116
Kim DG, Christopherson GT, Dong XN, Fyhrie DP, Yeni YN (2004) The effect of microcomputed tomography scanning and reconstruction voxel size on the accuracy of stereological measurements in human cancellous bone. Bone (NY) 35:1375–1382
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Chappard, C., Marchadier, A. & Benhamou, L. Interindividual and intraspecimen variability of 3-D bone microarchitectural parameters in iliac crest biopsies imaged by conventional micro-computed tomography. J Bone Miner Metab 26, 506–513 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00774-008-0856-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00774-008-0856-2