Abstract
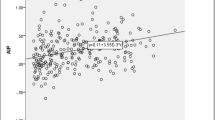
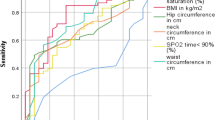
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is an independent risk factor for cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. However, the underlying mechanism is unclear. In this cross-sectional study, we investigated the influence of OSA on metabolic syndrome (MetS) and inflammation, which were considered as cardiovascular risks. A total of 144 consecutive male patients who underwent standard polysomnography were enrolled. Fasting blood samples were obtained from all patients for glucose, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) and lipids measurement. A metabolic score was established as the total number of the positive diagnostic criteria of metabolic syndrome for each patient. Systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, fasting glucose, hs-CRP and metabolic score significantly increased with the aggravation of OSA severity. Metabolic score increased from 1.74 ± 1.20 to 2.89 ± 0.99 with OSA severity (p = 0.000). hs-CRP increased from 0.68 (0.43–1.10) to 1.44 (0.62–4.02) mg/L with OSA severity (p = 0.002). After adjustment for confounders, apnea–hypopnea index and body mass index (BMI) were the major contributing factors for metabolic score (β = 0.257, p = 0.003 and β = 0.344, p = 0.000, respectively), lowest O2 saturation and BMI were the independent predictors of hs-CRP (β = −0.255, p = 0.003 and β = 0.295, p = 0.001, respectively). OSA is independently associated with sum of metabolic components and hs-CRP.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Young T, Peppard PE, Gottlieb DJ (2002) Epidemiology of obstructive sleep apnea: a population health perspective. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 165:1217–1239
Shahar E, Whitney CW, Redline S, Lee ET, Newman AB, Nieto FJ, O’Connor GT, Boland LL, Schwartz JE, Samet JM (2001) Sleep-disordered breathing and cardiovascular disease: cross-sectional results of the sleep heart health study. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 163:19–25
Chami HA, Resnick HE, Quan SF, Gottlieb DJ (2011) Association of incident cardiovascular disease with progression of sleep-disordered breathing. Circulation 123:1280–1286
Redline S, Yenokyan G, Gottlieb DJ, Shahar E, O’Connor GT, Resnick HE, Diener-West M, Sanders MH, Wolf PA, Geraghty EM, Ali T, Lebowitz M, Punjabi NM (2010) Obstructive sleep apnea–hypopnea and incident stroke: the sleep heart health study. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 182:269–277
Grundy SM, Cleeman JI, Daniels SR, Donato KA, Eckel RH, Franklin BA, Gordon DJ, Krauss RM, Savage PJ, Smith SC Jr, Spertus JA, Costa F (2005) Diagnosis and management of the metabolic syndrome: an American heart association/national heart, lung, and blood institute scientific statement. Circulation 112:2735–2752
Reaven GM (1988) Banting lecture 1988: role of insulin resistance in human disease. Diabetes 37:1595–1607
Lakka HM, Laaksonen DE, Lakka TA, Niskanen LK, Kumpusalo E, Tuomilehto J, Salonen JT (2002) The metabolic syndrome and total and cardiovascular disease mortality in middle-aged men. JAMA 288:2709–2716
Ho JS, Cannaday JJ, Barlow CE, Mitchell TL, Cooper KH, FitzGerald SJ (2008) Relation of the number of metabolic syndrome risk factors with all-cause and cardiovascular mortality. Am J Cardiol 102:689–692
Thomas GN, Phillips AC, Carroll D, Gale CR, Batty GD (2010) The metabolic syndrome adds utility to the prediction of mortality over its components: the Vietnam experience study. Atherosclerosis 210:256–261
Corrado E, Rizzo M, Coppola G, Fattouch K, Novo G, Marturana I, Ferrara F, Novo S (2010) An update on the role of markers of inflammation in atherosclerosis. J Atheroscler Thromb 17:1–11
Ikonomidis I, Stamatelopoulos K, Lekakis J, Vamvakou GD, Kremastinos DT (2008) Inflammatory and non-invasive vascular markers: the multimarker approach for risk stratification in coronary artery disease. Atherosclerosis 199:3–11
Libby P (2002) Inflammation in atherosclerosis. Nature 420:868–874
Ross R (1999) Atherosclerosis—an inflammatory disease. N Engl J Med 340:115–126
Rifai N, Tracy RP, Ridker PM (1999) Clinical efficacy of an automated high-sensitivity C-reactive protein assay. Clin Chem 45:2136–2141
Kono M, Tatsumi K, Saibara T, Nakamura A, Tanabe N, Takiguchi Y, Kuriyama T (2007) Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome is associated with some components of metabolic syndrome. Chest 131:1387–1392
Lam JC, Lam B, Lam CL, Fong D, Wang JK, Tse HF, Lam KS, Ip MS (2006) Obstructive sleep apnea and the metabolic syndrome in community-based Chinese adults in Hong Kong. Respir Med 100:980–987
Punjabi NM, Beamer BA (2007) C-reactive protein is associated with sleep disordered breathing independent of adiposity. Sleep 30:29–34
Lui MM, Lam JC, Mak HK, Xu A, Ooi C, Lam DC, Mak JC, Khong PL, Ip MS (2009) C-reactive protein is associated with obstructive sleep apnea independent of visceral obesity. Chest 135:950–956
