Abstract
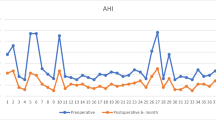
The objectives of the study are to assess adverse events and complications of hyoid suspension (HS) as a treatment of obstructive sleep apnea syndrome (OSAS). The study design was cohort. Thirty-nine patients with OSAS and obstruction at tongue base level, as assessed by sleep endoscopy, underwent HS. Information about adverse events and complications were obtained by reviewing charts and patient-completed questionnaires. The mean follow-up period from surgery to last control visit was 13.1 months (range 2–38). The charts demonstrated mainly adverse events. Minor complications occurred in six patients. No major complications were observed. The mean admission duration was 3.3 days (range 2–5). Twenty-six patients (67%) returned their questionnaires. No association was found between completing questionnaires and the success of the intervention (p = 0.73). The questionnaires were completed on average 25.9 months (range 3.5–51.5) after surgery. VAS scores showed a fast decline in complaints regarding taste, speech, swallowing and pain. No significant long-term differences were found, when comparing the postoperative VAS scores with the preoperative VAS scores. Of the 26 evaluable questionnaires, 20 patients (77%) would recommend HS to an acquaintance if they suffered from sleep apnea syndrome, when only taking side effects into consideration. The intention to give a positive recommendation did not seem to be related to the therapeutic success of the intervention. In conclusion, this study demonstrates that the complication rate of HS is low and that the discomfort is very acceptable.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chung KF (2000) Use of Epworth’s sleepiness scale in Chinese patients with OSA and normal employees. J Psychosom Res 49:367–372
Chesire K, Engleman H, Deary I, Shapiro C, Douglas NJ (1992) Factors impairing daytime performance in patients with sleep apnea/hypopnea syndrome. Arch Intern Med 152(3):538–541
Peppard PE, Young T, Palta M, Skatrud J (2000) Prospective study of the association between sleep-disordered breathing and hypertension. N Engl J Med 342:1378–1384
Shamsuzzaman ASM, Gersh BJ, Somers VK (2003) Obstructive sleep apnea, implications for cardiac and vascular disease. JAMA 290(14):1906–1914
Caples SM, Garcia-Touchard A, Somers VK (2007) Sleep-disordered breathing and cardiovascular risk. Sleep 30(3):291–303
Dyken ME, Somers VK, Yamada T, Ren ZY, Zimmerman MB (1996) Investigating the relationship between stroke and obstructive sleep apnea. Stroke 27:401–407
Teran-Santos J, Jimenez-Gomez A, Cordero-Guevara J (1999) The association between sleep apnea and the risk of traffic accidents. N Engl J Med 340(11):847–851
George CF, Smiley A (1999) Sleep apnea and automobile crashes. Sleep 22(6):790–795
Young T, Palta M, Dempsey J, Skatrud J, Weber S, Badr S (1993) The occurrence of sleep disordered breathing among middle-aged adults. N Engl J Med 328(17):1230–1235
Sullivan CE, Issa FG, Berthon-Jones M, Eves L (1981) Reversal of obstructive sleep apnoea by continuous positive airway pressure applied through the nares. Lancet 1(8225):862–865
(1994) Indications and standards for use of nasal continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) in sleep apnea syndromes. American Thoracic Society. Am J Crit Care Med 150:1738–1745
Schmidt-Nowara W, Lowe A, Wiegand L, Cartwright R, Perez-Guerra F, Menn S (1995) Oral appliances for the treatment of snoring and obstructive sleep apnea: a review. Sleep 18(6):501–510
Kushida CA, Morgenthaler TI, Littner MR, Alessi CA, Bailey D, Coleman J Jr, Friedman L, Hirshkowitz M, Kapen S, Kramer M, Lee-Chiong T, Owens J, Pancer JP (2006) Practice parameters for the treatment of snoring, obstructive sleep apnea with oral appliances: an update for 2005. An American academy of sleep medicine report. Sleep 29(2):240–243
Powell NB, Riley RW, Troell RJ, Li K, Blumen MB, Guilleminault C (1998) Radiofrequency volumetric tissue reduction of the palate in subjects with sleep-disordered breathing. Chest 113(5):1163–1174
Stuck BA, Köpke J, Maurer JT, Verse T, Eckert A, Bran G, Duber C, Hormann K (2003) Lesion formation in radiofrequency surgery of the tongue base. Laryngoscope 113:1572–1576
Den Herder C, Kox D, van Tinteren H, de Vries N (2006) Bipolar radiofrequency induced thermotherapy of the tongue base: its complications, acceptance and effectiveness under local anesthesia. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 263:1031–1040
Fujita S, Conway W, Zorick F, Roth T (1981) Surgical corrections of anatomical abnormalities in obstructive sleep apnea syndrome: uvulopalatopharyngoplasty. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 89:923–934
Riley RW, Powell NB, Guilleminault C (1994) Obstructive sleep apnea and the hyoid: a revised surgical procedure. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 111(6):717–721
Kerner MM, Hale RG, Kim Silva (2002) A novel three-piece anterior mandibular visor osteotomyfor genioglossus advancement in surgery for obstructive sleep apnea. Oper Techn Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 13(2):175–177
Hochban W, Brandenburg U, Peter JH (1994) Surgical treatment of obstructive sleep apnea by maxillomandibular advancement. Sleep 17(7):624–629
Prinsell JR (1999) Maxillomandibular advancement surgery in a site-specific treatment approach for obstructive sleep apnea in 50 consecutive patients. Chest 116:1519–1529
Datillo DJ, Drooger SA (2004) Outcome assessment of patients undergoing maxillofacial procedures for the treatment of sleep apnea: comparison of subjective and objective results. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 62:164–168
Simmons FB (1979) Tracheotomy in obstructive sleep apnea patients. Laryngoscope 89:1702–1703
Riley RW, Powell NB, Guilleminault C (1986) Inferior sagittal osteotomy of the mandible with hyoid myotomy-suspension: a new procedure for obstructive sleep apnea. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 94(5):589–593
Den Herder C, van Tinteren H, de Vries N (2005) Hyoidthyroidpexia: a surgical treatment for sleep apnea syndrome. Laryngoscope 115(4):740–745
(1999) Sleep-related breathing disorders in adults: recommendations for syndrome definition and measurement techniques in clinical research. The report of an American academy of sleep medicine task force. Sleep 22(5):667–689
Rombout J, de Vries N (2001) Complications in sinus surgery and new classification proposal. Am J Rhinol 15(6):363–370
Miller FR, Watson D, Boseley M (2004) The role of the genial bone advancement trephine system in conjunction with uvulopalatopharyngoplasty in the multilevel management of obstructive sleep apnea. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 130:73–79
Li KK, Riley RW, Powell NB, Troell R, Guilleminault C (1999) Overview of phase II surgery for obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Ear Nose Throat J 78(11):851, 854–857
Li KK, Troell RJ, Riley RW, Powell NB, Koester U, Guilleminault C (2001) Uvulopalatopharyngoplasty, maxillomandibular advancement, and the velopharynx. Laryngoscope 111:1075–1078
Kokki H, Nikanne E, Aho M, Virtaniemi J (2003) Pain intensity after laseruvulopalatoplasty and tonsillectomy. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 128(2):273–279
Conflict of interest
The authors do not have a financial relationship with an organization that sponsored the research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Richard, W., Timmer, F., van Tinteren, H. et al. Complications of hyoid suspension in the treatment of obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 268, 631–635 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-010-1419-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-010-1419-4