Abstract
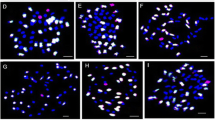
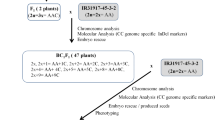
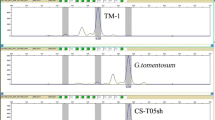
Gossypium bickii: (2n = 26, G1G1), a wild diploid cotton, carries many favourable traits. However, these favourable traits cannot be directly transferred into G. hirsutum (2n = 52, AADD) cultivars due to the differences in genomes. Monosomic alien addition lines (MAALs) are considered an invaluable tool for the introgression of genes of interest from wild relatives into cultivated crops. In this study, the G. hirsutum–G. bickii amphidiploid (2n = 78, AADDG1G1) was backcrossed with G. hirsutum to develop alien additions containing individual G. bickii chromosomes in a G. hirsutum background. Genomic in situ hybridization was employed to detect the number of alien chromosomes added to the backcross progenies. A total of 183 G. bickii-specific DNA markers were developed to discriminate the identities of the G. bickii chromosomes added to G. hirsutum and assess the alien chromosome transmissibility. Chromosomes 4Gb and 13Gb showed the highest transmissibility, while chromosomes 1Gb, 7Gb and 11Gb showed the lowest. Ten of the 13 possible G. hirsutum-G. bickii MAALs were isolated and characterized, which will lay the foundation for transferring resistance genes of G. bickii into G. hirsutum, as well as for gene assignment, physical mapping, and selective isolation and mapping of cDNAs for particular G. bickii chromosomes. The strategies of how to use MAALs to develop varieties with the trait of interest from wild species (such as glanded plant-glandless seed) were proposed and discussed.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahoton L, Lacape JM, Baudoin JP, Mergeai G (2003) Introduction of Australian diploid cotton genetic variation into Upland cotton. Crop Sci 43:1999–2005
Bottger G, Sheehan ET, Lukefahr M (1964) Relation of gossypol content of cotton plants to insect resistance. J Econ Entomol 57:283–285
Chen Y, Wang Y, Wang K, Zhu X, Guo W, Zhang T, Zhou B (2014) Construction of a complete set of alien chromosome addition lines from Gossypium australe in Gossypium hirsutum: morphological, cytological, and genotypic characterization. Theor Appl Genet 127:1105–1121
Du W, Wang J, Pang Y, Li Y, Chen X, Zhao J, Yang Q, Wu J (2013) Isolation and characterization of a Psathyrostachys huashanica Keng 6Ns chromosome addition in common wheat. PLoS One 8:e53921
Endrizzi JE, Ramsay G (1980) Identification of ten chromosome deficiencies of cotton: cytological identification of eight chromosomes and genetic analysis of chromosome deficiencies and marker genes. J Hered 71:45–48
Fryxell P (1992) A revised taxonomic interpretation of Gossypium L. (Malvaceae). Rheedea 2:108–165
Gao D, Jung C (2002) Monosomic addition lines of Beta corolliflora in sugar beet: plant morphology and leaf spot resistance. Plant Breed 121:81–86
Guo W, Cai C, Wang C, Han Z, Song X, Wang K, Niu X, Wang C, Lu K, Shi B (2007) A microsatellite-based, gene-rich linkage map reveals genome structure, function and evolution in Gossypium. Genetics 176:527–541
Hanson RE, Zwick MS, Choi S, Islam-Faridi MN, Wing RA, Price H, Stelly DM, McKnight TD (1995) Fluorescent in situ hybridization of a bacterial artificial chromosome. Genome 38:646–651
Hau B (1981) Lignées d’addition sur l’espèce Gossypium hirsutum L. 1. Utilisation de l’hybridation interspécifique et de la méthode des lignées d’addition pour l’amélioration du cotonnier. Cot Fib Trop 36:247–258
Kang H, Wang Y, Fedak G, Cao W, Zhang H, Fan X, Sha L, Xu L, Zheng Y, Zhou Y (2011) Introgression of chromosome 3Ns from Psathyrostachys huashanica into wheat specifying resistance to stripe rust. PLoS One 6:e21802
Lei MP, Li GR, Liu C, Yang ZJ (2012) Characterization of wheat—Secale africanum introgression lines reveals evolutionary aspects of chromosome 1R in rye. Genome 55:765–774
Luo XD, Dai LF, Cao JF, Jian SR, Chen YL, Hu BL, Xie JK (2012) Identification and molecular cytology analysis of cold tolerance introgression lines derived from Oryza sativa L. mating with O. rufipogon Griff. Euphytica 187:461–469