Peled N, Kassirer M, Shitrit D, Kogan Y, Shlomi D, Berliner AS, Kramer MR (2007) The association of OSA with insulin resistance, inflammation and metabolic syndrome. Respir Med 101:1696–1701
Sharma SK, Kumpawat S, Goel A, Banga A, Ramakrishnan L, Chaturvedi P (2007) Obesity, and not obstructive sleep apnea, is responsible for metabolic abnormalities in a cohort with sleep-disordered breathing. Sleep Med 8:12–17
Barcelo A, Barbe F, Llompart E, Mayoralas LR, Ladaria A, Bosch M, Agusti AG (2004) Effects of obesity on C-reactive protein level and metabolic disturbances in male patients with obstructive sleep apnea. Am J Med 117:118–121
Taheri S, Austin D, Lin L, Nieto FJ, Young T, Mignot E (2007) Correlates of serum C-reactive protein (CRP)—no association with sleep duration or sleep disordered breathing. Sleep 30:991–996
Guilleminault C, Kirisoglu C, Ohayon MM (2004) C-reactive protein and sleep-disordered breathing. Sleep 27:1507–1511
Physical status: the use and interpretation of anthropometry. Report of a WHO Expert Committee (1995). World Health Organ Tech Rep Ser 854:1-452
Schulz H (2007) Phasic or transient? Comment on the terminology of the AASM manual for the scoring of sleep and associated events. J Clin Sleep Med 3:752
Lam DC, Xu A, Lam KS, Lam B, Lam JC, Lui MM, Ip MS (2009) Serum adipocyte-fatty acid binding protein level is elevated in severe OSA and correlates with insulin resistance. Eur Respir J 33:346–351
Tan CE, Ma S, Wai D, Chew SK, Tai ES (2004) Can we apply the national cholesterol education program adult treatment panel definition of the metabolic syndrome to Asians? Diabetes Care 27:1182–1186
Oktay B, Akbal E, Firat H, Ardic S, Kizilgun M (2009) CPAP treatment in the coexistence of obstructive sleep apnea syndrome and metabolic syndrome, results of one year follow up. Acta Clin Belg 64:329–334
Mota PC, Drummond M, Winck JC, Santos AC, Almeida J, Marques JA (2011) APAP impact on metabolic syndrome in obstructive sleep apnea patients. Sleep Breath 15:665–672
Coughlin SR, Mawdsley L, Mugarza JA, Wilding JP, Calverley PM (2007) Cardiovascular and metabolic effects of CPAP in obese males with OSA. Eur Respir J 29:720–727
Shamsuzzaman AS, Winnicki M, Lanfranchi P, Wolk R, Kara T, Accurso V, Somers VK (2002) Elevated C-reactive protein in patients with obstructive sleep apnea. Circulation 105:2462–2464
Zouaoui Boudjeltia K, Van Meerhaeghe A, Doumit S, Guillaume M, Cauchie P, Brohee D, Vanhaeverbeek M, Kerkhofs M (2006) Sleep apnoea–hypopnoea index is an independent predictor of high-sensitivity C-reactive protein elevation. Respiration 73:243–246
Kapsimalis F, Varouchakis G, Manousaki A, Daskas S, Nikita D, Kryger M, Gourgoulianis K (2008) Association of sleep apnea severity and obesity with insulin resistance, C-reactive protein, and leptin levels in male patients with obstructive sleep apnea. Lung 186:209–217
Su MC, Chen YC, Huang KT, Wang CC, Lin MC, Lin HC (2013) Association of metabolic factors with high-sensitivity C-reactive protein in patients with sleep-disordered breathing. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 270:749–754
Sharma SK, Mishra HK, Sharma H, Goel A, Sreenivas V, Gulati V, Tahir M (2008) Obesity, and not obstructive sleep apnea, is responsible for increased serum hs-CRP levels in patients with sleep-disordered breathing in Delhi. Sleep Med 9:149–156
Ryan S, Nolan GM, Hannigan E, Cunningham S, Taylor C, McNicholas WT (2007) Cardiovascular risk markers in obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome and correlation with obesity. Thorax 62:509–514
Schiza SE, Mermigkis C, Panagiotis P, Bouloukaki I, Kallergis E, Tzanakis N, Tzortzaki E, Vlachaki E, Siafakas NM (2010) C-reactive protein evolution in obstructive sleep apnoea patients under CPAP therapy. Eur J Clin Invest 40:968–975
Ishida K, Kato M, Kato Y, Yanagihara K, Kinugasa Y, Kotani K, Igawa O, Hisatome I, Shigemasa C, Somers VK (2009) Appropriate use of nasal continuous positive airway pressure decreases elevated C-reactive protein in patients with obstructive sleep apnea. Chest 136:125–129
Kohler M, Ayers L, Pepperell JC, Packwood KL, Ferry B, Crosthwaite N, Craig S, Siccoli MM, Davies RJ, Stradling JR (2009) Effects of continuous positive airway pressure on systemic inflammation in patients with moderate to severe obstructive sleep apnoea: a randomised controlled trial. Thorax 64:67–73
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grant C07100008 for natural science foundation from Fujian province of China. We would like to thank Bin Yang for assistance with blood analysis. Xiao-Bin Zhang is thanked for his help with statistics.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, QC., Chen, LD., Yu, YH. et al. Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome is associated with metabolic syndrome and inflammation. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 271, 825–831 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-013-2669-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-013-2669-8