Abstract
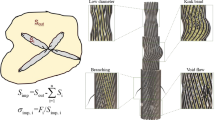
The paper deals with the experimental characterisation of damage evolution within the radial (R)–tangential (T) growth plane of softwood loaded in tension perpendicular to the grain. The reported investigations comprise in-situ monitoring of crack propagation by means of Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy (CLSM) and evaluations of crack patterns of broken specimens. Three types of notched specimens, representing different crack propagation systems, were tested; for all configurations, both, loading and crack propagation direction were located within the RT plane of wood. The CLSM pictures of broken specimens show distinct differences among the regarded configurations with respect to crack paths. Two different damage mechanisms were identified being rupture of earlywood cell walls in the case of crack propagation in tangential direction and debonding of wood fibers, i.e. rupture of the interface zone between adjacent tracheids, in case of crack progression in radial direction. In the case of an intermediate crack system with an angle of 45° between initial notch direction and radial direction the crack evolution was monitored in-situ during the tension test, whereby the combined action of both basic fracture mechanisms was observed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received 20 May 2000
The financial support of German Science Community (DFG) via grant to Sonderforschungsbereich 381 “Characterisation of damage development in composite materials using nondestructive test methods” and hereby to sub-project A8 “Damage and NDT of the natural fiber composite material wood” is gratefully acknowledged.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dill-Langer, G., Lütze, S. & Aicher, S. Microfracture in wood monitored by confocal laser scanning microscopy. Wood Science and Technology 36, 487–499 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-002-0151-7
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-002-0151-7