McMichael SC (1960) Combined effects of glandless genes gl2 and gl3 on pigment glands in the cotton plant. Agron J 52:385–386
Mergeai C (1992) New perspectives concerning the methodology to be used for introgression of the glanded-plant and glandless-seed character in cultivated cotton (G. hirsutum L.). Cot Fib Trop 47:113–119
Paterson AH, Brubaker CL, Wendel JF (1993) A rapid method for extraction of cotton (Gossypium spp.) genomic DNA suitable for RFLP or PCR analysis. Plant Mol Biol Rep 11:122–127
Rooney WL, Stelly DM, Altman DW (1991) Identification of four Gossypium sturtianum monosomic alien addition derivatives from a backcrossing program with G. hirsutum. Crop Sci 31:337–341
Sarr D, Lacape JM, Rodier-Goud M, Jacquemin JM, Benbouza H, Toussaint A, Palm R, Ahoton L, Baudoin JP, Mergeai G (2011) Isolation of five new monosomic alien addition lines of Gossypium australe F. Muell in G. hirsutum L. by SSR and GISH analyses. Plant Breed 130:60–66
Sears E (1956) The transfer of leaf-rust resistance from Aegilops umbellulata to wheat. Brookhaven Sym Biol 9:1–22
Sunilkumar G, Campbell LM, Puckhaber L, Stipanovic RD, Rathore K (2006) Engineering cottonseed for use in human nutrition by tissue-specific reduction of toxic gossypol. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:18054–18059
Tang X, Shi D, Xu J, Li Y, Li W, Ren Z, Fu T (2014) Molecular cytogenetic characteristics of a translocation line between common wheat and Thinopyrum intermedium with resistance to powdery mildew. Euphytica 197:201–210
Vu HQ, Yoshimatsu Y, Khrustaleva LI, Yamauchi N, Shigyo M (2012) Alien genes introgression and development of alien monosomic addition lines from a threatened species, Allium roylei Stearn, to Allium cepa L. Theor Appl Genet 124:1241–1257
Wang CY (2001) Protocol of cotton FISH of somatic chromosomes with rDNA as probes. Cotton Sci 13:75–77
Wang K, Song X, Han Z, Guo W, Yu JZ, Sun J, Pan J, Kohel RJ, Zhang T (2006) Complete assignment of the chromosomes of Gossypium hirsutum L. by translocation and fluorescence in situ hybridization mapping. Theor Appl Genet 113:73–80
Wang X, Wang Y, Wang C, Chen Y, Feng S, Zhao T, Zhou B (2016) Characterization of eleven monosomic alien addition lines added from Gossypium anomalum to Gossypium hirsutum using improved GISH and SSR markers. BMC Plant Biol 16:218
Zhang J, Wu Y, Guo W, Zhang T (2000) Fast screening of microsatellite markers in cotton with PAGE/silver staining. Acta Gossypii Sin 12:267–269
Zhou Z, Yu P, Liu G, He J, Chen J, Zhang X (2004) Morphological and molecular characterization of two G. somalense monosomic alien addition lines (MAALs). Chin Sci Bull 49:910–914
Zhu S, Ji D (2001) Inheritance of the delayed gland morphogenesis trait in Australian wild species of Gossypium. Chin Sci Bull 46:1168–1174
Zhu S, Jiang Y, Naganagouda R, Ji D (2004) Breeding, introgression and inheritance of delayed gland morphogenesis trait from Gossypium bickii into Upland cotton germplasm. Chin Sci Bull 49:2470–2476
Zhu S, Reddy N, Jiang Y (2005) Introgression of a gene for delayed pigment gland morphogenesis from Gossypium bickii into Upland cotton. Plant Breed 124:590–594
Funding
This study was funded by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2016YFD0100203), the National Key Technology Support Program of China during the Twelfth 5-year plan period (2013BAD01B03-04), the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions and Jiangsu Collaborative Innovation Center for Modern Crop Production.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest in the reported research.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Communicated by S. Hohmann.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, D., Feng, S., Li, S. et al. Ten alien chromosome additions of Gossypium hirsutum–Gossypium bickii developed by integrative uses of GISH and species-specific SSR markers. Mol Genet Genomics 293, 945–955 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-018-1434-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-018-1434-5