Abstract
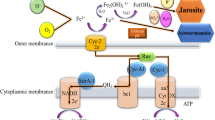
The immobilisation of the iron-oxidising bacteria Thiobacillus ferrooxidans on nickel alloy fibre as support is described. This matrix showed promise for application in iron oxidation under strongly acidic conditions. The influence on the colonisation process of T. ferrooxidans exerted by the initial pH of the medium and by temperature has also been studied. Results showed that immobilisation of T. ferrooxidans cells was affected by changes of temperature between 30 °C and 40 °C and in pH from 1.4 to 2.0.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 25 January 2000 / Received version: 20 April 2000 / Accepted: 1 May 2000
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gómez, J., Cantero, D. & Webb, C. Immobilisation of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans cells on nickel alloy fibre for ferrous sulfate oxidation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 54, 335–340 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002530000414
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002530000414